Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Financial Analysis and Reporting
Uploaded by
dmxv7s2ms20 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views6 pagesModule 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentModule 1
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views6 pagesFinancial Analysis and Reporting
Uploaded by
dmxv7s2ms2Module 1
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
months and 3 ● Used to reduce the
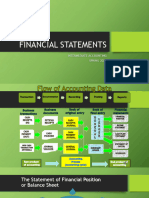
STATEMENT OF weeks overall value of
FINANCIAL POSITION ● Convertible to the assets
amount of cash
● Also known as the
which is subject to Trade and other
“balance sheet”
an insignificant risk receivables
● Shows: the
to changes in value Accounts receivable
condition of the
Marketable securities ● The amount
company as of a
● These are stocks collectible from the
given period
and bonds customer to whom
● It is a clear
purchased by the sales have been
representation of
enterprise and are made or rendered
the accounting
to be held for only ● On account/ credit
equation
a short period or ● E.g. inutang ni
● Formula: A=L+OE
short duration customer anf
Trades and other goods (AR) cause
ASSETS
receivable walang natanggap
2 types of assets
● Collectible amounts si company
1. Current asset
Inventories Notes receivable
2. Non-current asset
● Unsold goods at ● The client issued a
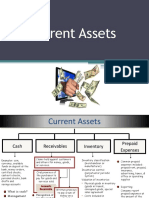
Current asset
the end of the promissory note in
● Classified and
accounting period exchange for
presented
● Raw goods, in services or goods
according to
progress goods (in received as
liquidity
the process but not evidence
● Most liquid asset
yet finished) ● Obligation to pay
● Convertible to cash
Prepaid expenses ● A written pledge
within 1 year
● Supplies bought for that the customer
use in the business will pay a fixed
Classification of current
or service amount of money
assets
● Paid in advance on a certain date
Cash
● Expenses paid in Interest receivable
● Coins, currencies,
business in ● Amounts of interest
checks, bank
advance collectible on
deposits, bills, bank
● E.g. apartment promissory notes
balances, & money
rental you need to received from the
orders
pay in advance customer
● Available for use in
even if you have Advances to employees
the operations of
used it yet ● Amounts of money
the business
Contra-asset account loaned to
Cash equivalents
● Account deducted employees payable
● Investment
from the related in cash or through
securities for a
asset account salary deduction
short-term
maximum of 2
Accrued income property , plant and 4. Utilities payable
● Income already equipment 5. Unearned
earned but not yet ● Tangible assets revenues
received or that held by an Accounts payable
recorded enterprise for use ● Debts arising from
in the production the purchase of an
Other current asset: ● Long-term assets asset of service on
Supplies vital to business account
operations & not ● The money owned
● Cost of supplies on
easily converted by the business to
hand to operate
into cash its supplier
● E.g. pen, paper, ink, ● E.g. land, building, ● E.g. the supplier of
clip equipment, shoes so you have
furniture and a pair of shoes
Contra-asset accounts fixture, and fixtures then next time you
1. Allowance for bad service vehicle will pay the pair of
debts Intangible assets shoes in short,
● Losses due to ● Not physical in supplies before
uncollectible nature (can’t touch) pay
amounts ● E.g. brand name, Notes payable
Accumulated patents, copyright ● Evidence by a
depreciation license franchise, promissory note
● Expired cost of trademark, ● Liability in writing
Property, pants, & subscription lists, Utilities payable
equipment as a secret processes, ● Obligation to pay
result of usage and the utility company
non-competition for services
Classification of agreements received from them
non-current assets ● A company owned
Non-current asset Liabilities for utility
● Convertible to cash 1. Current liabilities ● E.g. electricity,
within a year 2. Non-current water, gas
Long-term investment liabilities ● Explanation: a
● Enterprise for Current liabilities company received
accretion of wealth ● Debt of a business utility bill but hasn’t
through capital that they have to paid it yet
distribution pay in a short Unearned revenues
● E.g. interest, period of time ● Company receives
royalties, dividends payment from the
and rentals for Classification of current customer before
other benefits to liabilities providing the goods
the inventing 1. Account payable or services
enterprise 2. Notes payable ● Advance payments
