Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class 11 Economics Notes Chapter 9 Studyguide360
Uploaded by
aanjnay1234Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Class 11 Economics Notes Chapter 9 Studyguide360
Uploaded by
aanjnay1234Copyright:
Available Formats
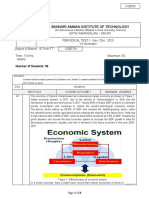
PART-B: INTRODUCTORY MICROECONOMICS
UNIT 1
INTRODUCTION
60
Microeconomics
Macro economics
E3
Economy
Positive economics
Central Problems
Introduction
Normative economics
ID
Production
Possibility
curve Economic problems
opportunity cost
U
Points to Remember
YG
Micro economics studies the behaviour of an individual economic
unit.
Example : Demand of an individual consumer, Production of a firm
et(c)
D
Macro economics studies the behaviour of the economy as a
whole.
Example : Aggregate Demand, National Income et(c)
U
An economy is a system that helps to produce good and services
and enables people to earn their living.
ST
Economic problem is the problem of making the choice of the use
of scarce resources for satisfying unlimited human wants.
Causes of economic problems are :
(a) Unlimited Human Wants
(b) Scarcity of Economic Resources
111 Class XI - Economics
(c) Alternative uses of Resources
Central Problems of an Economy
60
What to produce How to produce? For
Forwhom
whomtotoproduce?
produce?
(Selection of goods) (Selection of technique) (Distribution of income
(Distribution of income and
(Selection
and Selection of final useuse
of final
ofoffinal
finalgoods)
goods)
E3
Opportunity cost of a given resource can be defined as the value of
the next best use to which that resource could be put.
Production possibility frontier shows all possible combinations of
two goods that an economy can produce with given resources
and available technology, assuming that all resources are fully
and efficiently utilise(d)
ID
Economising of resources means use of resources in best possible
manner.
U
Features of Production Possibility Frontier
(a) Slopes downward from left to right because to increase the
production of one good, some units of other good has to be
YG
sacrifice(d)
(b) Concave to the origin because of increasing Marginal
Opportunity Cost (MOC) or Marginal Rate of Transformation
(MRT). MRT is increasing because all resources are not
equally efficient in the production of both goods.
D
Rightward shift of PPF indicates increase in resources or
improvement in technology of both goods.
Leftward shift of PPF indicates decrease in resources or
U
degradation in technology.
PPC will shift rightwards due to all those reasons which enhances
production potential, quantity and efficiency of resources in an
ST
economy.
Resons for Reasons for No. Change in PPC
Rightwards shift Leftward Shift
1. Increase in Resources 1. Decrease in Resources 1. Transfer of Resources
2. Improvement in technology 2. Technological obsoletion 2. Unemployment
Eradication Programme
112 Class XI - Economics
3. Skill Development 3. Natural Calamities (Flood,
Programme (Training) Earthquake, Tsunami,
Drought et(c))
4. Education for all (Health) 4. Migration
5. Clean India Campaign 5. War, terrorism
(Health)
60
6. Yoga Enhancement Plans
(Health).
7. Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao
(Education)
E3
8. Make in India (Investment)
9. Increase in Foreign Capital
(Foreign Investment)
ID
Marginal Rate of Transformation (MRT) is the ratio of number
of units of a good sacrificed to increase one more unit of the
other goo(d)
Y
U
MRT
X
MRT can also called Marginal Opportunity Cost. It is defined as
YG
the additional cost in terms of number of units of a good sacrificed
to produce an additional unit of the other goo(d)
When MOC increases, PPF is concave to origin. When MOC
decreases PPF is convex to origin and when MOC remains
constant, PPF is downward sloping straight line.
D
Positive Economic Analysis : It deals with the things 'as they are'.
It represents facts like what was? What is? What will be? et(c)
U
Example : 'India is overpopulated', Prices have been rising in India'.
It can be verifie(d)
Normative Economic Analysis : It deals with things as 'they ought
ST
to be'. It deals with idealistic situation instead of actual situation.
Example : 'Rich people should be taxed more'. Free education
should be given to the poor'. It can't be verifie(d)
113 Class XI - Economics
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (1 MARK)
1. Which of the following subject matter study in Micro Economics,
(a) Money supply
(b) Aggregate demand
60
(c) Market demand of a good
(d) National Income
2. Which subject matter does not study in macro economics,
E3
(a) Employment Level
(b) Aggregate Supply
(c) National Income
3.
