Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 viewsSyllabus of PIC
Syllabus of PIC
Uploaded by
thakarerohan345Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Intro To C SyllabusDocument1 pageIntro To C Syllabusashishpatel_99No ratings yet
- Cs 201Document1 pageCs 201api-340772707No ratings yet
- SL Topics Hours Marks Section - I: CurriculumDocument4 pagesSL Topics Hours Marks Section - I: CurriculumVikram Rao100% (1)
- Ece I Programming in C Data Structures 15PCD13 Solution PDFDocument46 pagesEce I Programming in C Data Structures 15PCD13 Solution PDFChethana NarayanNo ratings yet
- Python Question Bank 1Document4 pagesPython Question Bank 1ganesh moorthiNo ratings yet
- CDS Made Easy PDFDocument97 pagesCDS Made Easy PDFVivekananda Ganjigunta NarayanaNo ratings yet
- C Programming Module 1 C Programming BasicDocument33 pagesC Programming Module 1 C Programming BasicJm Potenciando100% (1)
- Bca & B. Sc.-It Sem-1 C-ProgrammingDocument102 pagesBca & B. Sc.-It Sem-1 C-ProgrammingVikas SharmaNo ratings yet
- Programming CDocument223 pagesProgramming CAbhishek PadvalNo ratings yet
- Cse PDFDocument55 pagesCse PDFNikhil PhulNo ratings yet
- Introduction To C ProgrammingDocument27 pagesIntroduction To C ProgrammingHitesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iii:: Overall OutcomesDocument2 pagesUnit - Iii:: Overall OutcomesSunny TalwarNo ratings yet
- PSPDocument6 pagesPSPRamu gopireddyNo ratings yet
- PPS-Important Questions With Answers-3!10!18Document41 pagesPPS-Important Questions With Answers-3!10!18Vaishnav KumarNo ratings yet
- C&DS NotesDocument98 pagesC&DS NotesAnanth NathNo ratings yet
- Programming For Problem SlovingDocument3 pagesProgramming For Problem SlovingBaswamy CseNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving in C and Python: Programming Exercises and Solutions, Part 1From EverandProblem Solving in C and Python: Programming Exercises and Solutions, Part 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Object Oriented Programming BookDocument310 pagesObject Oriented Programming BookNuhuMabiriiziNo ratings yet
- C Programming 3Document28 pagesC Programming 3Kavya MamillaNo ratings yet
- Pic 6-1-17 Co Pos MappedDocument6 pagesPic 6-1-17 Co Pos MappedVinay KorekarNo ratings yet
- Common To E&C, EI&C, CS&E, IS&E& MX: Department of Technical EducationDocument8 pagesCommon To E&C, EI&C, CS&E, IS&E& MX: Department of Technical EducationVikram RaoNo ratings yet
- Basic Elements of C++ PDFDocument12 pagesBasic Elements of C++ PDFemmrab824No ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument22 pagesIlovepdf MergedNahzgie GabzLac FloresNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Syllabus UG-1Document7 pagesComputer Science Syllabus UG-1lkNo ratings yet
- PARUL UNIVERSITY - Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyDocument4 pagesPARUL UNIVERSITY - Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyVeera saiNo ratings yet
- Programming CDocument223 pagesProgramming CChet ParyvathNo ratings yet
- Year & Sem: E1S1 Course Code: CS6101 Course Name: C No. of Credits: 4 L T&Ps P 2 2 0Document1 pageYear & Sem: E1S1 Course Code: CS6101 Course Name: C No. of Credits: 4 L T&Ps P 2 2 0balajiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Data Types. Program Structure / Input - Output. SelectionDocument42 pagesLesson 2: Data Types. Program Structure / Input - Output. SelectionJonny CerneiNo ratings yet
- Unit I - Basics of C ProgrammingDocument44 pagesUnit I - Basics of C ProgrammingHarsh DeshwalNo ratings yet
- Study FY BSC - Cs - Paper-IIDocument300 pagesStudy FY BSC - Cs - Paper-IInileshnemadeNo ratings yet
- C Programming: Sachin DaneDocument60 pagesC Programming: Sachin DaneTalha Nasir100% (1)
- Introduction To C Programming BasicsDocument25 pagesIntroduction To C Programming Basicssreelakshmi sajeevNo ratings yet
- B.Tech Syllabus 2012-17 22.12.17Document63 pagesB.Tech Syllabus 2012-17 22.12.17Khondekar Lutful HassanNo ratings yet
- C++ Chapter 2 SlidesDocument87 pagesC++ Chapter 2 SlidesJamie RandolphNo ratings yet
- Bca Odd SemDocument18 pagesBca Odd Sembhumikachauhan694No ratings yet
- Bachelor of Computer Applications Syllabus For 2018 & 2019 BatchDocument9 pagesBachelor of Computer Applications Syllabus For 2018 & 2019 BatchRaza KhanNo ratings yet