3. Loan payable received before
goods or services
Balance - Current the
are provided to the sheet assets business in
customer -Non its
● E.g. booking of current operation
ticket assets to produce
-liabilities revenues
Non-current liabilities (current
and non E.g. sell a
● Long term current) shirt of 600
liabilities/ and is the
obligations which cost of
are payable for the Owners Capital sales is
period longer than equity withdrawal 600
s
1 year
Salaries
Income Revenues expense:
Classification of statement expenses cost
non-current liabilities incurred to
pay
Mortgage payable employees
● Long term debt of
Utilities
the business with Owners Capital: expense:
security or equity original & cost
collateral in the additional incurred by
form of real investment using
of the utilities
property
owner of
● E.g. you lend a the Rent
money to a bank, business expense:s
the banks need a pace and
collateral (land) Withdrawa equipment
then the bank will ls: owners or other
give a money of the asset
business rentals
Bonds payable
removes
● Certificate of cash Insurance
indebtedness &other expense :
under the seal of a assets expired
corporation from the portion of
● Repayment and the business. insurance
rate of interest to For
personal Supplies
be charged expense:
use
expense of
expenses Cost of using
sales: supplies
Cost of
assets
used by
Week 3: why financial Transparency and 1. Entity concept
statement are important accountability 2. Periodicity
& the rules in financial ● Disclosing financial 3. Going concern
reporting information, Entity concept
ensuring ● Business separate
Financial statement accountability to from its owners and
● Crucial documents stakeholders, from other
that provide a regulators, and the business
snapshot of a public ● Business is
company's Basis for taxation and separated from
financial compliance personal money
performance ● Basis for tax Periodicity
● Important several calculations and ● Financial
reasons: decision regulatory accounting
making, compliance information about
performance ● Legal and standard the economic
evaluation, Financial reporting activities of an
transparency & ● Rules and principle enterprise
accountability, & to ensure 1. Fiscal year: feb to
basis for taxation accuracy, january * can start
and compliance consistency, and any months
Decision making comparability 2. Calendar year:
● Investors, Generally accepted january to
shareholders, use accounting principles( december
FS to make GAAP) ● Both have 12
informed decisions ● Rules and months
about investing, procedures Going concern
lending, or ● Serve as guides in ● Business
partnering with a the practice of enterprise will
company accounting continues to
Performance evaluation ● These are operate indefinitely
● Help to assess a standard, ● Infinity
company assumptions, and
profitability, concepts with Basic accounting
liquidity, solvency, general principle
and overall acceptability 1. Objectivity
performance over a ● It measure the principle
period techniques ans 2. Historical cost
● Allowing standards used in 3. Accrual principle
comparisons with the presentation 4. Adequate
industry standards and preparation of disclosure
and competitors financial 5. Materiality
statements 6. Consistency
Fundamental concepts Objectivity
● All business result between time single - step income
transactions that and periods statement
will be entered in ● It presents the
the accounting INCOME STATEMENT revenue, expenses
records must be ● It shows the and ultimately the
duly supported by company’s financial profit/ losses
verifiable performance during generated by a
evidence a particular period business
Historical cost ● It consist: revenue, ● Report information
● All properties and cost, & period by using 1 equation
services acquired ● FORMULA: to calculate profits
by the business REVENUE LESS: ● Straightforward
must be recorded EXPENSES= accounting of the
at their original PROFIT financial activity of
acquisition cost Revenue your business
Accrual principle ● Money a company ● Easy to understand
● Income should be actually receives & easy to prepare
recognized at the during a specific
time it is earned period
such as when Gains
goods are ● Increase in the
delivered or when value of an asset or
services have been property e.g.
rendered income from sale
Adequate disclosure of van Multi-step income
● All materials Expenses statement
facts that ● Economic costs a ● Same general
will affect business incurs in information
the financial order to revenue included in a
statements e.g. wages, rent, sing;e-step income
must be salaries, interest statement.