(d)
ID
Determination of market price
Economic Problem arises due to
U
(a) High population of a country
(b) Competition among buyers
YG
(c) Resources have alternative uses
(d) Producer wants maximum profit
4. Which of these is a central problem of an Economy?
(a) Deficit demand
D
(b) Equilibrium of an economy
(c) For whom to produce
U
(d) Decreasing return to a factor
5. Any point beyond the PPF shows:
ST
(a) Under utilisation of Resource
(b) Unattainable combination of output
(c) Efficient utilisation of Resources
(d) Decrease in resources.
114 Class XI - Economics
6. In which situation PPF shifts towards right
(a) Increase in foreign capital
(b) Resources are reduced
(c) Fully efficient use of resources
60
(d) Increase in employment
7. Production Possibility Frontier can be a straight line: when
(a) Decrease in production of both goods
E3
(b) More of both goods can be produced
(c) All resources are equally efficient in production of both goods
(d) All resources are not equally efficient in production of both
goods.
8.
ID
Which of the followings are assumptions of PPF
(a) Available Resources are fully and efficiently utilized
(b) Technology remain stable
U
(c) Resources are not equally efficient in production of all goods
YG
(d) All of the above
9. Which of these statement is correct about Opportunity cost?
(a) Opportunity cost is always higher than the given price.
(b) Opportunity cost is always less than the given price.
D
(c) Opportunity cost is always calculated in money.
(d) Opportunity cost can be less than, more than or equal to
U
given price.
10. Which of these is Normative Economics.
ST
(a) 25 percent population of India is below poverty line.
(b) Increase in FDI has increased the GDP of India.
(c) Equal distribution of income will make India poverty free.
(d) Higher welfare spending by government increases the
Aggregate Deman(d)
115 Class XI - Economics
11. ln which situation ,can PPC be a straight line:
(a) When MRT is decreasing
(b) When MRT is increasing
(c) When MRT is constant
60
(d) When MOC is decreasing
12. PPF is concave to the point of origin due to :
(a) increasing MRT
E3
(b) decreasing MRT
(c) constant MRT
(d) decreasing MOC
13.
(a)
(b)
increasing MRT
decreasing MRT
ID
PPF can be convex to the point of origin due to:
U
(c) constant MRT
(d) increasing MOC
YG
14. Which of the following central problem of an economy deals with
technique of production ?
(a) What to produce
(b) How to produce
D
(c) For whom to produce
U
(d) When to produce
15. Which of the following central problem of an economy deals with
deciding the quantity of goods to be produced?
ST
(a) What to produce
(b) How to produce
(c) For whom to produce
(d) When to produce
116 Class XI - Economics
16. Which of the following central problem of an economy deals with
selection of category of people who will ultimately consume the
goods?
(a) What to produce
(b) how to produce
60
(c) For whom to produce
(d) When to produce
17. Which of the following will not lead to shift in PPF?
E3
(a) Improvement in technology
(b) Growth of resources
(c) Degradation in technology
18.
(d) Unemployment
ID
Which of the following will lead to shift PPF rightward ?
(a) Improvement in technology
U
(b) Destruction of resources
YG
(c) Degradation in technology
(d) Unemployment
19. Which of the following will lead to shift PPF leftward?
(a) Improvement in technology
D
(b) Growth of resources
(c) Degradation in technology
U
(d) Unemployment
ST
20. A point outside the PPF indicates:
(a) Attainable combination
(b) Unattainable combination
(c) Fuller utilization of resources
(d) Under utilization of resources
117 Class XI - Economics
21. A point inside the PPF indicates:
(a) Efficient use of resources
(b) Unattainable combination
(c) Fuller utilization of resources
60
(d) Under utilization of resources
22. A point on the PPF indicates:
(a) Inefficient use of resources
E3
(b) Unattainable combination
(c) Fuller utilization and efficient use of resources
(d) Under utilization of resources
23.
ID
An economic problem arises due to :
