Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Demand
Demand
Uploaded by
andressookdeo29Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Demand
Demand
Uploaded by
andressookdeo29Copyright:
Available Formats
Market
a place where buyers and sellers meet for the purpose of buying
and selling.
Market Forces
Demand and Supply
Purpose of Market Forces
When market forces come together determine the equilibrium price/
quantity of good/service
Demand
desire and willingness to purchase a good/service in a
given time period
Demand influences consumers to maximize their satisfaction given
their income.
Effective Demand
Desire and willingness of a consumer to purchase a good/service
backed by the ability to purchase it.
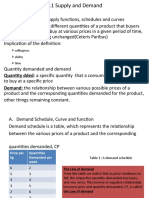
Quantity Demand
The desire/willingness of consumers to purchase a good/service at
various price levels in a given time period. Changes in quantity
demanded is influenced by the changes in price of the good/service
only.
• The diagram above refers to the quantity of a particular good/
service demanded at each given price level.
• The demand curve is downward sloping to reflect the inverse
relationship between the price of the good and the quantity
demanded.
Example:
In the diagram above, when the price increased from $10 to $13,
quantity demanded decreased from 28 units to 18 units. Conversely
when the price decreased from $10- $5 the quantity demanded by
the consumer increased fro 25- 30 units.
DIAGRAM SHOWING MADISON S DEMAND CURVE FOR
POTATO PIE
In the diagram above, as the price of potato pie increased from $7-
$10, Madison’s quantity demanded for potato pie decreased from 30
units to 9 units.
• Market Demand Curve is a horizontal summation of all
individual demand curves.
• In the diagram above, the market demand curve for chocolate is
found by summing Abia and Marita’s individual demand curves
for chocolate assuming there are only two individuals in the
market for chocolate.
• The market demand for chocolate at the price of $20 is 11 (3+8)
while the market demand at $5 is 22 (7+15).
MOVEMENTS ALONG THE
DEMAND CURVE
- The diagram above displays movement along the ‘s demand curve for
good X. When the price increase from $7- $10, there was an
upward movement along the demand curve from point A to B. This is
due to the decrease in quantity demanded for good X from 9- 5 units.
This is a contraction in demand for good X.
- Conversely a decrease in price of good X from $7 to $3 resulted in
a downward movement along the demand curve from point A-C due to
an increase in quantity demanded from 9-13 units. This is an
extension in demand for good X
• Movements are caused by changes in PRICE of the good only
(referred to as changes in quantity demanded.
• An increase in the price of the good will cause a decrease in
quantity demanded shown by an UPWARD movement along the
demand curve. This is termed a CONTRACTION IN DEMAND.
• A decrease in the price of a good will cause an increase in the
quantity demanded shown by a DOWNWARD movement along
the demand curve. This is termed EXTENSION IN DEMAND.
SHIFTS OF THE DEMAND
CURVE
’
You might also like
- A level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Newtons Laws of MotionDocument43 pagesNewtons Laws of MotionDenjie Magrimbao100% (1)
- Page 35 Answer Key Student Booklet - Classwork - 2: - Definitions of DemandDocument4 pagesPage 35 Answer Key Student Booklet - Classwork - 2: - Definitions of DemandRumana AliNo ratings yet
- Factor's Affecting Law of DemandDocument8 pagesFactor's Affecting Law of DemandSarwat PawarNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply: Eco101: Introduction To MicroeconomicsDocument10 pagesDemand and Supply: Eco101: Introduction To MicroeconomicsMuhtasim OyshikNo ratings yet
- Market ForcesDocument30 pagesMarket ForcesamorrisNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics - Topic 3Document25 pagesMicroeconomics - Topic 3Linh Trinh NgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document13 pagesChapter 3Bader F QasemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Price DeterminationDocument9 pagesChapter 6 Price DeterminationNeelabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter (Eng. Eco) 002Document23 pagesChapter (Eng. Eco) 002dsbsabirkhanNo ratings yet
- Demand 1Document5 pagesDemand 1korahjacobNo ratings yet
- Enotesmba: The Best References For MbaDocument36 pagesEnotesmba: The Best References For MbaShailesh PaiNo ratings yet
- Class 6-Theory of DemandDocument32 pagesClass 6-Theory of DemandskdfNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (Demand and Supply)Document18 pagesChapter 3 (Demand and Supply)Sharif HassanNo ratings yet
- Demand Curve: Economics Graph CommodityDocument16 pagesDemand Curve: Economics Graph CommodityHammad AbidNo ratings yet
