Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physical Sciences Post Test T 1 2023
Physical Sciences Post Test T 1 2023
Uploaded by
NtobekoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physical Sciences Post Test T 1 2023
Physical Sciences Post Test T 1 2023
Uploaded by
NtobekoCopyright:
Available Formats
Post-test March 2023 Physical sciences
QUESTION 1
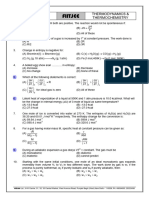
The vapour pressure versus temperature graph below was obtained for four straight chain
(unbranched) alkanes (P, Q, R and S).
FROM P TO S, EACH COMPOUND DIFFERS FROM THE PREVIOUS COMPOUND BY
A –CH2 GROUP.
The vapour pressures are measured in mmHg. Atmospheric pressure is 760 mmHg.
Graph of vapour pressure versus temperature
900
760
750
600 P
450 Q
300
P R
R S
Q
150
S
0 20 40 60 80 100
Temperature (°C)
1.1Give a reason why alkanes are said to be SATURATED. (1)
1.2Define vapour pressure. (2)
1.3Use the information in the graph above to answer the following questions.
1.3.1 What is the effect of an increase in temperature on vapour pressure? Choose
from INCREASES, DECREASES or
NO EFFECT. (1)
1.3.2 Which compound has a boiling point of approximately 68 °C? Give a reason
for the answer. (2)
1.3.3 Which compound has the longest chain length? Fully explain the answer(4)
Compound P has FIVE carbon atoms.
1.3.4 Draw the structural formula of a chain isomer of P. Write down the IUPAC
name of this isomer. (3)
1.3.5 How will the vapour pressure of this isomer compare with that of
compound P? Choose from HIGHER THAN, LOWER THAN or EQUAL
TO. (1)
[14]
Question 2
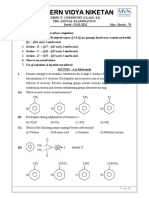
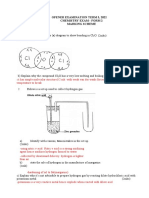
The flow diagram below shows how an alcohol (compound P) can be used to prepare
other organic compounds. The letters A to E represent different organic reactions. X, Y
and Z are organic compounds.
H H H H
Alkene
H C C C H Compound Y
B
(Major product)
H H H
H
H2, Pt
D
C HBr
Compound X Compound Z
(Organic product)
2.1 Is compound P a PRIMARY, SECONDARY or TERTIARY alcohol? Give a
reason for the answer. (2)
2.2 Write down the type of:
2.2.1 Elimination reaction represented by A (1)
2.2.2 Addition reaction represented by B (1)
2.2.3 Elimination reaction represented by D (1)
2.3 Sodium hydroxide is used as one of the reactants in reaction C.
2.3.1 What type of reaction takes place here? (1)
2.3.2 State the TWO reaction conditions for this reaction. (2)
2.3.3 Write down the IUPAC name of compound X. (2)
2.4 Write down the FORMULA of an inorganic reactant needed for reaction D. (1)
2.5 Using STRUCTURAL FORMULAE, write down a balanced equation for
reaction E. (3)
2.6 Write down the IUPAC name of compound Z. (1)
[15]
QUESTION 3
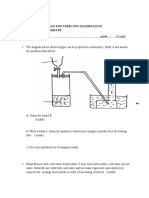
Stone A is projected vertically upwards at a speed of 12 m∙s -1 from a height h above the
ground. Ignore the effects of air resistance.
3.1 Calculate the time taken for stone A to reach its maximum height. (3)
At the same instant that stone A is projected upwards, stone B is thrown vertically downwards
from the same height at an unknown speed, v. Refer to the diagram below.
12 m∙s-1
A B
ground
When stone A reaches its maximum height, the speed of stone B is 3v.
3.2 Calculate the speed, v, with which stone B is thrown downwards. (4)
At the instant stone A passes its initial position on its way down, stone B hits
the ground.
3.3 Calculate the height h. (3)
3.4 Sketch velocity-time graphs for the complete motions of stones A and B on the same
set of axes. Label your graphs for stones A and B clearly.
Show the following on the graphs:
• The time taken for stone A to reach its maximum height
• The velocity with which stone B is thrown downwards (4)
[14]
QUESTION 4
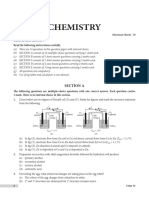
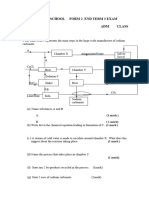
A 2 kg block is at rest on a smooth, frictionless, horizontal table. The length of the block is x.