(a) Limited human wants
U
(b) Unlimited human wants and unlimited resources
(c) Limited human wants and limited resources
YG
(d) Unlimited human wants and limited resources
24. Opportunity cost is the :
(a) Number of units gained
D
(b) Number of units sacrificed
(c) Cost of the next best alternative foregone
U
(d) Cost of the next best alternative gained
25. Which of the following is an example of microeconomics?
ST
(a) National income
(b) Income and employment
(c) Price of a commodity
(d) Price level
118 Class XI - Economics
26. Which of the following is an example of macroeconomics?
(a) Individual income
(b) Income and employment
(c) Price of a commodity
60
(d) Demand for a commodity
27. Which of the following in not an example of economic activity
(a) Production
E3
(b) Consumption
(c) Exchange
(d) social welfare
28. Positive economics deals with:
(a)
(b)
Opinions
Facts ID
U
(c) Value judgement
(d) Suggestions
YG
29. Normative economics deals with:
(a) what was
(b) what ought to be
(c) what is
D
(d) what would be
30. Main characteristics of resources are
U
(a) they are limited
(b) they are unlimited
ST
(c) they have alternative uses
(d) both (a) and (c)
Ans. 1. (c); 2. (d); 3. (c); 4. (c); 5. (b); 6. (a); 7. (c); 8. (d); 9. (d);
10. (c) 11. (c) 12. (a) 13. (b) 14. (b) 15. (a) 16. (c) 17. (d) 18. (a)
19. (c) 20. (b) 21. (d) 22. (c) 23. (d) 24. (c) 25. (c) 26. (b)
27. (d) 28. (b) 29. (b) 30. (d)
119 Class XI - Economics
Question no.2: Fill appropriate word in the blanks-
(i) Scarcity of resources gives rise to problem of .................(plenty/
choice)
(ii) Choice is the result of..................(excess/scarcity)
60
(iii) Production possibility curve is.................to the point of origin,
(convex/concave)
(iv) ................. is the ratio of number of units of a good sacrificed to
increase one more unit of other good.(opportunity cost/ marginal
E3
rate of transformation)
(v) ................. of a given resource can be defined as the value of the
next best use to which that resource could be put. (opportunity
cost/ marginal rate of transformation)
(vi)
Ans: (i) choice
ID
................. is the slope of production possibility curve, (marginal
rate of transformation/ marginal rate of substitution)
(ii) scarcity
U
(iii) concave (iv) marginal rate of transformation
(v) opportunity cost (vi) marginal rate of transformation
YG
Short Answer Type Questions (3-4 Marks)
1. Distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics. Give
example.
D
2. Why does an economic problem arise? Explain the problem of
'How to Produce'?
U
3. Explain the problem of 'What to Produce' with the help of an
example.
ST
4. 'For whom to produce' is a central problem of an economy. Explain.
5. Define opportunity cost with the help of an example, how does it
differ from marginal opportunity cost?
6. What is 'Marginal Rate of Transformation'? Explain with the help
of an example.
7. Why is a production possibility curve concave? Explain.
120 Class XI - Economics
8. What is PP Frontier? Write its assumptions.
9. Show the following situation with PPF (PPC).
(a) Fuller utilisation of resources
(b) Increase in the resources
60
(c) Under utilisation of resources.
10. Distingush between positive economics and normative economics.
11. A lot of people died and many factories were destroyed because
E3
of a severe earthquake in a country. How will it affect the country's
PPF?
12. Calculate MRT from following table. What will be the shape of
PPF and why?
Combinations
A ID
Green Chilly (Units)
100
Sugar Units
1
U
B 95 1
C 85 2
YG
D 70 3
E 50 4
F 25 5
D
13. Given that no resource is equally efficient in producing all goods.
Write name of such curve which shows production potential of an
U
economy. Explain features of this curve along with the reasons?
14. If an Economy is not able to utilise its available resources efficiently,
what will be the effect on PPF? What will you suggest for economic
ST
growth?
15. Govt started employment generation program MGNREGA explain
its impact on PPF.
17. 'Make in India' is a Govt. policy to attract foreign investment explain
its impact on PPF.
121 Class XI - Economics
Hints (3 Marks Questios)
12.
ΔY
Combinations MOC
ΔX
60
A –
B 5:1
C 10 : 1
E3
D 15 : 1
E 20 : 1
F 25 : 1
ID
U
YG
D
U
ST
122 Class XI - Economics
Exam. Oriented Questions with Answer
Very Short Answer Question (1 Mark)
Q. 1. Define Economy.
60
Ans. An economy is a system that helps to produce goods and services
and enables people to earn their living.
E3
Q. 2. What is the meaning of scarcity of resources?
Ans. Scarcity of resources means shortage of resources as compared
to its deman(d)
Q. 3. Write the meaning of Economic Problem.
Ans.
Q. 4.
ID
Economic problem is the problem of making the choice of the use
of scarce resources for satisfying unlimited human wants.
Define MRT.
U
Ans. Marginal Rate of Transformation (MRT) is the ratio of number of
units of a good sacrificed to increase one more unit of the other
YG
Y
good MRT
X
Q. 5. Define opportunity cost.
Ans. Opportunity cost of a resource is its value in next best alternative
D
use.
Q. 6. Government has started promoting foreign investments. What will
U
be its economic value in the context of PPF?
Ans. Production will increase with more foreign investments. Thus PPF
ST
will shift rightwar(d)
Q. 7. What is the meaning of economising of resources?
Ans. Economising of resources means best possible use of available
resources.
