Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Demand - Pertemuan Ke-3 - 10.10.2023
Uploaded by
jjk4515060 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views17 pagesSurat izin sakit
Original Title
demand - Pertemuan ke-3_10.10.2023 (2)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSurat izin sakit
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views17 pagesDemand - Pertemuan Ke-3 - 10.10.2023
Uploaded by
jjk451506Surat izin sakit
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
CHAPTER
The Market Forces of
Supply and Demand
Economics
ESSENTIALS OF
Dr. Nanda R. Nurdianto S.E., M.S.E.
© 2009 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning, all rights reserved
Markets and Competition
▪ A market is a group of buyers and sellers of a
particular product.
▪ A competitive market is one with many buyers
and sellers, each has a negligible effect on price.
▪ In a perfectly competitive market:
▪ All goods exactly the same
▪ Buyers & sellers so numerous that no one can
affect market price – each is a “price taker”
▪ In this chapter, we assume markets are perfectly
competitive.
THE MARKET FORCES OF SUPPLY AND DEMAND 1
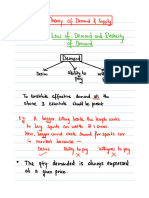
Demand
▪ The quantity demanded of any good is the
amount of the good that buyers are willing and
able to purchase.
▪ Law of demand: the claim that the quantity
demanded of a good falls when the price of the
good rises, other things equal
THE MARKET FORCES OF SUPPLY AND DEMAND 2
The Demand Schedule
▪ Demand schedule: a table that shows the
relationship between the price of a good and
the quantity demanded
THE MARKET FORCES OF SUPPLY AND DEMAND 3
THE MARKET FORCES OF SUPPLY AND DEMAND 4
Demand Curve Shifters
▪ The demand curve shows how price affects
quantity demanded, other things being equal.
▪ These “other things” are non-price determinants
of demand
▪ Changes in them shift the D curve…
THE MARKET FORCES OF SUPPLY AND DEMAND 5
THE MARKET FORCES OF SUPPLY AND DEMAND 6
THE MARKET FORCES OF SUPPLY AND DEMAND 7
Demand Curve Shifters: # of Buyers
▪ Increase in # of buyers
increases quantity demanded at each price,
shifts D curve to the right.
THE MARKET FORCES OF SUPPLY AND DEMAND 8
Demand Curve Shifters: Income
▪ Demand for a normal good is positively related
to income.
▪ Increase in income causes
increase in quantity demanded at each price,
shifts D curve to the right.
(Demand for an inferior good is negatively
related to income. An increase in income shifts
D curves for inferior goods to the left.)
THE MARKET FORCES OF SUPPLY AND DEMAND 9
THE MARKET FORCES OF SUPPLY AND DEMAND 10
Demand Curve Shifters: Prices of
Related Goods
▪ Two goods are substitutes if
an increase in the price of one
causes an increase in demand for the other.
▪ Example: pizza and hamburgers.
An increase in the price of pizza
increases demand for hamburgers,
shifting hamburger demand curve to the right.
▪ Other examples: Coke and Pepsi,
laptops and desktop computers,
CDs and music downloads
THE MARKET FORCES OF SUPPLY AND DEMAND 11
Demand Curve Shifters: Prices of
Related Goods
▪ Two goods are complements if
an increase in the price of one
causes a fall in demand for the other.
▪ Example: computers and software.
If price of computers rises, people buy fewer
computers, and therefore less software.
Software demand curve shifts left.
▪ Other examples: college tuition and textbooks,
bagels and cream cheese, eggs and bacon
THE MARKET FORCES OF SUPPLY AND DEMAND 12
Demand Curve Shifters: Tastes
▪ Anything that causes a shift in tastes toward a
good will increase demand for that good
and shift its D curve to the right.
▪ Example:
The Atkins diet became popular in the ’90s,
caused an increase in demand for eggs,
shifted the egg demand curve to the right.
THE MARKET FORCES OF SUPPLY AND DEMAND 13
Demand Curve Shifters: Expectations
▪ Expectations affect consumers’ buying
decisions.
▪ Examples:
▪ If people expect their incomes to rise,
their demand for meals at expensive
restaurants may increase now.
▪ If the economy sours and people worry about
their future job security, demand for new
autos may fall now.