- C Programming Basics Questions and AnswersDocument7 pagesC Programming Basics Questions and AnswerskathirdcnNo ratings yet
- C Programming Theory and Lab AktuDocument4 pagesC Programming Theory and Lab AktuSanjay GuptaNo ratings yet
- CL-1002 Programming Fundamentals: Basic Program Structure, Data Types, Math.h Library FunctionsDocument9 pagesCL-1002 Programming Fundamentals: Basic Program Structure, Data Types, Math.h Library Functionsjatin kesnaniNo ratings yet
- Index: Sr. No. Topic Page NoDocument43 pagesIndex: Sr. No. Topic Page NoAkshay PhadkeNo ratings yet
- Programming - Final ArcDocument64 pagesProgramming - Final ArcskewNo ratings yet
- 1 Scanning: COMP 3512 Assignment 2Document4 pages1 Scanning: COMP 3512 Assignment 2andyGILL100% (1)
- Advantages (Or) Features of C Language:: ModularityDocument44 pagesAdvantages (Or) Features of C Language:: ModularityGautham PabbaNo ratings yet
- C Programming For Problem SolvingDocument5 pagesC Programming For Problem SolvingkiranNo ratings yet
- Introduction To C ProgrammingDocument74 pagesIntroduction To C Programmingharshagowda0464No ratings yet
- C Full NoteDocument154 pagesC Full NoteRamaswamy MuthukrishnanNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1 Fundamentals of Problem Solving: Creating and Running ProgramsDocument13 pagesUNIT-1 Fundamentals of Problem Solving: Creating and Running ProgramsVimalesh RaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document107 pagesChapter 2Amruta RegeNo ratings yet
- C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis To Program Design,: Third EditionDocument87 pagesC++ Programming: From Problem Analysis To Program Design,: Third Editionrahafnsh33No ratings yet
- r19 C SyllabusDocument2 pagesr19 C SyllabusShaik ParveenNo ratings yet
- C Language Preliminaries: C-Programming Tutorial 1. Introduction and Basics of CDocument13 pagesC Language Preliminaries: C-Programming Tutorial 1. Introduction and Basics of CprathipkattekolaNo ratings yet
- Algorithm AND FlowchartsDocument17 pagesAlgorithm AND FlowchartsBrenndale SusasNo ratings yet
- PC QbankDocument32 pagesPC QbankvaratharajanNo ratings yet
- Ccs University, Meerut Bca Syllabus: Greater Noida Group of Educational InstitutesDocument34 pagesCcs University, Meerut Bca Syllabus: Greater Noida Group of Educational InstitutesRachna rachnaNo ratings yet
- B.E. /B.Tech in Computer Science & Business Systems Semester 1 Fundamentals of Computer Science + LabDocument2 pagesB.E. /B.Tech in Computer Science & Business Systems Semester 1 Fundamentals of Computer Science + LabcharanNo ratings yet
- BLOCK 1: An Introduction To C Unit 1: Problem SolvingDocument5 pagesBLOCK 1: An Introduction To C Unit 1: Problem SolvingMahadeva HerbalsNo ratings yet
- C-Language (All Concepts)Document129 pagesC-Language (All Concepts)Sunny Chaurasiya100% (1)
- Bca SYLLABUSpdfDocument33 pagesBca SYLLABUSpdfKunal GautamNo ratings yet
- C Programming Theory Syllabus - 2021-22Document3 pagesC Programming Theory Syllabus - 2021-2260 - R - OP ChoudharyNo ratings yet
Syllabus of PIC
Syllabus of PIC
Uploaded by
thakarerohan3450 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesOriginal Title
syllabus of PIC
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesSyllabus of PIC
Syllabus of PIC
Uploaded by
thakarerohan345Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
CHAPTER 1
1. Functions and Limits
Popular Posts
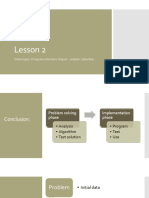
1. Fundamentals of algorithms:Notion of an algorithm. Pseudo-code
conventions like assignment
statements and basic control structures
2. Algorithmic problems: Develop fundamental algorithms to solve
simple problems such as:
solve simple arithmetic expression
2.1 find the greatest of three numbers
2.2 determine whether a given number is even or odd
2.3 determine whether a given number is prime.
3. Flowchart: Flowchart. Symbols of flowchart, Guidelines for
preparing Flowchart
CHAPTER 2
1. Introduction to C: History ofC General Structure of a C program:
Header files, main function.
2. Data Concepts: Character set, tokens, keywords, Identifiers,
Variables, Constant, data types. C operators, Arithmetic operators,
Arithmetic expression, declaring variables, and data type conversion.
