Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Brandcomms Intro
Uploaded by
indestructibelle0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesBrandcomms Intro
Uploaded by
indestructibelleCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
BRAND COMMUNICATIONS Branding in digital media
- Strategic planning Digital branding strategies:
- Relationship between branding and • Websites
design • Social media
Experience – real essence of branding • Online Advertising
Developing brand campaigns
Brand strategy and identity Developing brand campaigns
Developing a brand strategy: • Conceptualization
• Market Analysis • Evaluation
• Target Audience • Execution
• Competitive positioning
Basics of Design
Brand Identity Components: 1. Visual Hierarchy
1. Logo 2. Color Theory
2. Tagline 3. Typography
3. Brand colors 4. Layout
4. Visual Style
BRAND
Visual communication One of the most valuable elements in an
Visual Storytelling – Using images to advertising theme
convey brand narratives - Identity of a specific product, service
or business
Design elements in branding: - can take many forms, including a
1. Shapes name, sign, symbol, color
2. Symbols combination or slogan.
3. Icons - originally referred to a piece of
4. Patterns burning wood.
- began simply to tell one person’s
Messaging & copywriting cattle from another by means of a
hot iron stamp.
Importance of messaging
- Has continued to evolve to
- Crafting a brand voice and tone
encompass identity – it affects the
personality of a product, company,
Writing effective copies:
or service.
• Headlines
• Taglines
• Slogans
• Brand stories
The word brand dates to Old Norse - the Brandnomer - is a brand name that has
ancient North Germanic language from colloquially become a generic term for a
which modern Scandinavian languages product or service
derived.
It wasn’t used as a verb until late Middle Types of Brand Names
English, when it came to mean “mark 1. Initialism – brand names made of
permanently with a hot iron.” initials.
2. Combination – brand names
• 17th century - it referred to a mark of combining multiple words together
ownership by branding to create one.
• Trademark – a legally protected 3. Descriptive – brand names that
brand name relate directly to or describe the
product or benefit are derived from
Key constituencies:
a founder’s name.
Customers, staff, investors etc.
4. Alliteration and Rhyme – brand
names that are fun to say and stick
• Brand Management – art of creating
in the mind.
and maintaining a brand
5. Evocative – project the essence of
• Brand Orientation – orientation of
the brand without describing it.
whole organization towards a brand
6. Neologism – brand names with
completely made-up words.
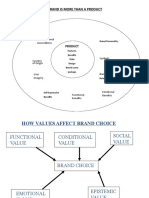
Brand Identity vs. Brand Image
Brand identity (Physical) - is the way you
The objectives that a good brand will
want folks to perceive you.
achieve include:
• Logo, tagline, aesthetic style, • Delivers the message clearly.
language tone, etc. • Confirms your credibility.
• Connects your target prospects
emotionally.
Brand image (Sensual) - is the way that they
• Motivates the buyer.
actually perceive you.
• Concretes user loyalty
• Reputation, emotion, impression,
belief, etc. Brand naming considerations:
• Easy to say and spell.
• Memorable
• Extendable, has room for growth.
Brand awareness - customers’ ability to • Positive feeling
recall and recognize the brand under • International; doesn’t have bad
different conditions meanings in other languages.
: name, logo, jingles etc. • Available; from trademark and
domain perspective
• Meaning has relevance to your
business. Brand recognition – Your brand is
recognized and is considered at decision
Types of brand shoppers making time.
Loyal customers –repeat purchases
• Marketing style: Regular, consistent Brand preference – When given a choice
communications – the more between two brands, the consumer will
personal the better. choose yours based on needs,
Discount customers – shops frequently; differentiation, value-add, service, and/or
make decisions based on reliability.
offers/deals/competitive or comparative
pricing. Brand loyalty – The consumer chooses your
• Marketing style: Alter-style brand consistently, even when faced with
communications via social media, viable alternatives or encounters occasional
email, online advertising, blog posts, poor service from your brand.
and content marketing.
Impulse customers – make purchases based
on what seems needed/good at the time.
• Marketing style: A mix of regular • Brand love -an emerging term
consistent communication and encompassing the perceived value of
altern-style communication the brand image.