THE MARKET FORCES OF SUPPLY AND DEMAND 14
Summary: Variables That Influence Buyers
Variable A change in this variable…
Price …causes a movement
along the D curve
# of buyers …shifts the D curve
Income …shifts the D curve
Price of
related goods …shifts the D curve
Tastes …shifts the D curve
Expectations …shifts the D curve
THE MARKET FORCES OF SUPPLY AND DEMAND 15
ACTIVE LEARNING 1
Demand Curve
Draw a demand curve for online music
streaming. What happens to it in each of
the following scenarios? Why?
A. The price of
handphone falls
B. The subscription fee
of online music
streaming falls
C. The price of CDs falls
16
You might also like
- The Market Forces of Supply and DemandDocument63 pagesThe Market Forces of Supply and DemandFayazul HasanNo ratings yet
- A level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Exam Success in Economics For Cambridge IGCSE AnswersDocument30 pagesExam Success in Economics For Cambridge IGCSE AnswersAKARESH JOSE EBOOKS100% (1)
- Microeconomics Canadian 1st Edition Karlan Test Bank DownloadDocument99 pagesMicroeconomics Canadian 1st Edition Karlan Test Bank DownloadDaniel Salazar100% (20)
- Principles of Agricultural EconomicsDocument116 pagesPrinciples of Agricultural EconomicsremankumarNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 The Market Forces of Supply and DemandDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 4 The Market Forces of Supply and DemandclaraNo ratings yet
- ECON200 Lecture 2 - Law of DemandDocument35 pagesECON200 Lecture 2 - Law of DemandDahlia Johnson-RoperNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply: Abu Naser Mohammad SaifDocument66 pagesDemand and Supply: Abu Naser Mohammad SaifSH RaihanNo ratings yet
- Principles 08F Lecture3Document12 pagesPrinciples 08F Lecture3Shiela MaeaNo ratings yet
- Micro Ch04 PresentationDocument62 pagesMicro Ch04 PresentationEmmangeorgeNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply: Dr. Aruna Kumar Dash Associate Professor, Ibs, HyderabadDocument44 pagesDemand and Supply: Dr. Aruna Kumar Dash Associate Professor, Ibs, HyderabadS V PNo ratings yet
- Supply ChainDocument32 pagesSupply ChainAMBWANI NAREN MAHESHNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply - Price Ceilling and FloorDocument56 pagesDemand and Supply - Price Ceilling and Floor0241ASHAYNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10,11,13Document10 pagesLecture 10,11,13Sankaranarayanan ANo ratings yet
- 02 Law of DemandDocument31 pages02 Law of Demandkowsalya18No ratings yet
- Session 2 PPT Demand-And-SupplyDocument53 pagesSession 2 PPT Demand-And-SupplyMuhammad AreebNo ratings yet
- Demand: Real World Issue: How Do Consumers and Producers Make Choices in Trying To Meet TheirDocument53 pagesDemand: Real World Issue: How Do Consumers and Producers Make Choices in Trying To Meet TheirCan ÖzkanNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply ModelDocument24 pagesDemand and Supply ModelШугыла Есимхан100% (1)
- ECO2011 Basic Microeconomics - Lecture 5Document34 pagesECO2011 Basic Microeconomics - Lecture 51194390705No ratings yet
- What Is Demand?Document24 pagesWhat Is Demand?ishankNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 EcoDocument35 pagesChapter 2 EcoRules of Survival MALAYSIANo ratings yet
- CH 4: The Market Forces of Supply and Demand: Monopoly. E.G. Local Cable Television CompanyDocument5 pagesCH 4: The Market Forces of Supply and Demand: Monopoly. E.G. Local Cable Television CompanyLiezel Garcia MacatuladNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document39 pagesChapter 2NASUHANo ratings yet
- Chapter (Eng. Eco) 002Document23 pagesChapter (Eng. Eco) 002dsbsabirkhanNo ratings yet
