Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Practice Based Learningin CRRT2019 Formulas
Practice Based Learningin CRRT2019 Formulas
Uploaded by
pj rak0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views5 pagesOriginal Title
PracticeBasedLearninginCRRT2019Formulas
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views5 pagesPractice Based Learningin CRRT2019 Formulas
Practice Based Learningin CRRT2019 Formulas
Uploaded by
pj rakCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
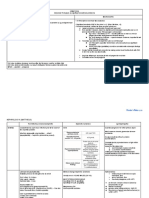
CRRT Formulas
BASIC DIALYSIS CONCEPTS
QB = Blood flow rate (ml/min)
QD = Dialysate rate (ml/hr)
QUF = Ultrafiltration rate (ml/hr)
QR = Replacement fluid rate (ml/hr)
QE = Effluent rate (ml/hr)
CRRT DOSE:
Recommended minimal effluent dose is 20-25 ml/kg/hr (target
25-30 ml/kg/hr to take into account downtime)
Dose = Effluent Rate (ml/hr) / Patient Weight (kg)
Effluent Rate (ml/hr) definition per CRRT modality:
§ CVVH: Total Ultrafiltration (UF) Rate (ml/hr) = Pre-Filter
Replacement Fluid Rate (ml/hr) + Post-Filter Replacement
Fluid Rate (ml/hr) + Fluid Removal Rate (ml/hr) + Pre-Blood
Pump (PBP) Fluid Rate (ml/hr)*
§ CVVHD: Dialysate Rate (ml/hr) + Fluid Removal Rate (ml/hr)
§ CVVHDF: Total UF Rate (ml/hr) + Dialysate Rate (ml/hr) = Pre-
Filter Replacement Fluid Rate (ml/hr) + Post-Filter
Replacement Fluid Rate (ml/hr) + Fluid Removal Rate (ml/hr)
+ Pre-Blood Pump (PBP) Fluid Rate (ml/hr)* + Dialysate Rate
(ml/hr)
CRRT DOSE DILUTION FACTOR:
When using Pre-Filter Replacement Fluid and/or Pre-Blood-Pump
(PBP) Fluid, the CRRT dose is diluted and therefore decreased.
CRRT effluent rate is multiplied by the dilution factor and then
divided by patient weight to reflect actual CRRT dose in ml/kg/hr;
this takes into account the dilution effect.
Dilution Factor = Plasma Flow Rate (ml/hr) / [Plasma Flow Rate
(ml/hr) + Pre-Filter Replacement Fluid Rate (ml/hr) + PBP Fluid
Rate (ml/hr)*]
§ Plasma Flow Rate (ml/hr) = Blood Flow Rate (ml/min) X 60
(min/hr) X (1-HCT)
CRRT FILTRATION FRACTION (FF):
Filter clotting occurs with FF > 20-25%.
Filtration Fraction (FF) = Total Ultrafiltration Rate / (Plasma Flow
Rate + Pre-Filter Replacement Fluid Rate + Pre-Blood Pump (PBP)
Fluid Rate*)
§ Total Ultrafiltration Rate (ml/hr) = Pre-Filter Replacement
Fluid Rate (ml/hr) + Post-Filter Replacement Fluid Rate
(ml/hr) + Fluid Removal Rate (ml/hr) + Pre-Blood Pump (PBP)
Fluid Rate (ml/hr)*
§ Plasma Flow Rate (ml/hr) = Blood Flow Rate (ml/min) X 60
(min/hr) X (1-HCT)
§ Note: dialysate rate does NOT factor into the FF equation
* For all formulas above, PBP Rate only applies if utilizing with
Prismaflex device
CITRATE TOXICITY
Detection
§ Rising anion gap, worsening metabolic acidosis
§ Falling systemic iCa2+
§ Escalating Ca2+ infusion requirements
§ Total Ca2+:Systemic iCa2+ Ratio > 2.5:1 (increased Ca2+ gap)**
**To convert Total Calcium in mg/dL to mmol/L, multiply Total
Calcium by 0.25
DYSNATREMIAS
Hyponatremia
1. Add free water into commercial CRRT solution bag
%'
𝑉#$$ = & & - 𝑉)
%(
2. Equivolume exchange of fluid with free water (exchange
volume in CRRT solution bag with sterile water)
𝑑𝑒𝑠𝑖𝑟𝑒𝑑 𝑁𝑎=
𝑉𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒 𝑡𝑜 𝑒𝑥𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 = 𝑉) − ×𝑉)
𝑖𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑎𝑙 [𝑁𝑎= ]
3. Use Post filter RF (or add as separate infusion)
D5W can be used as post-filter RF to slowly correct patients who
have hyponatremia:
D5W rate = [(140 - target Na) / 140] x desired clearance.