- Market EquilibriumDocument38 pagesMarket EquilibriumAbhi KumNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Reflects The Perfect Balance of Supply and DemandDocument8 pagesEquilibrium Reflects The Perfect Balance of Supply and DemandGözde GürlerNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Demand and SupplyDocument48 pagesCH 3 Demand and Supplyshaheduzaman ShahedNo ratings yet
- The Basic Analysis of Demand: Dr. Janice Rhea CabacunganDocument31 pagesThe Basic Analysis of Demand: Dr. Janice Rhea CabacunganmalindaNo ratings yet
- Supply and DemandDocument7 pagesSupply and DemandManoj K100% (1)
- Macroeconomics: Module 3: Supply and DemandDocument35 pagesMacroeconomics: Module 3: Supply and DemandtemedebereNo ratings yet
- Basic Demand and Supply AnalysisDocument48 pagesBasic Demand and Supply AnalysisabhinavkalaNo ratings yet
- Demand and SupplyDocument35 pagesDemand and SupplysiribandlaNo ratings yet
- Tips and Samples CH 3 Demand and SupplyDocument17 pagesTips and Samples CH 3 Demand and Supplytariku1234No ratings yet
- Demand 4Document2 pagesDemand 4mike tanNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics: Module 3: Supply and DemandDocument35 pagesMacroeconomics: Module 3: Supply and DemandEddie CalzadoraNo ratings yet
- DemandDocument24 pagesDemandStive JohnNo ratings yet
- College Physics: Chapter # Chapter Title Demand and SupplyDocument37 pagesCollege Physics: Chapter # Chapter Title Demand and Supplysathvik RekapalliNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document116 pagesLecture 4Nikoli MajorNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Man EcoDocument29 pagesChapter-2 Man Ecolyzel kayeNo ratings yet
- Lements of Emand AND UpplyDocument20 pagesLements of Emand AND UpplyLester John Gabriel OrosNo ratings yet
- Theory of DemandDocument64 pagesTheory of DemandGEORGENo ratings yet
- Supply, Demand and Market EquilibriumDocument64 pagesSupply, Demand and Market EquilibriumSamanthaGailLopez50% (2)
- Business & MarketsDocument35 pagesBusiness & MarketsMai ShhhNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Basic Elements of Demand and Supply 5-1-2017Document28 pagesTopic 3 - Basic Elements of Demand and Supply 5-1-2017apexNo ratings yet
- No Change in Demand and Increase in Supply: Hypothetical ExampleDocument7 pagesNo Change in Demand and Increase in Supply: Hypothetical Exampleishita sabooNo ratings yet
- Demand AnalysisDocument10 pagesDemand Analysisarchana_anuragiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Demand, Supply, and Market EquilibriumDocument65 pagesUnit 2 - Demand, Supply, and Market EquilibriumsikanjiticliffordNo ratings yet
- Change in Quantity Demanded and Change in DemandDocument54 pagesChange in Quantity Demanded and Change in DemandToluwaniiyi Praise Aramide-AtolagbeNo ratings yet
- Demand: DR Vighneswara SwamyDocument28 pagesDemand: DR Vighneswara Swamy0886Praneetha BayanaNo ratings yet
- Demand (Notes)Document28 pagesDemand (Notes)Abhijeet kumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2. Supply and DemandDocument51 pagesLecture 2. Supply and DemandNoroNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economics & Management: Week 2 Prepared By: Miss. Fatima M. SaleemDocument81 pagesEngineering Economics & Management: Week 2 Prepared By: Miss. Fatima M. SaleemJehangir VakilNo ratings yet
- Supply and Demand: For Other Uses, SeeDocument18 pagesSupply and Demand: For Other Uses, SeeCDanielle ArejolaNo ratings yet
- Supply and DemandDocument20 pagesSupply and DemandmingwoonNo ratings yet
- Report - MBA 103 - Supply, Demand, Equilibrium PriceDocument28 pagesReport - MBA 103 - Supply, Demand, Equilibrium PriceJamil DiligNo ratings yet
- LESSON III - II Demand Schedule Demand Curve Supply Schedule Supply CurveDocument20 pagesLESSON III - II Demand Schedule Demand Curve Supply Schedule Supply Curvedaleajon03No ratings yet
- Macroeconomics-Compiled TopicsDocument12 pagesMacroeconomics-Compiled Topicskrystel basaNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics 2: Chapter 4: The Market Forces of Supply and DemandDocument15 pagesMicroeconomics 2: Chapter 4: The Market Forces of Supply and DemandSegismundo Gutiérrez LugoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document18 pagesLecture 2cristianaNo ratings yet
- Law of Supply and DemandDocument4 pagesLaw of Supply and DemandSteven MoisesNo ratings yet
- Chapter (Eng. Eco) 003Document16 pagesChapter (Eng. Eco) 003dsbsabirkhanNo ratings yet
- Untitled 1Document36 pagesUntitled 1Khalid AbdulkarimNo ratings yet
- What Is Demand?Document24 pagesWhat Is Demand?ishankNo ratings yet