indicated paid ● Uses multiple
Materiality Losses equations to
● Financial reporting ● Portion of an determine the net
is only concerned insurance income, or profit of
with information company’s the company
that affects reserves for unpaid
decisions losses and costs of
Consistency investigation and
● Used in reporting adjustment losses
must be uniformly e.g. settlement
employed from cost of consumer
period to period to lawsuit
all comparison of
Net sales Salaries and wages
● The sum of a expense
company’s gross ● Compose of all the
sales minus its payments made to
return, employees or
allowances,& workers for rending
discounts services to the
company
Utilities expense
● Expenses related
Accounts in the single- to the use of
step income statement electricity, & water
1. Service income Supplies expense
2. Salaries or eagles ● Covers office
expenses supplies used by
3. Utilities expense the company in the
4. Supplies expense conduct of its daily
5. Insurance operation
expense Insurance expense
6. Depreciation ● Amount that the
expense company pays to
7. Uncollectible get an insurance
accounts cintract and any
expenses/ additional premium
doubtful account payments
expense/ bad ● Once they expire,
debts expense recorded as
8. Interest expense expense
Depreciation expense
Service income ● Annual portion of
● Revenue earned or the cost of tangible
generated by the assets such as
business in buildings,
performing service machineries, and
for a customer equipment charged
● E.g. laundry as expense for the
service by laundry year
shop (laundry ● E.g.
income), dental
services by dentist
(dental fees),
medical services by
doctores (medical
fees)
You might also like
- Example of Non-Current AssetDocument4 pagesExample of Non-Current AssetPatricia Isabelle Smith FloresNo ratings yet
- Sofp NotesDocument4 pagesSofp NotesLyka MillorNo ratings yet
- Accounting Midterm ReviewerDocument14 pagesAccounting Midterm Reviewerlorenadelejero14No ratings yet
- FM ReviewerDocument7 pagesFM ReviewerBianca MalinabNo ratings yet
- SSLIDES - VATEL - LSLIDES - Chap 4Document36 pagesSSLIDES - VATEL - LSLIDES - Chap 4uyenthanhtran2312No ratings yet
- Types of Accounts and The Account TitlesDocument25 pagesTypes of Accounts and The Account TitlesSeung BatumbakalNo ratings yet
- Accounting Finals 1 ReviewerDocument5 pagesAccounting Finals 1 ReviewerlaurenNo ratings yet
- Business MathDocument4 pagesBusiness MathPamela MarieNo ratings yet
- Accounting NotesDocument6 pagesAccounting NotesD AngelaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Slides - Introducing Financial StatementsDocument12 pagesModule 2 - Slides - Introducing Financial StatementsElizabethNo ratings yet
- Accounting Reviewer 2nd Long TestDocument45 pagesAccounting Reviewer 2nd Long TestZachary Job YuipcoNo ratings yet
- Fabm12 1ST QTRDocument4 pagesFabm12 1ST QTRAraNo ratings yet
- Topic - Explaining The Concept of Cash Flow Statement (Operating, Investing and Financing Activities)Document15 pagesTopic - Explaining The Concept of Cash Flow Statement (Operating, Investing and Financing Activities)Sakshi koulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Accounting Equation and The Double Entry SystemDocument3 pagesChapter 2 - The Accounting Equation and The Double Entry SystemalonNo ratings yet
- Accounts ReceivablesDocument37 pagesAccounts ReceivablesYassi CurtisNo ratings yet
- Fabm 1 PS 11 Q3 0602Document49 pagesFabm 1 PS 11 Q3 0602ABM 11-5 Maneja, Ford Zedrick R.No ratings yet
- Fabm 1 - Week 4Document3 pagesFabm 1 - Week 4FERNANDO TAMZ2003No ratings yet
- Short Notes Financial AccountigDocument9 pagesShort Notes Financial AccountigNajihah AbNo ratings yet