Need-based customers – have a specific • Brand Promise – owner’s vision of
intention to buy a particular type of item. what the brand must be and do for
• Marketing style: Website, catalog, the consumer.
and reference/search friendly Global Brand
channels
- perceived to reflect the same set of
Wandering customers – no specific need or values around the world.
desire in mind
• Marketing style: Combine reference Benefits
and guidance channels with • Economies of scale (Production and
attractive offers distribution)
• Lower marketing costs
Stages of brand awareness • Laying the groundwork for future
Brand rejection/non-recognition – extensions worldwide
Avoidance of your products due to negative • Maintaining consistent brand
perception or experience. imagery
• Quicker identification and
Brand non-recognition – Your brand doesn’t integration of innovations
enter consumer’s mind at decision time (Discovered worldwide)
(lack of awareness or differentiation)
• Preempting international
competitors from entering domestic
markets or locking you out of other
geographic markets
• Increasing international media reach
(Especially with the explosion of the
internet) is an enabler.
• Increases in international business
and tourism are also enablers.
Variables
The following elements may differ from
country to country:
• Corporate slogan
• Products and services
• Product names
• Product features
• Positionings
• Marketing mixes (including
pricing, distribution, media and
advertising execution)
You might also like
- Communicating Brand IdentityDocument18 pagesCommunicating Brand IdentityizanNo ratings yet
- Brand Your Business like a Pro: Branding Strategy & Inspiration for Entrepreneurs. the Branding Guide Toolkit for Powerful, Results-driven Branding That Means Business& Impressive Results Every Time!From EverandBrand Your Business like a Pro: Branding Strategy & Inspiration for Entrepreneurs. the Branding Guide Toolkit for Powerful, Results-driven Branding That Means Business& Impressive Results Every Time!No ratings yet
- Session 2 - Concept of Brand and Brand PositioningDocument32 pagesSession 2 - Concept of Brand and Brand PositioningAkhil SinghNo ratings yet
- Top Ten Ways to Brand Yourself as an Author: Top Ten SeriesFrom EverandTop Ten Ways to Brand Yourself as an Author: Top Ten SeriesNo ratings yet
- LP3. Brand Management FrameworkDocument9 pagesLP3. Brand Management FrameworkSENTHIL KUMAR NNo ratings yet
- The Brand Identity Handbook: A Designer's Guide to Creating Unique BrandsFrom EverandThe Brand Identity Handbook: A Designer's Guide to Creating Unique BrandsNo ratings yet
- Product and Brand Management Unit 3Document62 pagesProduct and Brand Management Unit 3Chaudhary Rajat DubeyNo ratings yet
- Designing Corporate Visuals: A Beginner’s Guide to Corporate Graphic DesignFrom EverandDesigning Corporate Visuals: A Beginner’s Guide to Corporate Graphic DesignNo ratings yet
- 04 Brand Management (Clean)Document33 pages04 Brand Management (Clean)Eugene ChanNo ratings yet
- Process Is Defined As Involving FourDocument3 pagesProcess Is Defined As Involving FourPunya SukraliaNo ratings yet
- Brand EquityDocument69 pagesBrand EquityVinay SuriNo ratings yet
- Designing IdentityDocument29 pagesDesigning IdentityNeha PandeNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - Branding StrategiesDocument3 pagesModule 7 - Branding StrategiesMICHELLE MILANANo ratings yet
- Brand ManagementDocument21 pagesBrand ManagementAbhinav SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Brand Enumeration ReviewerDocument6 pagesBrand Enumeration ReviewerJi NahNo ratings yet
- Brand IdentityDocument37 pagesBrand IdentityAnuranjanSinha80% (5)
- BUSM2412 - Topic 9 - Branding, New Products, Product Strategy - SS-2-1Document43 pagesBUSM2412 - Topic 9 - Branding, New Products, Product Strategy - SS-2-1Thuy Duong LaiNo ratings yet
- Marketing 04Document24 pagesMarketing 04Hammad NaqviNo ratings yet
- 04 Brand ManagementDocument53 pages04 Brand ManagementEugene ChanNo ratings yet
- Brand Equity 1233909894459040 1Document26 pagesBrand Equity 1233909894459040 1Awais SiddiqiNo ratings yet
- How Brands Work: Week 2Document42 pagesHow Brands Work: Week 2Victor Gabriel MincuNo ratings yet
- Brand Management - Book SummaryDocument50 pagesBrand Management - Book Summaryfrancescacarrieri303No ratings yet
- Communicating Brand IdentityDocument18 pagesCommunicating Brand IdentityizanNo ratings yet
- SBM ch-3 Brand - Resonance - and - Value - ChainDocument22 pagesSBM ch-3 Brand - Resonance - and - Value - ChainSana Ijaz100% (1)