A bullet of mass 0,015 kg, travelling east at 400 m∙s-1, strikes the block and passes
straight through it with constant acceleration. Refer to the diagram below. Ignore any
loss of mass of the bullet and the block.
BEFORE AFTER N
-1
400 m∙s-1 0,7 m∙s W E
bullet 2 kg
S
x x
4.1 State the principle of conservation of linear momentum in words (2)
The block moves eastwards at 0,7 m∙s-1 after the bullet has emerged from it.
4.2 Calculate the magnitude of the velocity of the bullet immediately after it emerges
from the block. (4)
4.3 If the bullet takes 0,002 s to travel through the block, calculate the length, x, of
the block. (5)
[11]
You might also like
- Aqueous LiCl CaCl2 Solution Props UnlockedDocument31 pagesAqueous LiCl CaCl2 Solution Props UnlockedExal Eduardo Cabrera VelazquezNo ratings yet
- Ngatataek Mixed Secondary School Chemistry (Theory) Paper 1 Form 3 Mid-Term Exam NAME ..ADM CLASS . Time: 2 HoursDocument10 pagesNgatataek Mixed Secondary School Chemistry (Theory) Paper 1 Form 3 Mid-Term Exam NAME ..ADM CLASS . Time: 2 HoursDavyieNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS - (12th & 13th) Paper-2Document3 pagesMATHEMATICS - (12th & 13th) Paper-2Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Che - Jee Main (Jan) - 2023 - 24-01-2023 - Maths - QuestionsDocument7 pagesChe - Jee Main (Jan) - 2023 - 24-01-2023 - Maths - QuestionsAditya Dev SinghNo ratings yet
- .Archphys Sciences p2 Gr12 QP Sept2023 - EnglishDocument23 pages.Archphys Sciences p2 Gr12 QP Sept2023 - EnglishZNo ratings yet
- Chem 1 Monduli District Pre-NationDocument6 pagesChem 1 Monduli District Pre-NationJackson KilasiNo ratings yet
- Chem - Paper-I Ifs 2018Document6 pagesChem - Paper-I Ifs 2018ashishNo ratings yet
- PYQs Chemistry 2017-18Document20 pagesPYQs Chemistry 2017-18avika.thapliyalNo ratings yet
- XI CHEM Pre-Annual QPDocument5 pagesXI CHEM Pre-Annual QPAbhinandan SinhaNo ratings yet
- S.5 P525 Chemistry 2 EOT1-2Document6 pagesS.5 P525 Chemistry 2 EOT1-2Talemwa ALFRED KAKORAKINo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics & ThermochemistryDocument4 pagesThermodynamics & Thermochemistrytimeforpass80No ratings yet
- PAHANG Question of STPM Chemistry Trial P1 2020Document10 pagesPAHANG Question of STPM Chemistry Trial P1 2020Chan Yek FungNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument12 pagesChemistrybishnuprasadmohapatra01No ratings yet
- Chemistry P1 MSC F3 2021 Term 3Document14 pagesChemistry P1 MSC F3 2021 Term 3q5h2f25wp5No ratings yet
- Solutions Manual Chemical Reactions Teacher EditableDocument20 pagesSolutions Manual Chemical Reactions Teacher EditableogmightyrizzlerNo ratings yet
- Section A Kimia Kertas 2 Ujian2Document12 pagesSection A Kimia Kertas 2 Ujian2Faisal ApardiNo ratings yet
- XI Chemistry Pre-Annual 02.02.2022Document5 pagesXI Chemistry Pre-Annual 02.02.2022Ankit TanwarNo ratings yet
- Chem F3 QS2Document6 pagesChem F3 QS2Okumu KevinsNo ratings yet
- Chem HolidayDocument4 pagesChem HolidayeddahyoloNo ratings yet
- Che - Jee Main (Jan) - 2023 - 24-01-2023 - F.N (Maths) Memory Based QuestionsDocument7 pagesChe - Jee Main (Jan) - 2023 - 24-01-2023 - F.N (Maths) Memory Based QuestionsTaaha BaigNo ratings yet
- ALEVELREVISIONQUESTIONSDocument7 pagesALEVELREVISIONQUESTIONSAnthony AndyNo ratings yet
- Term 3 Test QuestionsDocument8 pagesTerm 3 Test QuestionsAdelaide MonyethabengNo ratings yet
- 2012 Revision Package 2 - StudentsDocument15 pages2012 Revision Package 2 - StudentsAlvin HanNo ratings yet
- Real XI Chemistry Session Ending PapersDocument4 pagesReal XI Chemistry Session Ending PaperssauravsinghpahatiaNo ratings yet
