Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Network Address Translation (NAT) & Port Address Translation (PAT)
Uploaded by
devanasontaniya738Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Network Address Translation (NAT) & Port Address Translation (PAT)
Uploaded by
devanasontaniya738Copyright:
Available Formats
DSE-Sem2-Computer Networks
Network Address Translation (NAT) & Port Address Translation (PAT)
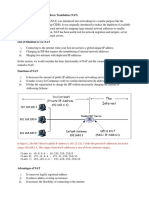
NAT is designed for IP address conservation/ saving/mapping. It enables private IP networks
that use unregistered IP addresses to connect to the Internet. NAT operates on a router,
usually connecting two networks together, and translates the private (not globally unique)
addresses in the internal network into real/legal addresses, before packets are forwarded to
another network.
As part of this capability, NAT can be configured to advertise only one address for the entire
network to the outside world. This provides additional security by effectively hiding the
entire internal network behind that address. NAT offers the dual functions of security and
address conservation.
Dynamic NAT - Is used when you have a “pool” of public IP addresses that you want to
assign to your internal hosts dynamically. Don’t use dynamic NAT for servers or other
devices that need to be accessible from the Internet.
NAT Overload (Sometimes also called PAT) - Is probably the most used type of NAT. You
have only one public IP address allocated by your ISP. In this case, NAT maps all your inside
hosts to the available public IP address.
Static NAT - Is used to do a one-to-one mapping between an inside address and an outside
address. Static NAT also allows connections from an outside host to an inside host. Usually,
static NAT is used for servers inside your network.
National Institute of Business Management 1
You might also like
- CiscoDocument7 pagesCiscoJill_xyinz14589No ratings yet
- Nat Basics PDFDocument48 pagesNat Basics PDFeveswan2008No ratings yet
- Information About NATDocument24 pagesInformation About NATsrikanth kNo ratings yet
- Configuring Network Address Translation (NAT)Document19 pagesConfiguring Network Address Translation (NAT)telecom_457036100% (1)
- Fatima Jinnah Women University: Items DescriptionDocument5 pagesFatima Jinnah Women University: Items DescriptionfaizaNo ratings yet
- NAT (Network Address Translation) : Defining NAT Inside and Outside InterfacesDocument6 pagesNAT (Network Address Translation) : Defining NAT Inside and Outside Interfacesimb2No ratings yet
- Introduction To NATDocument9 pagesIntroduction To NATShaba MichaelNo ratings yet
- NAT and PATDocument2 pagesNAT and PATAtik Israk Lemon100% (1)
- NAT For FTDDocument108 pagesNAT For FTDTim BurchmoreNo ratings yet
- Network Address Translation NAT For Threat DefenseDocument66 pagesNetwork Address Translation NAT For Threat DefensesaurabhNo ratings yet
- NAT and PATDocument4 pagesNAT and PATAbenezer TarikuNo ratings yet
- How NAT WorksDocument10 pagesHow NAT WorksRajNo ratings yet
- Configuring Static NAT in Cisco RouterDocument10 pagesConfiguring Static NAT in Cisco RouterDeepthi. rajshekarNo ratings yet
- Configuring Static and Dynamic Nat TranslationDocument24 pagesConfiguring Static and Dynamic Nat TranslationMiguel Angel FeriaNo ratings yet
- What Is NATDocument9 pagesWhat Is NATBelete TilahunNo ratings yet
- Nat Basics PDFDocument46 pagesNat Basics PDFDorivaldoNo ratings yet
- How Network Address Translation WorksDocument8 pagesHow Network Address Translation WorksPhaniraj LenkalapallyNo ratings yet
- Network Address Translation NAT TutorialDocument4 pagesNetwork Address Translation NAT Tutorialjorge jaramillo coronellNo ratings yet
- Cis 192 - Simranpreet Kaur - 300200432 - Assignment#6Document18 pagesCis 192 - Simranpreet Kaur - 300200432 - Assignment#6Simran KaurNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 NATDocument11 pagesLab 6 NATCharles CarpenterNo ratings yet
- Network Address Translation (NAT)Document7 pagesNetwork Address Translation (NAT)Rashmi HarneNo ratings yet
- New Network ProjectDocument13 pagesNew Network ProjectSubham PandeyNo ratings yet
- Network Address Translation (NAT) Is A Process in Which One or More Local IP AddressDocument10 pagesNetwork Address Translation (NAT) Is A Process in Which One or More Local IP AddresslijmatiosNo ratings yet