- Quantity Dded: A Specific Quantity That A Consumer Is Willing and Able Demand: The Relationship Between Various Possible Prices of ADocument84 pagesQuantity Dded: A Specific Quantity That A Consumer Is Willing and Able Demand: The Relationship Between Various Possible Prices of Aanduamlak wondimagegnNo ratings yet
- Anylisis & Finding: Efective Management Demand and SupplyDocument12 pagesAnylisis & Finding: Efective Management Demand and SupplyainonlelaNo ratings yet
- 2.theory of Demand and Supply.Document30 pages2.theory of Demand and Supply.punte77100% (1)
- Solved Problems of McconellDocument64 pagesSolved Problems of McconellAhsan Jalal0% (1)
- Demand TheoryDocument10 pagesDemand TheoryVinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Presentation Demand & Supply 1453886502 164314Document22 pagesPresentation Demand & Supply 1453886502 164314Avish GargNo ratings yet
- Catalytic ReformingDocument18 pagesCatalytic ReformingAleem AhmedNo ratings yet
- FT Panou Mono 400-415W DS - YLM-J 108 CELL M10 - 37e - 30mmDocument2 pagesFT Panou Mono 400-415W DS - YLM-J 108 CELL M10 - 37e - 30mmPetrica MunteanuNo ratings yet
- How Do You Calculate The Prefix, Network, Subnet, and Host Numbers?Document6 pagesHow Do You Calculate The Prefix, Network, Subnet, and Host Numbers?mayoori75No ratings yet
- Time Study ExampleDocument2 pagesTime Study ExampleShardon Ibo100% (1)
- Sample Size and Power CalculationDocument31 pagesSample Size and Power CalculationRendy Adhitya PratamaNo ratings yet
- Visit Braindump2go and Download Full Version 200-301 Exam DumpsDocument4 pagesVisit Braindump2go and Download Full Version 200-301 Exam DumpsSouvik ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- KOONS & ALEX 2014 - Revised Moche Chronology Based On Bayesian Models of Reliable Radiocarbon Dates PDFDocument17 pagesKOONS & ALEX 2014 - Revised Moche Chronology Based On Bayesian Models of Reliable Radiocarbon Dates PDFJoseeIsmaelNo ratings yet
- 12 Maths (Formula Sheet)Document15 pages12 Maths (Formula Sheet)Javeria RasoolNo ratings yet
- Limay Senior High School Duale, Limay, BataanDocument3 pagesLimay Senior High School Duale, Limay, BataanCecille DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Big Data Dan Penerapan Nya Dalam BisnisDocument41 pagesBig Data Dan Penerapan Nya Dalam BisnisZee ZioaNo ratings yet
- DEP 30.55.03.30-Gen. - 4Document19 pagesDEP 30.55.03.30-Gen. - 4Vipul PanchalNo ratings yet
- Microlights Micropan 2 150W CMH T Narrow /: Luminaire Data SheetDocument12 pagesMicrolights Micropan 2 150W CMH T Narrow /: Luminaire Data SheetHusnain AssociatesNo ratings yet
- Presented By, Sangeetha Bharath.GDocument16 pagesPresented By, Sangeetha Bharath.GG VigneshNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Matra LautDocument32 pagesJurnal Matra LautFebrian DumaNo ratings yet
- B. G. Clarke - Pressuremeters in Geotechnical Design-CRC Press (2022)Document407 pagesB. G. Clarke - Pressuremeters in Geotechnical Design-CRC Press (2022)JANDIRA NOVAISNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Ethical Hacking - Syllabus - Hacking ClubDocument33 pagesDiploma in Ethical Hacking - Syllabus - Hacking ClubWaseem AkramNo ratings yet
- Livre Mecanique Rationnelle 2017Document246 pagesLivre Mecanique Rationnelle 2017cham goldNo ratings yet
- Annealing PDFDocument5 pagesAnnealing PDFKamran ShakeelNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Ii: Quadratic EquationsDocument29 pagesMathematics Ii: Quadratic Equationsbernadeth villanuevaNo ratings yet
- Section 9 - Compact SpacesDocument9 pagesSection 9 - Compact SpacesJaZz SFNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument533 pagesUntitledDude345No ratings yet
- Magento 2 Install InstructionsDocument2 pagesMagento 2 Install InstructionsSyed Qaiser MoinNo ratings yet
- Drinking Water Treatment Using Hybrid Biosand Filter With Locally Produced Coconut Shell Carbon For Brgy. San Juan, Kalayaan, Laguna, PhilippinesDocument12 pagesDrinking Water Treatment Using Hybrid Biosand Filter With Locally Produced Coconut Shell Carbon For Brgy. San Juan, Kalayaan, Laguna, PhilippinesMyca Macompal HinampasNo ratings yet
- Mental Strategies For Multiplication and DivisionDocument4 pagesMental Strategies For Multiplication and DivisiontizuliveNo ratings yet
- CS8492 DBMS - Part A & Part BDocument26 pagesCS8492 DBMS - Part A & Part BRAJA.S 41No ratings yet
- Unit 4-TractionDocument37 pagesUnit 4-TractionHemadharshini RJNo ratings yet
- Ramanujan's Lost Notebook, Part III PDFDocument439 pagesRamanujan's Lost Notebook, Part III PDFSau L.100% (2)
- Seasonal Thermal Energy Storage ConceptsDocument11 pagesSeasonal Thermal Energy Storage Conceptsbhavya sreeNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet: Practical Research 2Document8 pagesActivity Sheet: Practical Research 2Evelyn Guevarra100% (1)