- Brand Equity and Brand Elements: Lucy - Ting@manchester - Ac.ukDocument27 pagesBrand Equity and Brand Elements: Lucy - Ting@manchester - Ac.ukHojjat AzadbakhtNo ratings yet
- BrandingDocument79 pagesBrandingHojjat AzadbakhtNo ratings yet
- A Brand Is More Than A Product: Organizational AssociationsDocument47 pagesA Brand Is More Than A Product: Organizational AssociationsMohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Imc and BrandsDocument41 pagesImc and BrandsBinisha ShahNo ratings yet
- Brand ManagementDocument43 pagesBrand ManagementMrinal MendonNo ratings yet
- Brand Management RutujaDocument9 pagesBrand Management RutujaDhaval TamhankarNo ratings yet
- Sri Krishna Adithya: College of Arts and ScienceDocument13 pagesSri Krishna Adithya: College of Arts and ScienceAkash RajaNo ratings yet
- Brand and Branding: Jean - Noel KapfererDocument19 pagesBrand and Branding: Jean - Noel Kapferersun girlNo ratings yet
- Brand Elements 2. Choosing Brand Elements To Create Brand EquityDocument20 pagesBrand Elements 2. Choosing Brand Elements To Create Brand EquityAmy KhanNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: - Shruti PendharkarDocument23 pagesSubmitted By: - Shruti PendharkarAhmed AminNo ratings yet
- BM MK2102C Group 3Document111 pagesBM MK2102C Group 3Mỹ LinhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 6 CBBEDocument18 pagesLecture 5 6 CBBEAyushi SaklechaNo ratings yet
- 1 1 - BrandDocument47 pages1 1 - BrandsengguruhNo ratings yet
- Branding: Sujit R JagadaleDocument32 pagesBranding: Sujit R Jagadalesunit dasNo ratings yet
- Branding - Lecture 1 - 1 March 2022Document48 pagesBranding - Lecture 1 - 1 March 2022Ntokozo Hakeem MalgasNo ratings yet
- Brand Elements BUSN 484 PresentationDocument17 pagesBrand Elements BUSN 484 PresentationAhmed RahimNo ratings yet
- Mod - 1Document49 pagesMod - 1sanganuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Creating A BrandDocument18 pagesChapter 2 Creating A BrandThirumal ReddyNo ratings yet
- CH 4 - Brands and Brand Management - ProductDocument44 pagesCH 4 - Brands and Brand Management - ProductAa yishhhNo ratings yet
- B G N I D N A R: BY Arpit Kumar Rastogi Mba (Ii)Document58 pagesB G N I D N A R: BY Arpit Kumar Rastogi Mba (Ii)Smriti KhannaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Branding StrategiesDocument4 pagesLesson 6 - Branding Strategieskaye edquilaNo ratings yet
- Prof. Antre GaneshDocument45 pagesProf. Antre GaneshGanesh AntreNo ratings yet
- Building The Living, Breathing BrandDocument52 pagesBuilding The Living, Breathing BrandWaqasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Brand Elements, Slogans, Jingles, Packaging & Innovation Branding Without Mass MediaDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Brand Elements, Slogans, Jingles, Packaging & Innovation Branding Without Mass Mediayogitaggarwal11No ratings yet
- Edited Brand ManagementDocument47 pagesEdited Brand ManagementRafi ChemmadNo ratings yet
- Session - 30 Sept Choosing Brand Elements To Build Brand EquityDocument12 pagesSession - 30 Sept Choosing Brand Elements To Build Brand EquityUmang ShahNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 (Chap 4)Document25 pagesUnit 2 (Chap 4)wasim shaikhNo ratings yet
- Brand Management: L2: Customer-Based Brand EquityDocument42 pagesBrand Management: L2: Customer-Based Brand EquityMunirNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - BrandingDocument25 pagesModule 6 - Brandingsramana_palNo ratings yet
- CBBE Pyramid of Brand EquityDocument29 pagesCBBE Pyramid of Brand EquityTech ZenithNo ratings yet
- Brand ManagementDocument47 pagesBrand ManagementRafi ChemmadNo ratings yet
- Ch1. Brands Brand Management-1Document14 pagesCh1. Brands Brand Management-1Малика КамалNo ratings yet
- Pomegranate Brand ProcessDocument15 pagesPomegranate Brand Processhello6144No ratings yet
- 2 Brand Personality LatestDocument44 pages2 Brand Personality LatestSarang Kulkarni100% (1)
- PBM - Module 5Document80 pagesPBM - Module 5merinNo ratings yet
- Component AccountingDocument2 pagesComponent AccountingtouseefNo ratings yet
- Advertisement Elasticity of Demand On Sale of Two WheelerDocument19 pagesAdvertisement Elasticity of Demand On Sale of Two WheelercadalalNo ratings yet
- Assignment Balanced Scorecard Group AssignmentDocument6 pagesAssignment Balanced Scorecard Group AssignmentM ArmahNo ratings yet
- Marketing NewwwwDocument25 pagesMarketing NewwwwAhmer RazaNo ratings yet
- APEC SchoolsDocument3 pagesAPEC Schoolsjieun100% (2)
- Assessing The Profitability of Intraday Opening Range Breakout StrategiesDocument11 pagesAssessing The Profitability of Intraday Opening Range Breakout StrategiestechkasambaNo ratings yet
