0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views5 pagesLathe Machine Parts Overview
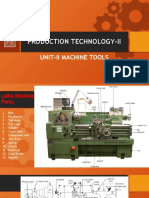
The document describes the main parts of a lathe machine, including the headstock, tailstock, saddle, and bed. The headstock holds the spindle and gears. The tailstock supports the workpiece from the right side. The saddle mounts the cross-slide and apron and moves along the bed ways.
Uploaded by
Echee NikeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views5 pagesLathe Machine Parts Overview
The document describes the main parts of a lathe machine, including the headstock, tailstock, saddle, and bed. The headstock holds the spindle and gears. The tailstock supports the workpiece from the right side. The saddle mounts the cross-slide and apron and moves along the bed ways.
Uploaded by
Echee NikeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd