Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Elephants
Uploaded by
linhnmhs173423Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Elephants
Uploaded by
linhnmhs173423Copyright:
Available Formats
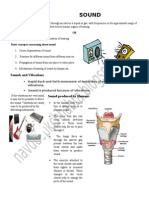
Elephants Humans
How they make sounds - The loud trumpet-like sound - The voice cords are shorter,
made by elephants through thinner, tighter
their trunks
- Elephants can make many
different sounds from deep,
very low-frequency rumbles
(like the sound of thunder) to
higher-frequency roars and
cries
- Pushing air out of the lungs
through the larynx and
causing the vocal cords.
- They also use the tongue,
mouth and trunk to make a
more accurate sound for
communication.
How they hear sounds -When the elephant's vocal cords
are moved by the passing air, it
can make very-low-frequency
rumbling noises-often so low that
people cannot hear them.
1. The loud trumpet-like sound made by elephants through their trunks is one of the most
famous noises of the animal world, but it is not the only sound that elephants make.
Elephants can make many different sounds from deep, very low-frequency rumbles (like the
sound of thunder) to higher-frequency roars and cries. Over the last few decades, scientists
have learned more and more about how elephants make all these sounds.
2. Though humans and elephants look very different on the outside, they both have similar
body parts for making sounds. Like humans, elephants have a larynx (or voice box) in their
throats. Air that is pushed out from the lungs travels over the larynx and makes the vocal
cords (which are part of the larynx) move-similar to the way a flag moves in the wind. This
movement makes a sound, which can then be changed by the tongue, mouth, and trunk to
make more exact sounds for communication.
3. There are also differences in the ways elephants and humans make sounds. Most
importantly, the vocal cords in an elephant's larynx are much longer, thicker, and looser than
a human's. When the elephant's vocal cords are moved by the passing air, it can make very-
low-frequency rumbling noises-often so low that people cannot hear them. This is similar to
how frequency works with musical instruments: the short, tight strings on a violin make a
high-frequency sound; the long, thick, and looser strings of a bass violin make a deep, low-
frequency sound.
4. While an elephant's call starts with air passing over the larynx, other parts of the animal's
body are also important in controlling the sound. Scientists believe that elephants move their
heads, neck, and ears to change the position of the larynx so they can create different
sounds. Of course, the elephant also has a very large body, and this means the sounds can
strongly vibrate through the body and be amplified (i.e., the sound's volume increases),
When the trunk is fully extended, stretched out to its full length, the sound is amplified even
more powerfully. This means that the low rumbling noises that elephants make can travel
long distances. These long-range rumbles are not only useful for communication, but they
can also tell the listening elephant how far away the sender is.
HOW THE ELEPHANTS CAN MAKE AND HEAR SOUNDS
The way elephants communicate to others is by producing and hearing sounds. The first
should be how the elephants producing sound. Because they have a larynx (or voice box) in
their throats like humans. So to make a sound, they push air out from their lungs, travel over
the larynx and make the vocal cords (which are part of the larynx).
They can also use their mouth, tongue or trunk to make more exact sounds for
communication. When an elephant make sounds, those sounds travel through the air and
enter another elephant or some other animal ear where they are received by the eardrum.
About how elephants can hear sounds: Due to the special structure of the head, ears and
body of elephants compared to other species, they can all emit low-frequency sounds, so
they can hear low-frequency sounds. The elephant's hearing ability falls between 14 and
20000 Hz. When the trunk is fully extended and extended, the sound is amplified more
strongly. And the small rumbling noises that elephants make can travel long distances, very
useful for communication, warning of danger to fellow humans (because there are animals
that can't hear low frequencies), let them know how far apart they are,...
You might also like
- How Elephants CommunicateDocument8 pagesHow Elephants CommunicateTawanda ChibweNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Sound Energy Through Vibrations SMP Bangun Insan Mandiri Sec 2-Sciene Ms. Corry PasaribuDocument30 pagesTransfer of Sound Energy Through Vibrations SMP Bangun Insan Mandiri Sec 2-Sciene Ms. Corry PasaribuCorry SepviaNo ratings yet
- My Ears are Special : The Science of Sound - Physics Book for Children | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandMy Ears are Special : The Science of Sound - Physics Book for Children | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Adventures in Sound with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandAdventures in Sound with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Sound: Sounds and VibrationsDocument7 pagesSound: Sounds and Vibrationschhabra navdeepNo ratings yet
- Bouncing Sounds: Echo, Echo, Echo - Sounds for Kids - Children's Acoustics & Sound BooksFrom EverandBouncing Sounds: Echo, Echo, Echo - Sounds for Kids - Children's Acoustics & Sound BooksNo ratings yet
- Sound: Sound Produced by Human: A Human Being Produces Sound Because of Vibration of HisDocument2 pagesSound: Sound Produced by Human: A Human Being Produces Sound Because of Vibration of HisRavi ThakurNo ratings yet
- Theme 1 The Beautiful of Togetherness: Creative ThinkingDocument8 pagesTheme 1 The Beautiful of Togetherness: Creative ThinkingFitria Istikomah DewiNo ratings yet
- Sound PPT-2Document16 pagesSound PPT-2prabhavkalsiNo ratings yet
- C Yx QW6 Fa 5 IQizz VSDocument2 pagesC Yx QW6 Fa 5 IQizz VSujwvobaqgrgpfrcubaNo ratings yet
- Phonetics & Phonology LecturesDocument10 pagesPhonetics & Phonology LecturesJo O ConnorNo ratings yet
- The Organs of Speech: Vocal Cords GlottisDocument1 pageThe Organs of Speech: Vocal Cords GlottisImran AliNo ratings yet
- Hearing and Sound Study SheetDocument4 pagesHearing and Sound Study Sheetapi-269680921No ratings yet
- Sound WavesDocument11 pagesSound WavesMuhammad Iqbal SulthoniNo ratings yet
- Sound WavesDocument11 pagesSound Wavesccg jjNo ratings yet
- Sound MLPDocument2 pagesSound MLPPianoPianistNo ratings yet
- Sound: The Vibrations That PropagatesDocument31 pagesSound: The Vibrations That PropagatesSarika AhujaNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 Handout: Sound Travels Through The Air in WavesDocument12 pagesActivity 3 Handout: Sound Travels Through The Air in Wavesapi-112265046No ratings yet
- SoundDocument5 pagesSoundOnlymexxNo ratings yet
- Time, Light, Sound: Rutvi KundaliyaDocument6 pagesTime, Light, Sound: Rutvi KundaliyaRutvi KundaliyaNo ratings yet
- Sound NotesDocument4 pagesSound NotesBuddhini JNo ratings yet
- Phonetic ADocument28 pagesPhonetic ANina BandalacNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Sound Waves - Student'sDocument3 pagesLesson 7 Sound Waves - Student'smanilamidwest26No ratings yet
- Sound 8 THDocument34 pagesSound 8 THPrakash KvsNo ratings yet
- Ound NotesDocument5 pagesOund Notesmokshithakapoor657No ratings yet
- How Does Echolocation Work? Science Book 4th Grade | Children's Science & Nature BooksFrom EverandHow Does Echolocation Work? Science Book 4th Grade | Children's Science & Nature BooksNo ratings yet
- Name: Eka Uchi M.Sirait NPM:2101030052 Subject: Phonology LecturerDocument3 pagesName: Eka Uchi M.Sirait NPM:2101030052 Subject: Phonology LecturerMaretta SiadariNo ratings yet