3. Basic Input output: Input and Output statements, using printf) and
scanf() character input/output statements, Input/output formatting, Use
of comments.
CHAPTER 3
1. Decision making and branching:Relational and logical
operators, if statement, if else statement, nested if-else, if-else ladder
The switch statement.
2. Looping: While loop, Do While loop For loop, Go to statement. Use
of break and continue statements.
CHAPTER 4
1. Characteristics of an array. One dimension and two dimension
arrays.
2. Array declaration and Initialization.
3. Array of characters, Operation on array.
4. Character and String input/output.
5. Introduction and Features of Structures. Declaration and
Initialization of Structures.
6. Type numerated Data Type, using structures in C Program.
CHAPTER 5
1. Concept and need of functions.
2. Library functions: Math functions, String handling functions, other
miscellaneous functions.
3. Writing User defined functions, scope of variables.
4. Parameter passing: call by value, call by reference.
5. Recursive functions.
CHAPTER 6
1. Concepts of pointers: declaring, initializing, accessing.
2. Pointer arithmetic.
3. Handling arrays using pointers.
4. Handling functions using pointers.
5. Handling structures using pointers.
You might also like
- Intro To C SyllabusDocument1 pageIntro To C Syllabusashishpatel_99No ratings yet
- Cs 201Document1 pageCs 201api-340772707No ratings yet
- SL Topics Hours Marks Section - I: CurriculumDocument4 pagesSL Topics Hours Marks Section - I: CurriculumVikram Rao100% (1)
- Ece I Programming in C Data Structures 15PCD13 Solution PDFDocument46 pagesEce I Programming in C Data Structures 15PCD13 Solution PDFChethana NarayanNo ratings yet
- Python Question Bank 1Document4 pagesPython Question Bank 1ganesh moorthiNo ratings yet
- CDS Made Easy PDFDocument97 pagesCDS Made Easy PDFVivekananda Ganjigunta NarayanaNo ratings yet
- C Programming Module 1 C Programming BasicDocument33 pagesC Programming Module 1 C Programming BasicJm Potenciando100% (1)
- Bca & B. Sc.-It Sem-1 C-ProgrammingDocument102 pagesBca & B. Sc.-It Sem-1 C-ProgrammingVikas SharmaNo ratings yet
- Programming CDocument223 pagesProgramming CAbhishek PadvalNo ratings yet
- Cse PDFDocument55 pagesCse PDFNikhil PhulNo ratings yet
- Introduction To C ProgrammingDocument27 pagesIntroduction To C ProgrammingHitesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iii:: Overall OutcomesDocument2 pagesUnit - Iii:: Overall OutcomesSunny TalwarNo ratings yet
- PSPDocument6 pagesPSPRamu gopireddyNo ratings yet
- PPS-Important Questions With Answers-3!10!18Document41 pagesPPS-Important Questions With Answers-3!10!18Vaishnav KumarNo ratings yet
- C&DS NotesDocument98 pagesC&DS NotesAnanth NathNo ratings yet
- Programming For Problem SlovingDocument3 pagesProgramming For Problem SlovingBaswamy CseNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving in C and Python: Programming Exercises and Solutions, Part 1From EverandProblem Solving in C and Python: Programming Exercises and Solutions, Part 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Object Oriented Programming BookDocument310 pagesObject Oriented Programming BookNuhuMabiriiziNo ratings yet
- C Programming 3Document28 pagesC Programming 3Kavya MamillaNo ratings yet
- Pic 6-1-17 Co Pos MappedDocument6 pagesPic 6-1-17 Co Pos MappedVinay KorekarNo ratings yet
- Common To E&C, EI&C, CS&E, IS&E& MX: Department of Technical EducationDocument8 pagesCommon To E&C, EI&C, CS&E, IS&E& MX: Department of Technical EducationVikram RaoNo ratings yet
- Basic Elements of C++ PDFDocument12 pagesBasic Elements of C++ PDFemmrab824No ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument22 pagesIlovepdf MergedNahzgie GabzLac FloresNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Syllabus UG-1Document7 pagesComputer Science Syllabus UG-1lkNo ratings yet
- PARUL UNIVERSITY - Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyDocument4 pagesPARUL UNIVERSITY - Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyVeera saiNo ratings yet
- Programming CDocument223 pagesProgramming CChet ParyvathNo ratings yet