For example, using post-dilution CVVHDF in a patient with initial
sodium of 120 mEq/L with target sodium concentration of 130
mEq/L at a desired clearance of 3 L/hr using RF/dialysate with
140 mEq/L of sodium, the D5W infusion rate would be [(140 –
130)] / 140] x 3 L = 0.214 L/hr. So the post filter RF would be 210
ml/hr and the dialysate/pre-filter RF should be 2,790 ml/hr (2.79
L/hr + 0.210 L/hr = 3 L/hr)
Hypernatremia
In patients with cerebral edema who need 3% saline to maintain
serum Na concentration in range 150 to 155 mEq/L, 3% saline
can be delivered as the post-filter RF.
3% infusion rate = [(target Na – 140) / (513 – 140)] x desired
clearance.
For example, in a patient with an initial sodium 140 mEq/L with
target sodium concentration of 155 mEq/L at a desired clearance
of 3 L/hr, the 3% saline infusion rate would be [(155-140)/513-
140)] x 3 = 0.120 L/hr or 120 ml/hr. The dialysate/pre-filter RF
should be 2880 ml/hr (2.880 L/hr + 0.120 L/hr = 3 L/hr)
Prediction of Serum Sodium Concentration
HIJ
𝑁𝑎(B) = 𝑁𝑎D + 𝑁𝑎$)#F − 𝑁𝑎D × 1 − 𝑒 K
D = CRRT effluent dose ml/kg/hr
T = Time (ie 24 hr)
V = Volume of distribution
You might also like
- Nephrology A (Mattheus) : HematuriaDocument10 pagesNephrology A (Mattheus) : HematuriaShekinah MalimbanNo ratings yet
- CKD Algorithm EBG Approved April09Document1 pageCKD Algorithm EBG Approved April09Merry Aprila RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Nephropathy: Assisstant Professor Dr. Mihaela-Dora DonciuDocument65 pagesDiabetic Nephropathy: Assisstant Professor Dr. Mihaela-Dora DonciuFloreaAndreiNo ratings yet
- Case Novo Nordisk PDFDocument43 pagesCase Novo Nordisk PDFArnab AzadNo ratings yet
- On Admission:: STROKE MANAGEMENT (Beaumont Hospital)Document3 pagesOn Admission:: STROKE MANAGEMENT (Beaumont Hospital)Nadia SalwaniNo ratings yet
- Nephrology: Edward F. Foote, Pharm.D., FCCP, BCPSDocument32 pagesNephrology: Edward F. Foote, Pharm.D., FCCP, BCPSandirio7486No ratings yet
- Hepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Renovascular Hypertension (RVH) SeminarDocument58 pagesRenovascular Hypertension (RVH) SeminarfaizalmasoodiNo ratings yet
- Identification of CKD: Algorithm ADocument3 pagesIdentification of CKD: Algorithm ArawanNo ratings yet
- Renew Life Probiotics Information GuideDocument69 pagesRenew Life Probiotics Information GuideCameronNo ratings yet
- Peds Drug CalcDocument4 pagesPeds Drug CalcJelena Obrenovic StankovicNo ratings yet
- ACCP 2018 NephrologyDocument31 pagesACCP 2018 NephrologyMonica Febri Andari100% (1)
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 5Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 5JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion Services in Sub Saharan Africa: Challenges and ConstraintsFrom EverandBlood Transfusion Services in Sub Saharan Africa: Challenges and ConstraintsNo ratings yet
- Cases in Nephrology by Muhammad Rafiqul AlamDocument9 pagesCases in Nephrology by Muhammad Rafiqul AlamSELLULARNo ratings yet
- ccpc15 Principles Renal Clearance Acute Kidney Renal Replacement WorkbookDocument22 pagesccpc15 Principles Renal Clearance Acute Kidney Renal Replacement WorkbookJeremy Hampton67% (3)
- 2010-2011 Antibiotic GuidelinesDocument78 pages2010-2011 Antibiotic GuidelinesMuhammad Rizki BachtiarNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus PDFDocument7 pagesGestational Diabetes Mellitus PDFMaxenia FaboresNo ratings yet