- Sound EnergyDocument13 pagesSound EnergyBassel ZeitouniNo ratings yet
- Sound Notes 9 BDocument3 pagesSound Notes 9 Bsmi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- Unit 3-PhoneticsDocument58 pagesUnit 3-Phoneticsdev448230No ratings yet
- Sound EnergyDocument13 pagesSound Energyash jackkNo ratings yet
- English PhoneticsDocument36 pagesEnglish PhoneticsNorbinkoNotorickoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Sound WaveDocument27 pagesLesson 4 - Sound WaveElijah AlcorezaNo ratings yet
- Audio Frequency Range and Principles-Revised - 2Document57 pagesAudio Frequency Range and Principles-Revised - 2stdesereeditanNo ratings yet
- The Voice Production Process: Presented By: Group 3Document24 pagesThe Voice Production Process: Presented By: Group 3Anjene MarieNo ratings yet
- Physiology of EarDocument20 pagesPhysiology of EarChippy SinghNo ratings yet
- Hearing: How Your Ears WorkDocument3 pagesHearing: How Your Ears WorkKelsey HillNo ratings yet
- MUSIC 10 Q2 2nd ModulesDocument8 pagesMUSIC 10 Q2 2nd ModulescharlitoskNo ratings yet
- Lecture No.17. Auditory or Acoustic Communication in Insects PDFDocument2 pagesLecture No.17. Auditory or Acoustic Communication in Insects PDFmuhammad hassanNo ratings yet
- Lecture No.17. Auditory or Acoustic Communication in Insects PDFDocument2 pagesLecture No.17. Auditory or Acoustic Communication in Insects PDFmuhammad hassanNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument2 pagesNotesRUPANo ratings yet
- The Voice: and The Musical InstrumentsDocument12 pagesThe Voice: and The Musical InstrumentsnireadaetaNo ratings yet
- How Hearing WorksDocument8 pagesHow Hearing WorksbostermanNo ratings yet
- SOUND IntroDocument26 pagesSOUND IntroHelmiyanto IsmoyoNo ratings yet
- Speech OrganDocument35 pagesSpeech OrganAnonymous AisyzyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13 - Sound (Physics - Science) (PA-2 Portion)Document4 pagesLesson 13 - Sound (Physics - Science) (PA-2 Portion)Suganthi GajamurthyNo ratings yet
- Art Integration ProjectDocument14 pagesArt Integration Projectkislay kathuriaNo ratings yet
- Mid-Term PhoneticsDocument17 pagesMid-Term Phoneticsngothuong854No ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document5 pagesLecture 3Jeevan jyoti vnsNo ratings yet
- Reading ComprehensionDocument2 pagesReading ComprehensionGhina ItaniNo ratings yet
- Q-A CH 13-Sound (Topics Covered - 13.1,13.2,13.3,13.4)Document2 pagesQ-A CH 13-Sound (Topics Covered - 13.1,13.2,13.3,13.4)LolDudeNo ratings yet
- Learn How The Vocal Cords Work - Transcript of YouTube VideoDocument3 pagesLearn How The Vocal Cords Work - Transcript of YouTube VideoLaurie ThomasNo ratings yet
- Organs of SpeechDocument5 pagesOrgans of SpeechRhaenyra TargaryenNo ratings yet
- Sound: A Science A-Z Physical Series Word Count: 1,093Document11 pagesSound: A Science A-Z Physical Series Word Count: 1,093grammarandNo ratings yet
- How Speech Organs Work in Producing The Speech Sounds?Document33 pagesHow Speech Organs Work in Producing The Speech Sounds?shangar omerNo ratings yet
- Elng 101 Module 2Document24 pagesElng 101 Module 2Mutya Kismet LogroñoNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 TestDocument2 pagesUnit 6 TestRaphael LogaNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Bring Us o Lord God Sir William Henry Harris and at Eventide We Have Seen LightDocument13 pagesDokumen - Tips Bring Us o Lord God Sir William Henry Harris and at Eventide We Have Seen Lightapronia noblefrancaNo ratings yet