- Demand A Learning Objective: Theory of Demand, Demand Schedule and Curve, and Market Demand PriceDocument7 pagesDemand A Learning Objective: Theory of Demand, Demand Schedule and Curve, and Market Demand PriceRohitPatialNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply - Price Ceilling and Floor (Autosaved)Document56 pagesDemand and Supply - Price Ceilling and Floor (Autosaved)swakrit banikNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Price Theory - DemandDocument24 pagesLecture 2 Price Theory - DemandAlex WongNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Price Theory - DemandDocument24 pagesLecture 2 Price Theory - DemandAlex WongNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Demand, Supply, and Market EquilibriumDocument65 pagesUnit 2 - Demand, Supply, and Market EquilibriumsikanjiticliffordNo ratings yet
- 03 - Law of DemandDocument23 pages03 - Law of DemandZain Dar100% (1)
- Fundamental Law of EconomicsDocument12 pagesFundamental Law of Economicsbrigitte shane gedorioNo ratings yet
- 1 Supply and DemandDocument56 pages1 Supply and DemandYash ShindeNo ratings yet
- Demand TheoryDocument19 pagesDemand TheoryRohit GoyalNo ratings yet
- Demond Thoery - NotesDocument10 pagesDemond Thoery - Noteschikkegowda k gNo ratings yet
- (ECON 1N) Chapter 3 - Demand and SupplyDocument65 pages(ECON 1N) Chapter 3 - Demand and SupplyCliff Sean Kyle OtadoyNo ratings yet
- DemandDocument32 pagesDemandAlli PNo ratings yet
- Section 2 7demandDocument43 pagesSection 2 7demands-zhangyuchengNo ratings yet
- Chap2-110306024813market Structure-Phpapp02Document53 pagesChap2-110306024813market Structure-Phpapp02Poonam Khurana GandhiNo ratings yet
- M2 Demand Suppy EquillibriumDocument57 pagesM2 Demand Suppy EquillibriumYASHAS MOHAN 2150240No ratings yet
- Day 2 PDFDocument91 pagesDay 2 PDFNgoc Anh LeNo ratings yet
- Demand & Supply: A First Look: FosterDocument18 pagesDemand & Supply: A First Look: FosterCutler FisherNo ratings yet
- ECON Lecture 2 - Market Equilibrium (Apr2020)Document51 pagesECON Lecture 2 - Market Equilibrium (Apr2020)Hussein JahangeerNo ratings yet
- EWS - Introduction To DemandDocument28 pagesEWS - Introduction To DemandShriyaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Demand and Supply: Teach A Parrot To Say "Demand and Supply" and You Have An Economist (Campbell R.)Document17 pagesTheory of Demand and Supply: Teach A Parrot To Say "Demand and Supply" and You Have An Economist (Campbell R.)Ishimwe oliveNo ratings yet
- Principles of Microeconomics Chapter 2 - Thinking Like An EconomistDocument35 pagesPrinciples of Microeconomics Chapter 2 - Thinking Like An EconomistKing SigueNo ratings yet
- Hul211 Unit2a Demand Supply BasicsDocument23 pagesHul211 Unit2a Demand Supply BasicsTanayJohariNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Lesson 1 - Competitive Markets DemandDocument18 pagesUnit 2 - Lesson 1 - Competitive Markets Demandapi-260512563No ratings yet
- Supply and DemandDocument30 pagesSupply and DemandMickey EustaquioNo ratings yet
- DemandDocument86 pagesDemandAveeraj singh maanNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply-MinDocument18 pagesDemand and Supply-MinHoang Minh HienNo ratings yet
- ManEcon Module 2Document7 pagesManEcon Module 2Lili PadNo ratings yet
- Theory of DemandDocument8 pagesTheory of Demandakb000007No ratings yet
- Microeconomics 2: Chapter 4: The Market Forces of Supply and DemandDocument15 pagesMicroeconomics 2: Chapter 4: The Market Forces of Supply and DemandSegismundo Gutiérrez LugoNo ratings yet
- Chapter (Eng. Eco) 003Document16 pagesChapter (Eng. Eco) 003dsbsabirkhanNo ratings yet
- Untitled 1Document36 pagesUntitled 1Khalid AbdulkarimNo ratings yet
- Supply and DemandDocument20 pagesSupply and DemandmingwoonNo ratings yet
- Demand and SupplyDocument52 pagesDemand and SupplyAvanthicka MohanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Demand and Supply Review: C. BennettDocument33 pagesUnit 1: Demand and Supply Review: C. BennettCheraleda ExantusNo ratings yet