- 50 Milisimal PotencyDocument8 pages50 Milisimal PotencyDr. Surendra Singh100% (3)
- Renal - Replacement - TherapyDocument128 pagesRenal - Replacement - TherapyEmNo ratings yet
- ABG AnalysisDocument15 pagesABG AnalysisPabhat Kumar100% (2)
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument22 pagesTetralogy of FallotHusna Aje100% (1)
- Acute Hemodialysis PrescriptionDocument18 pagesAcute Hemodialysis PrescriptionOlga BabiiNo ratings yet
- HemodialysisDocument6 pagesHemodialysisAnonymous 7LI78gu4VDNo ratings yet
- Hemodialysis Emergencies: Core Curriculum 2021.Document14 pagesHemodialysis Emergencies: Core Curriculum 2021.Tariq ZayanNo ratings yet
- A Review of Thromboelastography PDFDocument5 pagesA Review of Thromboelastography PDFmarceloNo ratings yet
- Acls GuidelineDocument10 pagesAcls GuidelineReynaldoBinsarNo ratings yet
- OET Reading Test 7 - Part BDocument13 pagesOET Reading Test 7 - Part BLOTSOFTESTS80% (5)
- Basic Baby CardiganDocument4 pagesBasic Baby CardiganJelena Obrenovic StankovicNo ratings yet
- Management of Diabetes MellitusDocument42 pagesManagement of Diabetes Mellitusayu ersa lestari100% (1)
- Blood Transfusion On Dialysis Guidelines Aug 2017 PDFDocument5 pagesBlood Transfusion On Dialysis Guidelines Aug 2017 PDFYolanda IrawatiNo ratings yet
- Beyond Basic NephrologyDocument1 pageBeyond Basic NephrologyexpensivecareNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approach To RPRF PDFDocument6 pagesClinical Approach To RPRF PDFshankarNo ratings yet
- Dialysis Dose Prescription: Presented by Dr. UjjawalDocument54 pagesDialysis Dose Prescription: Presented by Dr. UjjawalZH. omg sarNo ratings yet
- PD Prescription Present 4-8-52Document74 pagesPD Prescription Present 4-8-52Kong Kong KongNo ratings yet
- Peritoneal Dialysis AdequacyDocument33 pagesPeritoneal Dialysis AdequacyKong Kong KongNo ratings yet
- Free Pattern Mirjana Zpagetti HaakpatroonDocument1 pageFree Pattern Mirjana Zpagetti HaakpatroonJelena Obrenovic StankovicNo ratings yet
- 02 BTS Antibody Guidelines-1Document69 pages02 BTS Antibody Guidelines-1watztanjaNo ratings yet
- Lange Nephrology EssentialsDocument9 pagesLange Nephrology EssentialsAlejandro GarcíaNo ratings yet
- FCPS II Nephrology Clinical and VivaDocument2 pagesFCPS II Nephrology Clinical and Vivateena6506763No ratings yet
- How To Give Grand RoundsDocument12 pagesHow To Give Grand RoundsNephrology On-DemandNo ratings yet
- NQQ AnswersDocument16 pagesNQQ AnswersNizar ShormanNo ratings yet
- Hypernatremia From HarrisonDocument3 pagesHypernatremia From HarrisonNobel LaureateNo ratings yet
- Writing The Home Hemodialysis PrescriptionDocument22 pagesWriting The Home Hemodialysis Prescriptionstudent_physicianNo ratings yet
- Management of Acute Glomerulonephritis in Children: Children's Services Medical GuidelinesDocument7 pagesManagement of Acute Glomerulonephritis in Children: Children's Services Medical GuidelinesdaypranitaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pearls in NephrologyDocument5 pagesClinical Pearls in NephrologyEdmilson R. LimaNo ratings yet
- An Update On Glomerulopathies - Clinical and Treatment AspectsDocument482 pagesAn Update On Glomerulopathies - Clinical and Treatment AspectsJulio SobremazasNo ratings yet
- Peritoneal Dialysis Adequacy & Prescription ManagementDocument49 pagesPeritoneal Dialysis Adequacy & Prescription Managementsurya kristyoadiNo ratings yet