- Forms of Market - Economics Class 12 Notes, Ebook Free PDF DownloadDocument9 pagesForms of Market - Economics Class 12 Notes, Ebook Free PDF DownloadHarsh PatraNo ratings yet
- Islamic Banking MidDocument24 pagesIslamic Banking MidRomeshaNo ratings yet
- List of Record - HseDocument2 pagesList of Record - HseMohd FadlyNo ratings yet
- Anya's Cleaning ServiceDocument22 pagesAnya's Cleaning ServiceArya HerdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Theory of ProductionDocument19 pagesTheory of ProductionJessica Perez Pastorfide II100% (1)
- General Growth Properties: To The Brink and BackDocument121 pagesGeneral Growth Properties: To The Brink and BackEric MooreNo ratings yet
- ECONOMIC SYSTEMS NotesDocument3 pagesECONOMIC SYSTEMS NotesndumisoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Regulatory FrameworkDocument29 pagesLecture 2 - Regulatory FrameworkFarwa AroojNo ratings yet
- DisplayDocument120 pagesDisplaySid Michael50% (2)
- Paper 12Document63 pagesPaper 12Jay PatelNo ratings yet
- Income Statement 1Document4 pagesIncome Statement 1Mhaye Aguinaldo0% (1)
- Report On Financial Analysis of National Buildings Construction Corporation Ltd. (NBCC) .Document19 pagesReport On Financial Analysis of National Buildings Construction Corporation Ltd. (NBCC) .arnabgogoiNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On How Ebay Failed in ChinaDocument6 pagesA Case Study On How Ebay Failed in ChinaHazel ArrocenaNo ratings yet
- Colegio de Sta, Teresa de Avila Foundation IncDocument3 pagesColegio de Sta, Teresa de Avila Foundation IncHarold LuceroNo ratings yet
- Account TitlesDocument28 pagesAccount TitlesTom FernandoNo ratings yet
- AUDIT Purchase & PaymentDocument40 pagesAUDIT Purchase & Paymenttia87100% (1)
- IAS 16 PPE Lecture Slides (Updated)Document39 pagesIAS 16 PPE Lecture Slides (Updated)Ndila mangalisoNo ratings yet
- Proposed Business Case Analysis 1Document19 pagesProposed Business Case Analysis 1Kathlene JaoNo ratings yet
- Uts Asistensi Pengantar Akuntansi 2Document5 pagesUts Asistensi Pengantar Akuntansi 2Falhan AuliaNo ratings yet
- Salesman ReportDocument10 pagesSalesman ReportJaninne BianesNo ratings yet
- Group 2-Fin 6000BDocument7 pagesGroup 2-Fin 6000BBellindah wNo ratings yet
- InstructionsDocument36 pagesInstructionsjhouvan50% (6)
- Compensation& Benefit - Pay Levels, Mix, and Structure (S06)Document32 pagesCompensation& Benefit - Pay Levels, Mix, and Structure (S06)Yoga Nur HadinataNo ratings yet
- CHUYỂN SƠN NĂM 2019 okDocument157 pagesCHUYỂN SƠN NĂM 2019 okTrương Văn NamNo ratings yet
- $100M Offers: How to Make Offers So Good People Feel Stupid Saying NoFrom Everand$100M Offers: How to Make Offers So Good People Feel Stupid Saying NoRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (21)
- How to Read People: The Complete Psychology Guide to Analyzing People, Reading Body Language, and Persuading, Manipulating and Understanding How to Influence Human BehaviorFrom EverandHow to Read People: The Complete Psychology Guide to Analyzing People, Reading Body Language, and Persuading, Manipulating and Understanding How to Influence Human BehaviorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (33)
- Fascinate: How to Make Your Brand Impossible to ResistFrom EverandFascinate: How to Make Your Brand Impossible to ResistRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Obviously Awesome: How to Nail Product Positioning so Customers Get It, Buy It, Love ItFrom EverandObviously Awesome: How to Nail Product Positioning so Customers Get It, Buy It, Love ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (152)
- $100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your StuffFrom Everand$100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your StuffRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (18)
- Summary: Range: Why Generalists Triumph in a Specialized World by David Epstein: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: Range: Why Generalists Triumph in a Specialized World by David Epstein: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- The Catalyst: How to Change Anyone's MindFrom EverandThe Catalyst: How to Change Anyone's MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (273)
- Ca$hvertising: How to Use More than 100 Secrets of Ad-Agency Psychology to Make Big Money Selling Anything to AnyoneFrom EverandCa$hvertising: How to Use More than 100 Secrets of Ad-Agency Psychology to Make Big Money Selling Anything to AnyoneRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (114)