- Structured Questions: HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View Part X Chemical EquilibriumDocument26 pagesStructured Questions: HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View Part X Chemical EquilibriumNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Vakev Chemistry-Examination-Of-The-Third-Term-2021-For-S6Document15 pagesVakev Chemistry-Examination-Of-The-Third-Term-2021-For-S6vigiraneza0No ratings yet
- Chemistry SQPDocument4 pagesChemistry SQPstressNo ratings yet
- AP-IPE-2023 Question PaperDocument12 pagesAP-IPE-2023 Question PaperangadibalajithkumarNo ratings yet
- XII Chemistry EveningDocument15 pagesXII Chemistry EveningAyush Kumar singhNo ratings yet
- U9 - 4 - Equilibrium & KDocument1 pageU9 - 4 - Equilibrium & Khelloworldhello123No ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument12 pagesChemistryrs9070515No ratings yet
- Document PDF 493Document10 pagesDocument PDF 493Vandita KumariNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form2 Endterm2 OPENERDocument12 pagesChemistry Form2 Endterm2 OPENERBenjamin mwanikiNo ratings yet
- Deepawali Assignment 11th (J-Batch) ChemDocument11 pagesDeepawali Assignment 11th (J-Batch) ChemRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- MCQ AnsweredDocument29 pagesMCQ AnsweredSara MohamedNo ratings yet
- Topik 3.1 Section A Kertas 2Document13 pagesTopik 3.1 Section A Kertas 2Yuslidiawati JahaminNo ratings yet
- 11 Sci P2 Nov 16Document15 pages11 Sci P2 Nov 16Levi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- 38 Daily Tutorial SheetDocument7 pages38 Daily Tutorial SheetMeera SarangapaniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PSPM 1 2008/2009Document3 pagesChemistry PSPM 1 2008/2009Viknish Arumugam50% (2)
- CU-2021 B.Sc. (Honours) Biochemistry Part-I Paper-IA QPDocument3 pagesCU-2021 B.Sc. (Honours) Biochemistry Part-I Paper-IA QPsh50.257.22No ratings yet
- Chemistry f2 2022 MsDocument9 pagesChemistry f2 2022 MsMAGDALENE MWANGANGINo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced 2020 Paper 1 Chemistry Question Paper PDFDocument8 pagesJEE Advanced 2020 Paper 1 Chemistry Question Paper PDFHasnain AnsariNo ratings yet
- Trial STPM Term1 2017Document12 pagesTrial STPM Term1 2017Earliany Mohd ShahriNo ratings yet
- Kcse Chemistry Marking SchemeDocument174 pagesKcse Chemistry Marking SchemeDavid Musila ToywaNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry MC WorkshopDocument6 pagesAP Chemistry MC WorkshopSNIGDHA PATLOLANo ratings yet
- Form 1 ChemDocument5 pagesForm 1 ChemJack MainaNo ratings yet
- Titq) 4: Indian Institute of Technology, KharagpurDocument3 pagesTitq) 4: Indian Institute of Technology, KharagpurAnurag TiwariNo ratings yet
- Chem Form 2 End Term 3Document8 pagesChem Form 2 End Term 3DenisNo ratings yet
- Diwali Assignment Physical Chemistry (13th) WADocument6 pagesDiwali Assignment Physical Chemistry (13th) WARaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Mock Test-2 Revision ExamDocument4 pagesMock Test-2 Revision Examariasinghhh07No ratings yet
- CHEM2017 1 Chemistry 2Y Single 202104Document17 pagesCHEM2017 1 Chemistry 2Y Single 202104maddie.jngNo ratings yet
- CAPE 2019 - Suggested Answers-1Document14 pagesCAPE 2019 - Suggested Answers-1NICKELIA RAMDONNo ratings yet
- Mock TestDocument3 pagesMock Testariasinghhh07No ratings yet
- STPM Trials 2009 Chemistry Paper 2 (SMJK Sam Tet Ipoh)Document11 pagesSTPM Trials 2009 Chemistry Paper 2 (SMJK Sam Tet Ipoh)sherry_christyNo ratings yet
- General Instructions: Board Preparatory Part Test-1 BPT-PT-1 (FOR SESSION 2012-13)Document4 pagesGeneral Instructions: Board Preparatory Part Test-1 BPT-PT-1 (FOR SESSION 2012-13)Harsha GandikotaNo ratings yet
- 2011 CcoDocument4 pages2011 CcoАрхи́пNo ratings yet
- VJC H2 Chem P1Document19 pagesVJC H2 Chem P1clarissa yeoNo ratings yet
- Prepared by v. Aditya VardhanDocument6 pagesPrepared by v. Aditya Vardhankrishna kanthNo ratings yet
- Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsFrom EverandCritical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsNo ratings yet