- Renal Questions by Dr. OkashaDocument78 pagesRenal Questions by Dr. Okashamohammed okashaNo ratings yet
- Outpt. Recommendation of Renal Transplant Patients.Document86 pagesOutpt. Recommendation of Renal Transplant Patients.Nephrology On-DemandNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 7Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 7JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Intra and Intradialytic Hypotension and Hypertension InrigDocument29 pagesIntra and Intradialytic Hypotension and Hypertension InrigMonica HerreraNo ratings yet
- Decision Algorithm For Prescribing SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Receptor AgonistsDocument11 pagesDecision Algorithm For Prescribing SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Receptor AgonistsNati BocciaNo ratings yet
- Continuous Veno-Venous Hemofiltra Tion: Mazen Kherallah, MD, FCCPDocument65 pagesContinuous Veno-Venous Hemofiltra Tion: Mazen Kherallah, MD, FCCPdesikristiyantiNo ratings yet
- Blood Component TherapyDocument8 pagesBlood Component TherapyquerokeropiNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury: KDIGO 2012 Clinical Practice GuidelineDocument40 pagesAcute Kidney Injury: KDIGO 2012 Clinical Practice GuidelineAbedDabajaNo ratings yet
- Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy - Who, When, Why, and HowDocument13 pagesContinuous Renal Replacement Therapy - Who, When, Why, and HowLee Foo WengNo ratings yet
- CRRT ProtocolDocument21 pagesCRRT ProtocolBejo UtomoNo ratings yet
- Diabetes and NephrologyDocument36 pagesDiabetes and NephrologydrpbendreNo ratings yet
- Hemodiafiltration KuhlmannDocument31 pagesHemodiafiltration Kuhlmanntigercat100% (1)
- Nephrology: Omar K MRCP IrelandDocument54 pagesNephrology: Omar K MRCP IrelandManmeet SNo ratings yet
- AKI in SepsisDocument45 pagesAKI in SepsisIkeBundaAdellulaNo ratings yet
- CRRT Mod 1 Edwards 9may07Document60 pagesCRRT Mod 1 Edwards 9may07Omar Elsayed RamadanNo ratings yet
- Abg PrimerDocument22 pagesAbg PrimerAraceli Ecot CalunodNo ratings yet
- Management of HIV/AIDS by DR Gireesh Kumar K P, Department of Emergency Medicine, Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences, Kochi, KeralaDocument13 pagesManagement of HIV/AIDS by DR Gireesh Kumar K P, Department of Emergency Medicine, Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences, Kochi, KeralaSreekrishnan TrikkurNo ratings yet
- Nephrology Best RDocument6 pagesNephrology Best Rfrabzi100% (1)
- Tubulointerstitial Diseases: Dr. Raid JastaniaDocument48 pagesTubulointerstitial Diseases: Dr. Raid JastaniaThomas McconnellNo ratings yet
- Platelet, FFP and Cryoprecipitate Transfusion in Emergency Room by DR Riaz AhamedDocument31 pagesPlatelet, FFP and Cryoprecipitate Transfusion in Emergency Room by DR Riaz AhamedAETCM Emergency medicineNo ratings yet
- Vascular Responses to PathogensFrom EverandVascular Responses to PathogensFelicity N.E. GavinsNo ratings yet
- Renal Replacement Therapy in Critical Care: Choice of ModeDocument15 pagesRenal Replacement Therapy in Critical Care: Choice of ModeJelena Obrenovic StankovicNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Concise Definitive Review: Focused Critical Care Echocardiography in The ICUDocument17 pagesNIH Public Access: Concise Definitive Review: Focused Critical Care Echocardiography in The ICUJelena Obrenovic StankovicNo ratings yet