- Pointers To Review: FABM 2: Recording Phase: Answer KeyDocument9 pagesPointers To Review: FABM 2: Recording Phase: Answer KeyMaria Janelle BlanzaNo ratings yet
- Fabm Week 4 Study GuideDocument3 pagesFabm Week 4 Study GuideFERNANDO TAMZ2003No ratings yet
- 4types of Major Accounts-For Observation2Document13 pages4types of Major Accounts-For Observation2Marilyn Nelmida TamayoNo ratings yet
- Basics of Accounting 3 Double Entry Book Keeping RulesDocument44 pagesBasics of Accounting 3 Double Entry Book Keeping Rulesjiten zopeNo ratings yet
- Financial StatementsDocument32 pagesFinancial Statementspeterpark0903No ratings yet
- 7 Elements of FS-specific AccountsDocument28 pages7 Elements of FS-specific Accountsivygem saanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 NLKTDocument58 pagesChapter 2 NLKTPhan Lê Anh Đào100% (1)
- Pertemuan 3 Current AssetDocument46 pagesPertemuan 3 Current AssetJason wibisonoNo ratings yet
- Accounting TerminologyDocument37 pagesAccounting Terminologyjhj01No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document20 pagesChapter 3Nareen RajNo ratings yet
- 1five Major AccountsDocument30 pages1five Major AccountsEaster LumangNo ratings yet
- Financial Concepts 18 AprilDocument33 pagesFinancial Concepts 18 Aprilapi-295284877100% (1)
- Types of Major AccountsDocument6 pagesTypes of Major Accountsks505eNo ratings yet
- ACCOUNTING CYCLE STEP 1 TO 4 With IllustrationsDocument6 pagesACCOUNTING CYCLE STEP 1 TO 4 With IllustrationsmallarilecarNo ratings yet
- CONFRAS 1 (Practice Quiz)Document4 pagesCONFRAS 1 (Practice Quiz)Jessica MalabananNo ratings yet
- Fabm 4THDocument3 pagesFabm 4THDrahneel MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Essential Elements of The Definition of AccountingDocument9 pagesEssential Elements of The Definition of AccountingPamela Diane Varilla AndalNo ratings yet
- FABM2-Chapter 1Document31 pagesFABM2-Chapter 1Marjon GarabelNo ratings yet
- ACCOUNTINGDocument7 pagesACCOUNTINGGaga LalaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Current AssetsccDocument46 pages3 - Current AssetsccrintoatgpNo ratings yet
- Ey Terms: 3 3 4 Chapter 8 - ReceivablesDocument11 pagesEy Terms: 3 3 4 Chapter 8 - ReceivablesRaffay Maqbool100% (1)
- ConceptDocument2 pagesConceptYan YangNo ratings yet
- Cfas - ReceivablesDocument9 pagesCfas - ReceivablesYna SarrondoNo ratings yet
- Account TitlesDocument5 pagesAccount TitlesalyNo ratings yet
- Accounting: Nature of Accounting Business OrganizationDocument2 pagesAccounting: Nature of Accounting Business OrganizationRochelle Joy CruzNo ratings yet
- (ACCCOB2) Chapters 3-5 Receivables, Investments, InventoryDocument11 pages(ACCCOB2) Chapters 3-5 Receivables, Investments, InventoryMichaella PurgananNo ratings yet
- Acct 018 Chapter 4 5Document4 pagesAcct 018 Chapter 4 5rivera.roshelleNo ratings yet
- 5 6138856670966580425Document4 pages5 6138856670966580425sssNo ratings yet
- 1 LiabilitiesDocument39 pages1 LiabilitiesDiana Faith TaycoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Statement of Financial Position and Income StatementDocument28 pagesChapter 3 - Statement of Financial Position and Income Statementshemida75% (4)
- Chap 3 - Acctg Clasification Element of FSDocument21 pagesChap 3 - Acctg Clasification Element of FSEli Syahirah100% (1)
- Chapter 2Document22 pagesChapter 2John Edwinson JaraNo ratings yet
- Pas 7Document3 pagesPas 7Sacedon, Trishia Mae C.No ratings yet
- Balance Sheet - Ratio AnalysisDocument49 pagesBalance Sheet - Ratio AnalysisKarishmaAshuNo ratings yet
- Audit Group AssignmentDocument23 pagesAudit Group AssignmentShavi GurugeNo ratings yet