- Plasma Chemistry: International Symposium on Plasma ChemistryFrom EverandPlasma Chemistry: International Symposium on Plasma ChemistryD. E. JensenNo ratings yet
- Tables of Coefficients for the Analysis of Triple Angular Correlations of Gamma-Rays from Aligned NucleiFrom EverandTables of Coefficients for the Analysis of Triple Angular Correlations of Gamma-Rays from Aligned NucleiNo ratings yet
- Thermophysical Properties of Propane, National Bureau of Standars.Document256 pagesThermophysical Properties of Propane, National Bureau of Standars.Ezra E. Rangel AcedoNo ratings yet
- 2 Pure Substance PDFDocument17 pages2 Pure Substance PDFalamzaibkhanNo ratings yet
- OCIMF Specification Tables For Marine Loading Arms: Guidance NotesDocument25 pagesOCIMF Specification Tables For Marine Loading Arms: Guidance NotesOvais0% (1)
- Equations of State and PVT AnalysisDocument37 pagesEquations of State and PVT AnalysisJanickNo ratings yet
- Ionic Liquids As Heat-Transfer Fluids: Comparison With Conventional Thermal Fluids, Applications, Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument17 pagesIonic Liquids As Heat-Transfer Fluids: Comparison With Conventional Thermal Fluids, Applications, Advantages and Disadvantagesthehoang12310No ratings yet
- Question Bank Class Xii ChemistryDocument75 pagesQuestion Bank Class Xii ChemistryArvindNarayanNo ratings yet
- Astm E1907Document8 pagesAstm E1907ArielNo ratings yet
- Cae331 513 Lecture11 Psychrometric-ChartDocument78 pagesCae331 513 Lecture11 Psychrometric-Charthabtish2000No ratings yet
- NPSH Ebook-2018Document11 pagesNPSH Ebook-2018Arnab Bhattacharya100% (1)
- Methods For Calculating Brine Evaporation Rates During Salt ProductionDocument11 pagesMethods For Calculating Brine Evaporation Rates During Salt ProductionMarcusNo ratings yet
- EVAPORATIONDocument52 pagesEVAPORATIONRica Marie MarilaoNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of DistillationDocument51 pagesFundamentals of DistillationmujeebtalibNo ratings yet
- CH - 2 (Thermodynamic Potentials) (Class-2)Document5 pagesCH - 2 (Thermodynamic Potentials) (Class-2)Beat SpNo ratings yet
- ASTM D 323 (Presión de Vapor Reid)Document11 pagesASTM D 323 (Presión de Vapor Reid)Shirley GutierrezNo ratings yet
- KMT ws2Document10 pagesKMT ws2Troy MateoNo ratings yet
- 5880-HYDROLOGY - 3 - 14 - 01 - 2017 - FULL Copy2193630314102022692Document43 pages5880-HYDROLOGY - 3 - 14 - 01 - 2017 - FULL Copy2193630314102022692Ahemd AhemdNo ratings yet
- Rich Gen ChemDocument4 pagesRich Gen ChemRaymond MaristelaNo ratings yet
- Simple Distill4ti0n and Ste4m Distill4ti0nDocument17 pagesSimple Distill4ti0n and Ste4m Distill4ti0nTimothy DrakeNo ratings yet
- Vapor Pressure of Petroleum Products - REID Method - RVP & PA (Digital)Document3 pagesVapor Pressure of Petroleum Products - REID Method - RVP & PA (Digital)rajesh_rbpNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document44 pagesChapter 6Annerlynn SolanoNo ratings yet
- Boiling PointDocument10 pagesBoiling PointAshish Malgawa67% (3)
- CH 6503 Cet IiDocument66 pagesCH 6503 Cet IiDrVishwanatha HNNo ratings yet
- Notes On Mass TransferDocument5 pagesNotes On Mass Transferleonard katundaNo ratings yet
- Distillation Non IdealDocument11 pagesDistillation Non IdealKashif RiazNo ratings yet
- (Lec6) Phase EquilibriaDocument52 pages(Lec6) Phase EquilibriadinurjNo ratings yet
- Fire TacticsDocument127 pagesFire Tacticsaquatr100% (2)
- 4th Article On Small Volume Prover (SVP)Document7 pages4th Article On Small Volume Prover (SVP)Chijioke ObiNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics PDFDocument196 pagesFluid Mechanics PDFMayordz JonixNo ratings yet
- Cbse Xii Chem Chap 2 SolutionDocument19 pagesCbse Xii Chem Chap 2 SolutionNihal TandonNo ratings yet