- Pom+Pom+Hats+ +yarn+ +Free+Knitting+Patterns+ +Crochet+Patterns+ +yarnspirationsDocument3 pagesPom+Pom+Hats+ +yarn+ +Free+Knitting+Patterns+ +Crochet+Patterns+ +yarnspirationsJelena Obrenovic StankovicNo ratings yet
- Rib ElationDocument1 pageRib ElationJelena Obrenovic StankovicNo ratings yet
- CNT 0010362 02 PDFDocument10 pagesCNT 0010362 02 PDFJelena Obrenovic StankovicNo ratings yet
- Anexate IVsolnDocument7 pagesAnexate IVsolnJelena Obrenovic StankovicNo ratings yet
- UCSD Anesthesia Manual of Intraoperative Events: July 2012 Edited By: 1 Edition Preetham Suresh, MDDocument21 pagesUCSD Anesthesia Manual of Intraoperative Events: July 2012 Edited By: 1 Edition Preetham Suresh, MDJelena Obrenovic StankovicNo ratings yet
- A4 Metabolic and EndocrineDocument50 pagesA4 Metabolic and Endocrinemineb9631No ratings yet
- Premature Rupture of Membranes (Prom)Document12 pagesPremature Rupture of Membranes (Prom)KABERA RENENo ratings yet
- Period MythsDocument4 pagesPeriod MythsEm Boquiren CarreonNo ratings yet
- SLS Dan SARDocument1 pageSLS Dan SARNia DamayantiNo ratings yet
- Microbiology 3 RD SemesterDocument12 pagesMicrobiology 3 RD SemesterbethelNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Airway Card (Dual)Document1 pagePediatric Airway Card (Dual)Brian CloughNo ratings yet
- Alcoholic Liver Disease PDFDocument13 pagesAlcoholic Liver Disease PDFPrabhakaran ganjuNo ratings yet
- Dr. K. Sendhil Kumar Dr. Piyush Patwa Dr. Latif Bagwan Gateway Clinic & Hospitals Coimbatore, INDIADocument62 pagesDr. K. Sendhil Kumar Dr. Piyush Patwa Dr. Latif Bagwan Gateway Clinic & Hospitals Coimbatore, INDIAJOPEARL MAE DELA TORRE100% (1)
- Pharmacology of Drugs For AnemiaDocument49 pagesPharmacology of Drugs For AnemiaTeus Fatamorgana100% (2)
- Tooth Morphology For: Introduction ToDocument94 pagesTooth Morphology For: Introduction Toapi-152953067No ratings yet
- ETO NA TALAGA - Tapos Na Ang Lahat !!!Document32 pagesETO NA TALAGA - Tapos Na Ang Lahat !!!Keenen Engel Bonifacio Pascua100% (1)
- Primary Glomerulonephritis UG LectureDocument50 pagesPrimary Glomerulonephritis UG LectureMalik Mohammad AzharuddinNo ratings yet
- Minimum Standard of CareDocument136 pagesMinimum Standard of CareBibin Vengathanam0% (1)
- A Drug Study On: Furosemide TabletDocument7 pagesA Drug Study On: Furosemide TabletRaijenne VersolaNo ratings yet
- 10 Community Oriented Primary CareDocument3 pages10 Community Oriented Primary CareIrene Veron Bernardo ChicoNo ratings yet
- Renal Function TestsDocument13 pagesRenal Function TestsJennifer CollinsNo ratings yet
- The Conundrum of Gluten SensitivityDocument9 pagesThe Conundrum of Gluten SensitivityParis FernándezNo ratings yet
- No Nama Alat Merk Type Nomor SeriDocument16 pagesNo Nama Alat Merk Type Nomor SeriRamadhan FebriNo ratings yet
- Health Programme Manager's Manual PDFDocument140 pagesHealth Programme Manager's Manual PDFLakshmi SethNo ratings yet
- Prosthesis SelectionDocument41 pagesProsthesis Selectionshahinshamshiri0% (1)
- Holter - Lifecard CFDocument1 pageHolter - Lifecard CFSuki YakiNo ratings yet
- NeumanDocument3 pagesNeumanjmogikonyoNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Hand-Arm Vibration Syndrome TherDocument7 pagesAssessment of The Hand-Arm Vibration Syndrome TherTri Noor Cahyo WidodoNo ratings yet