- Reviewer FinanceDocument4 pagesReviewer FinanceCalivo, Carl JohnNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting For Managers: Shailesh PeriwalDocument7 pagesFinancial Accounting For Managers: Shailesh PeriwalNatasha DassNo ratings yet
- FabmDocument5 pagesFabmJihane TanogNo ratings yet
- Accounting PPT - Intangible AssetDocument58 pagesAccounting PPT - Intangible AssetGokul RamNo ratings yet
- FA1 NotesDocument270 pagesFA1 NotesNida KhanNo ratings yet
- Business Analysis & ValuationDocument50 pagesBusiness Analysis & ValuationAimee EemiaNo ratings yet
- Collateral Document Delivery Request Form v2Document1 pageCollateral Document Delivery Request Form v2Teena BarrettoNo ratings yet
- Presentation On IOCL - PPT On SUMMER INTERNSHIP PROJECTDocument15 pagesPresentation On IOCL - PPT On SUMMER INTERNSHIP PROJECTMAHENDRA SHIVAJI DHENAK33% (3)
- Cancellation Acord Form - CX149661-Ramon Aguilar-Aguila Trucking PDFDocument1 pageCancellation Acord Form - CX149661-Ramon Aguilar-Aguila Trucking PDFBryan ArenasNo ratings yet
- Hanlon Heitzman 2010Document53 pagesHanlon Heitzman 2010vita cahyanaNo ratings yet
- Igcse Accounting Multiple Choice FDocument43 pagesIgcse Accounting Multiple Choice FAung Zaw HtweNo ratings yet
- Slm-Strategic Financial Management - 0 PDFDocument137 pagesSlm-Strategic Financial Management - 0 PDFdadapeer h mNo ratings yet
- Important Points of Our Notes/Books:: TH THDocument42 pagesImportant Points of Our Notes/Books:: TH THpuru sharmaNo ratings yet
- 1557278181265Document12 pages1557278181265Hema VarmanNo ratings yet
- Philippine Red Cross (Non-Government Organization) : University of Perpetual Help System DALTADocument15 pagesPhilippine Red Cross (Non-Government Organization) : University of Perpetual Help System DALTAFroilan Arlando BandulaNo ratings yet
- PricingDocument2 pagesPricingKishore kandurlaNo ratings yet
- Doing Business in BrazilDocument164 pagesDoing Business in BrazilVarupNo ratings yet
- ADVANCED FA Chap IIIDocument7 pagesADVANCED FA Chap IIIFasiko Asmaro100% (1)
- ADMS 1010, ADMS 3530, ADMS 2511, All York BAS Course MaterialsDocument6 pagesADMS 1010, ADMS 3530, ADMS 2511, All York BAS Course MaterialsFahad33% (3)
- Lecture3 Sem2 2023Document35 pagesLecture3 Sem2 2023gregNo ratings yet
- PW Department CodesDocument19 pagesPW Department CodesanilNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Water and Power Development Authority: (In Quadruplicate)Document2 pagesPakistan Water and Power Development Authority: (In Quadruplicate)AsadAli100% (1)
- 14 Excise Invoice FormatDocument1 page14 Excise Invoice FormatZahirabbas BhimaniNo ratings yet
- Unit IvDocument26 pagesUnit Ivthella deva prasadNo ratings yet
- M Form 2019Document4 pagesM Form 2019Kamille Ann RiveraNo ratings yet
- 26nov2022 - 30jan2023Document12 pages26nov2022 - 30jan2023Srishti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Daily Report MonitoringDocument9 pagesDaily Report MonitoringMaasin BranchNo ratings yet
- 201FIN Tutorial 3 Financial Statements Analysis and RatiosDocument3 pages201FIN Tutorial 3 Financial Statements Analysis and RatiosAbdulaziz HNo ratings yet
- (Sarvesh Dhatrak) Derivatives in Stock Market and Their Importance in HedgingDocument79 pages(Sarvesh Dhatrak) Derivatives in Stock Market and Their Importance in Hedgingsarvesh dhatrakNo ratings yet
- Project Report LissstDocument6 pagesProject Report LissstShivareddyNo ratings yet
- Sat YamDocument39 pagesSat YamShashank GuptaNo ratings yet
- Direst Selling Agent Policy-Retail & Consumer LendingDocument13 pagesDirest Selling Agent Policy-Retail & Consumer LendingVijay DubeyNo ratings yet
- AdmissionDocument23 pagesAdmissionPawan TalrejaNo ratings yet
- InflationDocument40 pagesInflationmaanyaagrawal65No ratings yet