- Edexcel (B) Economics A-Level: Theme FirmsDocument4 pagesEdexcel (B) Economics A-Level: Theme FirmsMohamed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: The Market Forces of Supply and DemandDocument17 pagesChapter 4: The Market Forces of Supply and DemandFarNo ratings yet
- Demand Supply and Markets Keat and Young - 2Document96 pagesDemand Supply and Markets Keat and Young - 2Dhruv SoodNo ratings yet
- The Amount of The Commodity That The Buyer Is Willing and Able To Buy, at A Particular Price in A Given Time Period Is Called DemandDocument42 pagesThe Amount of The Commodity That The Buyer Is Willing and Able To Buy, at A Particular Price in A Given Time Period Is Called Demandabdulmuqsit0555No ratings yet
- Demand - Engineering EconomicsDocument15 pagesDemand - Engineering EconomicsPankaj Gill0% (1)
- He Defines Economics As The Science of Choice. It Studies How People Choose To Use Scarce Resources orDocument5 pagesHe Defines Economics As The Science of Choice. It Studies How People Choose To Use Scarce Resources orMarilyn GarciaNo ratings yet
- Business in Action 8th Edition Chapter 2:building The Framework: Business Ownership and EntrepreneurshipDocument5 pagesBusiness in Action 8th Edition Chapter 2:building The Framework: Business Ownership and EntrepreneurshipFatima MajidliNo ratings yet
- Bam 040 ReviewerDocument7 pagesBam 040 ReviewerAndrea Vila VelascoNo ratings yet
- 微观经济学笔记Document130 pages微观经济学笔记Alyse97No ratings yet
- Principles OF Microeconomics: Lecturer: Kinwah LoDocument17 pagesPrinciples OF Microeconomics: Lecturer: Kinwah Longọc phạmNo ratings yet
- Elasticity - Part Three Question With AnswersDocument4 pagesElasticity - Part Three Question With Answersragheb hanfiNo ratings yet
- 8.economics Chalisa by Manish DuaDocument57 pages8.economics Chalisa by Manish DuaPushpinder KumarNo ratings yet
- Mergedtest 1 Nov6Document137 pagesMergedtest 1 Nov6BLESSEDNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics ReviewerDocument6 pagesManagerial Economics ReviewerDrieya KadiNo ratings yet
- Econ 107Document14 pagesEcon 107hazem 00No ratings yet
- Supply ChainDocument32 pagesSupply ChainAMBWANI NAREN MAHESHNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics & Business Strategy: Market Forces: Demand and SupplyDocument36 pagesManagerial Economics & Business Strategy: Market Forces: Demand and SupplychandasumaNo ratings yet
- ArthaSutra - Day 1Document7 pagesArthaSutra - Day 1phoenixankurNo ratings yet
- Economics 5 MCQ C5 2Document24 pagesEconomics 5 MCQ C5 2tshepangmathobela188No ratings yet
- Market EquilibriumDocument8 pagesMarket EquilibriumSourav SinghNo ratings yet
- Choose The Correct AnswerDocument6 pagesChoose The Correct AnswerGowtham RajNo ratings yet
- Theory of Demand & Supply Revision NotesDocument58 pagesTheory of Demand & Supply Revision Noteswosihit898No ratings yet
- Calculus For Bus and Econ Sample PDFDocument5 pagesCalculus For Bus and Econ Sample PDFWade GrayNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Core Fundamentals For Trading OilDocument12 pagesUnderstanding The Core Fundamentals For Trading Oilhilquias otinielNo ratings yet
- Economics 6th Edition Hubbard Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesEconomics 6th Edition Hubbard Solutions Manual 1zacharyricenodmczkyrt100% (25)
- Pre Test FM1Document14 pagesPre Test FM1Kryzzel Anne JonNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1 AkeyDocument14 pagesMidterm 1 AkeyLayomi Dele-DareNo ratings yet
- Business Economics Presentation ON Law of Demand & Elasticity of DemandDocument20 pagesBusiness Economics Presentation ON Law of Demand & Elasticity of DemandTushar BhatiNo ratings yet
- Applied Economicshons. Hsk1Document61 pagesApplied Economicshons. Hsk1Srishti SethiNo ratings yet
- NCERT Class 12 Economics Market EquilibriumDocument17 pagesNCERT Class 12 Economics Market EquilibriumMahesh k KNo ratings yet
- Asmah Frank PDFDocument44 pagesAsmah Frank PDFmr. sharifNo ratings yet
- Questions SOLVEDDocument10 pagesQuestions SOLVEDNafisul AbrarNo ratings yet