- Pre-Suasion: Channeling Attention for ChangeFrom EverandPre-Suasion: Channeling Attention for ChangeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (277)
- Dealers of Lightning: Xerox PARC and the Dawn of the Computer AgeFrom EverandDealers of Lightning: Xerox PARC and the Dawn of the Computer AgeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (88)
- Jab, Jab, Jab, Right Hook: How to Tell Your Story in a Noisy Social WorldFrom EverandJab, Jab, Jab, Right Hook: How to Tell Your Story in a Noisy Social WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- ChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessFrom EverandChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessNo ratings yet
- Summary: Traction: Get a Grip on Your Business: by Gino Wickman: Key Takeaways, Summary, and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Traction: Get a Grip on Your Business: by Gino Wickman: Key Takeaways, Summary, and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (10)
- Summary: Dotcom Secrets: The Underground Playbook for Growing Your Company Online with Sales Funnels by Russell Brunson: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: Dotcom Secrets: The Underground Playbook for Growing Your Company Online with Sales Funnels by Russell Brunson: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Brand Identity Breakthrough: How to Craft Your Company's Unique Story to Make Your Products IrresistibleFrom EverandBrand Identity Breakthrough: How to Craft Your Company's Unique Story to Make Your Products IrresistibleRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- Scientific Advertising: "Master of Effective Advertising"From EverandScientific Advertising: "Master of Effective Advertising"Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (163)
- Create Once, Distribute Forever: How Great Creators Spread Their Ideas and How You Can TooFrom EverandCreate Once, Distribute Forever: How Great Creators Spread Their Ideas and How You Can TooNo ratings yet
- Summary: $100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your Stuff by Alex Hormozi: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: $100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your Stuff by Alex Hormozi: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (6)
- Marketing Made Simple: A Step-by-Step StoryBrand Guide for Any BusinessFrom EverandMarketing Made Simple: A Step-by-Step StoryBrand Guide for Any BusinessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (203)
- Blue Ocean Strategy, Expanded Edition: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition IrrelevantFrom EverandBlue Ocean Strategy, Expanded Edition: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition IrrelevantRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (387)
- How To Win Customers And Keep Them For Life: An Action-Ready Blueprint for Achieving the Winner's Edge!From EverandHow To Win Customers And Keep Them For Life: An Action-Ready Blueprint for Achieving the Winner's Edge!Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Invisible Influence: The Hidden Forces that Shape BehaviorFrom EverandInvisible Influence: The Hidden Forces that Shape BehaviorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (131)
- Understanding Digital Marketing: Marketing Strategies for Engaging the Digital GenerationFrom EverandUnderstanding Digital Marketing: Marketing Strategies for Engaging the Digital GenerationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (22)
- How to Get a Meeting with Anyone: The Untapped Selling Power of Contact MarketingFrom EverandHow to Get a Meeting with Anyone: The Untapped Selling Power of Contact MarketingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (28)
- Yes!: 50 Scientifically Proven Ways to Be PersuasiveFrom EverandYes!: 50 Scientifically Proven Ways to Be PersuasiveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (153)
- Summary: Influence: The Psychology of Persuasion by Robert B. Cialdini Ph.D.: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Influence: The Psychology of Persuasion by Robert B. Cialdini Ph.D.: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Summary: The 1-Page Marketing Plan: Get New Customers, Make More Money, And Stand Out From The Crowd by Allan Dib: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: The 1-Page Marketing Plan: Get New Customers, Make More Money, And Stand Out From The Crowd by Allan Dib: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (7)
- The Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetFrom EverandThe Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetNo ratings yet