- Honk Jr. Character ListDocument2 pagesHonk Jr. Character Listfalconsfables100% (1)
- Pe3 Paso DobleDocument21 pagesPe3 Paso DobleNba luxNo ratings yet
- Ragtime AnnieDocument1 pageRagtime AnnieIvan ManoelNo ratings yet
- Sacred Music in The Middles AgesDocument2 pagesSacred Music in The Middles AgesMarian Bernadette Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- AlphabetsDocument1 pageAlphabetsTedzNo ratings yet
- Jazz Repertoire ListDocument10 pagesJazz Repertoire Listapi-532840947100% (1)
- Early Life: Mariah Carey (Document15 pagesEarly Life: Mariah Carey (Агеева АлинаNo ratings yet
- CM Mapeh 7Document3 pagesCM Mapeh 7shiela manalaysayNo ratings yet
- Every Breath You Take Tab by StingDocument1 pageEvery Breath You Take Tab by StingCath WongNo ratings yet
- Reel em in and Rachet em Down: Irene Guggenheim-TrianaDocument2 pagesReel em in and Rachet em Down: Irene Guggenheim-TrianaIrene Guggenheim-TrianaNo ratings yet
- The List of Hitc Nominations Received Upto 27-04-2009Document22 pagesThe List of Hitc Nominations Received Upto 27-04-2009Vinod Naraya100% (1)
- Birdland (Live From 8:30) : Weather ReportDocument13 pagesBirdland (Live From 8:30) : Weather ReportJakira Ebony BrophyNo ratings yet
- Digital Booklet - Batman - Arkham OriginsDocument6 pagesDigital Booklet - Batman - Arkham Originsmarcelo_souza_41No ratings yet
- FLY CHORDS (Ver 3) by Nicki Minaj Feat. Rihanna at Ultimate-GuitarDocument3 pagesFLY CHORDS (Ver 3) by Nicki Minaj Feat. Rihanna at Ultimate-GuitarroxNo ratings yet
- WWWW#WWWBWWBW#WWBWBWB & & & & & & &: Chord Scales For Lydian Dominant and Altered 7th ChordsDocument1 pageWWWW#WWWBWWBW#WWBWBWB & & & & & & &: Chord Scales For Lydian Dominant and Altered 7th ChordsghanaruNo ratings yet
- Hisaishi Joe-Always With Me11Document4 pagesHisaishi Joe-Always With Me11Truong NguyenchiNo ratings yet
- THATS THE WAY IT IS CHORDS by Celine Dion @Document1 pageTHATS THE WAY IT IS CHORDS by Celine Dion @Sarah Rakoto AndrianjakaNo ratings yet
- Band Midterm Study Sheet 2019Document6 pagesBand Midterm Study Sheet 2019Melissa MorganNo ratings yet
- Hughes & Kettner - MetroverbDocument23 pagesHughes & Kettner - MetroverbFrans HeestersNo ratings yet
- W1 MusicDocument5 pagesW1 MusicHERSHEY SAMSONNo ratings yet
- Cifra Club - Led Zeppelin - Stairway To HeavenDocument17 pagesCifra Club - Led Zeppelin - Stairway To HeavenKenzariNo ratings yet
- MAPEH 7 Quarter 1 - FinalDocument8 pagesMAPEH 7 Quarter 1 - FinalGladys CandidoNo ratings yet
- A Canon For ChristmasDocument6 pagesA Canon For ChristmasDrenia AgustinNo ratings yet
- A Group Assignment: in A Flexible-Offline ClassesDocument28 pagesA Group Assignment: in A Flexible-Offline ClassesRecca CuraNo ratings yet
- Glenn Gould - Bazzana Kevin - Thirty-Two Short Films About Glenn GouldDocument13 pagesGlenn Gould - Bazzana Kevin - Thirty-Two Short Films About Glenn GouldCarlos Montes de Oca GuerreroNo ratings yet
- 3 Duets BachDocument1 page3 Duets BachАрсен ХизриевNo ratings yet
- Social Call Gigi Gryce LeadsheetDocument2 pagesSocial Call Gigi Gryce LeadsheetAnthony Healy87% (15)
- Quarter 3 Music Lesson 1 Week 1Document80 pagesQuarter 3 Music Lesson 1 Week 1RYAN C. ENRIQUEZNo ratings yet