- NAT in DetailDocument12 pagesNAT in DetailRahul MishraNo ratings yet
- Notes For Lecture-11 MCA 206: Advanced Computer NetworksDocument8 pagesNotes For Lecture-11 MCA 206: Advanced Computer NetworksDilip DubeyNo ratings yet
- Nat - Overview 8.3 and LaterDocument24 pagesNat - Overview 8.3 and LaterThomas SchmelingNo ratings yet
- NAT and PATDocument17 pagesNAT and PATAbhishrkNo ratings yet
- Network Address Translation: Presented by Varsha HondeDocument22 pagesNetwork Address Translation: Presented by Varsha HondeTú HoàngNo ratings yet
- Configuration of DHCP & DNS Along With PAT ConfigurationDocument28 pagesConfiguration of DHCP & DNS Along With PAT ConfigurationKoushik Q SarkarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Network Address Translation (NAT)Document4 pagesIntroduction To Network Address Translation (NAT)Firemandeheavenly InamenNo ratings yet
- IW U4 Clase11Document43 pagesIW U4 Clase11Alfred MosqueraNo ratings yet
- NATDocument2 pagesNAToips sweetNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Network Address TranslationDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Network Address Translationpabup1hebyl2100% (1)
- Jurnal NAT OverloadingDocument7 pagesJurnal NAT OverloadingMohammad NowafNo ratings yet
- DHCP and NAT - Knowledge BaseDocument6 pagesDHCP and NAT - Knowledge BaseHasib Hamidul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Nat For Ipv4: Instructor MaterialsDocument62 pagesChapter 9: Nat For Ipv4: Instructor MaterialsAmjad hassanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Nat For Ipv4: Ccna Routing and Switching Routing and Switching Essentials V6.0Document53 pagesChapter 9: Nat For Ipv4: Ccna Routing and Switching Routing and Switching Essentials V6.0Richard CheccaNo ratings yet
- Network Address Translation (NAT)Document16 pagesNetwork Address Translation (NAT)Mubarik Ali MuhumedNo ratings yet
- Configuring and Deploying NAT (Network Address Translation) On A Cisco RouterDocument6 pagesConfiguring and Deploying NAT (Network Address Translation) On A Cisco RoutercursoNo ratings yet
- UCCN2003-2243 - Lect03 - Network Address TranslationDocument85 pagesUCCN2003-2243 - Lect03 - Network Address Translationhowiee0730No ratings yet
- Smart NAT Feature For LinkProof NGDocument3 pagesSmart NAT Feature For LinkProof NGAyanNo ratings yet
- Iadnat Addr ConsvDocument48 pagesIadnat Addr ConsvEapapagalos PapagalidisNo ratings yet
- 52 Nat PatDocument5 pages52 Nat PatBHARYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 v.1Document21 pagesChapter 12 v.1sujeet_hatNo ratings yet
- NAT TypesDocument48 pagesNAT TypesMarselNo ratings yet
- Natting in DepthDocument31 pagesNatting in DepthJunior foxNo ratings yet
- Network Address TranslationDocument16 pagesNetwork Address TranslationsovannarathNo ratings yet
- 046 Krishanu Mondal BCAC602Document5 pages046 Krishanu Mondal BCAC602Krishanu MondalNo ratings yet
- 09 - NAT For IPv4Document51 pages09 - NAT For IPv4eztog006No ratings yet
- Network Address Translation (NAT) : Khawar Butt Ccie # 12353 (R/S, Security, SP, DC, Voice, Storage & Ccde)Document11 pagesNetwork Address Translation (NAT) : Khawar Butt Ccie # 12353 (R/S, Security, SP, DC, Voice, Storage & Ccde)sans mahe1No ratings yet
- Networking BasicsDocument19 pagesNetworking BasicsRamraje ShindeNo ratings yet
- Private IP Address: Home Learn IP AddressesDocument10 pagesPrivate IP Address: Home Learn IP AddressesSundareshNo ratings yet
- Network Address Translation (NAT)Document49 pagesNetwork Address Translation (NAT)Kero MaalosaNo ratings yet
- Online Supplements: Domain 1.0 Networking ConceptsDocument8 pagesOnline Supplements: Domain 1.0 Networking ConceptsLampZOSNo ratings yet
- 24 Network Address TranslationDocument20 pages24 Network Address TranslationRakesh CharyNo ratings yet
- Topology Hiding - Vijay - TopDocument52 pagesTopology Hiding - Vijay - TopnepoznateNo ratings yet
- Cisco TAC Entry Training - 9 - Network Address Translation (NAT)Document40 pagesCisco TAC Entry Training - 9 - Network Address Translation (NAT)FerasHamdanNo ratings yet
- NatDocument12 pagesNatAnh TranNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1From EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)