- Year & Sem: E1S1 Course Code: CS6101 Course Name: C No. of Credits: 4 L T&Ps P 2 2 0Document1 pageYear & Sem: E1S1 Course Code: CS6101 Course Name: C No. of Credits: 4 L T&Ps P 2 2 0balajiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Data Types. Program Structure / Input - Output. SelectionDocument42 pagesLesson 2: Data Types. Program Structure / Input - Output. SelectionJonny CerneiNo ratings yet
- Unit I - Basics of C ProgrammingDocument44 pagesUnit I - Basics of C ProgrammingHarsh DeshwalNo ratings yet
- Study FY BSC - Cs - Paper-IIDocument300 pagesStudy FY BSC - Cs - Paper-IInileshnemadeNo ratings yet
- C Programming: Sachin DaneDocument60 pagesC Programming: Sachin DaneTalha Nasir100% (1)
- Introduction To C Programming BasicsDocument25 pagesIntroduction To C Programming Basicssreelakshmi sajeevNo ratings yet
- B.Tech Syllabus 2012-17 22.12.17Document63 pagesB.Tech Syllabus 2012-17 22.12.17Khondekar Lutful HassanNo ratings yet
- C++ Chapter 2 SlidesDocument87 pagesC++ Chapter 2 SlidesJamie RandolphNo ratings yet
- Bca Odd SemDocument18 pagesBca Odd Sembhumikachauhan694No ratings yet
- Bachelor of Computer Applications Syllabus For 2018 & 2019 BatchDocument9 pagesBachelor of Computer Applications Syllabus For 2018 & 2019 BatchRaza KhanNo ratings yet
- C Programming Basics Questions and AnswersDocument7 pagesC Programming Basics Questions and AnswerskathirdcnNo ratings yet
- C Programming Theory and Lab AktuDocument4 pagesC Programming Theory and Lab AktuSanjay GuptaNo ratings yet
- CL-1002 Programming Fundamentals: Basic Program Structure, Data Types, Math.h Library FunctionsDocument9 pagesCL-1002 Programming Fundamentals: Basic Program Structure, Data Types, Math.h Library Functionsjatin kesnaniNo ratings yet
- Index: Sr. No. Topic Page NoDocument43 pagesIndex: Sr. No. Topic Page NoAkshay PhadkeNo ratings yet
- Programming - Final ArcDocument64 pagesProgramming - Final ArcskewNo ratings yet
- 1 Scanning: COMP 3512 Assignment 2Document4 pages1 Scanning: COMP 3512 Assignment 2andyGILL100% (1)
- Advantages (Or) Features of C Language:: ModularityDocument44 pagesAdvantages (Or) Features of C Language:: ModularityGautham PabbaNo ratings yet
- C Programming For Problem SolvingDocument5 pagesC Programming For Problem SolvingkiranNo ratings yet
- Introduction To C ProgrammingDocument74 pagesIntroduction To C Programmingharshagowda0464No ratings yet
- C Full NoteDocument154 pagesC Full NoteRamaswamy MuthukrishnanNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1 Fundamentals of Problem Solving: Creating and Running ProgramsDocument13 pagesUNIT-1 Fundamentals of Problem Solving: Creating and Running ProgramsVimalesh RaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document107 pagesChapter 2Amruta RegeNo ratings yet
- C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis To Program Design,: Third EditionDocument87 pagesC++ Programming: From Problem Analysis To Program Design,: Third Editionrahafnsh33No ratings yet
- r19 C SyllabusDocument2 pagesr19 C SyllabusShaik ParveenNo ratings yet
- C Language Preliminaries: C-Programming Tutorial 1. Introduction and Basics of CDocument13 pagesC Language Preliminaries: C-Programming Tutorial 1. Introduction and Basics of CprathipkattekolaNo ratings yet
- Algorithm AND FlowchartsDocument17 pagesAlgorithm AND FlowchartsBrenndale SusasNo ratings yet
- PC QbankDocument32 pagesPC QbankvaratharajanNo ratings yet
- Ccs University, Meerut Bca Syllabus: Greater Noida Group of Educational InstitutesDocument34 pagesCcs University, Meerut Bca Syllabus: Greater Noida Group of Educational InstitutesRachna rachnaNo ratings yet
- B.E. /B.Tech in Computer Science & Business Systems Semester 1 Fundamentals of Computer Science + LabDocument2 pagesB.E. /B.Tech in Computer Science & Business Systems Semester 1 Fundamentals of Computer Science + LabcharanNo ratings yet
- BLOCK 1: An Introduction To C Unit 1: Problem SolvingDocument5 pagesBLOCK 1: An Introduction To C Unit 1: Problem SolvingMahadeva HerbalsNo ratings yet
- C-Language (All Concepts)Document129 pagesC-Language (All Concepts)Sunny Chaurasiya100% (1)
- Bca SYLLABUSpdfDocument33 pagesBca SYLLABUSpdfKunal GautamNo ratings yet
- C Programming Theory Syllabus - 2021-22Document3 pagesC Programming Theory Syllabus - 2021-2260 - R - OP ChoudharyNo ratings yet