123 Class XI - Economics
3 - 4 Marks Questions
Q. 1. Why is a production possibility curve concave? Explain.
Ans. The production possibility curve being concave means that MRT
increases as we move downward along the curve. MRT increases
because it is assumed that no resource is equally efficient in
60
production of all goods. As resources are transferred from one
good to another, less and less efficient resources have to be
employe(d) This raises cost and raises MRT.
Q. 2. Explain properties of a production possibility curve.
E3
Ans. There are two properties of a production possibility curve.
1. Downward sloping : It is because as more quantity of one good
is produced some quantity of the other good must be sacrificed
as resources are scarce. More of both goods cannot be produce(d)
ID
2. Concave to the origin : It is because the marginal rate of
transformation increases as more of one good is produce(d)
Q. 3. Explain the problem of 'what to produce'.
Ans. An economy can produce different possible combinations of goods
U
and services with given resrouces. The problem is that, out of
these different combinations, which combination is produce(d) If
YG
production of one good increases then less resources will be
available for other goods, because resources are limited and have
alternative uses.
Q. 4. What is 'Marginal Rate of Transformation'? Explain with the help
of an example.
Ans. MRT is the rate at which the units of one good have to be sacrificed
D
to produce one more unit of the other good in a two goods economy.
Suppose an economy produces only two goods X and Y. Further
suppose that by employing these resources fully and efficiently,
U
the economy produces 1X + 10Y. If the economy decides to
produce 2X, it has to cut down production of Y by 2 units. Then 2Y
ST
is the opportunity cost of producing 1X. Then 2Y : 1X is the MRT.
Q. 5. Explain the problem 'How to produce'.
Ans. The central problem 'How to Produce' is the problem of choosing
the appropriate technique of production for producing goods. There
can be more than one method for producing a goo(d) More labour
and less capital (i.e., labour intensive technique) or more capital
and less labour (i.e., capital intensive technique) can be used for
124 Class XI - Economics
production of a goo(d) Since resources are scarce, decision has
to be taken about which technique should be used on the basis of
availability of recources.
Example : A given quantity of cloth can be manufactured by
combining factors of production in different proportions, making it
capital-intensive or labour intensive metho(d)
60
Q. 6. For labourers working under MGNREGA Government has
increased minimum employment from 100 to 150 days. How will
this affect real and potential level of production.
Ans. Real level of production will be increased by improvement in
E3
employment. But potential level of production will not increase
(No shifting of PPC will take place). Reason being PPC is based
on the assumption that available resources are fully utilise(d)
Q. 7. Explain the central problem 'for whom to produce'.
Ans. For whom to produce means that who will buy the goods and
Q. 8.
ID
services produce(d) Clearly, those people who have income will
be able to buy. So, the problem amounts to how the national
income is distributed in an economy.
Giving reason comment on the shape of Production Possibilities
U
curve based on the following schedule :
God X (units) 0 1 2 3 4
YG
Good Y (units) 10 9 7 4 0
Ans.
Good X (units) Good Y (Units) MRT
0 10 –
D
1 9 1Y : 1X
2 7 2Y : 1X
U
3 4 3Y : 1X
4 0 4Y : 1X
ST
Since MRT is increasing, the PP curve is downward sloping and
concave to the origin.
Q. 9. Explain the effects of floods in Jammu and Kashmir on its production
possibilities frontier.
Ans. Floods have damaged and reduced resources. Since potential
production declines, the production possibility frontier shifts to the
left.
125 Class XI - Economics
You might also like
- Valuation of Internet and Technology Stocks: Implications for Investment AnalysisFrom EverandValuation of Internet and Technology Stocks: Implications for Investment AnalysisNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument178 pagesEconomicsVrinda GuptaNo ratings yet
- ECODocument185 pagesECOSenthil Kumar GanesanNo ratings yet
- Introduction EconomicsDocument9 pagesIntroduction EconomicsJasleen KaurNo ratings yet
- General Instructions:: (A) When MRT Is Decreasing (B) When MRT Is Increasing (C) When MRT Is Constant (D) None of TheseDocument4 pagesGeneral Instructions:: (A) When MRT Is Decreasing (B) When MRT Is Increasing (C) When MRT Is Constant (D) None of Thesesvps gorishaNo ratings yet
- Ch1. Introduction To Economics (AK) 2023-24Document16 pagesCh1. Introduction To Economics (AK) 2023-24Aarav GroverNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument5 pagesEconomicsYomi AmvNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument21 pagesIntroductionDr. Karuppasamy PandianNo ratings yet
- ch.1 Micro Class 11 NotesDocument4 pagesch.1 Micro Class 11 NotesKanak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Reader - Micro I II - 1Document9 pagesReader - Micro I II - 1Samuel AbdurahmanNo ratings yet
- PPF WorksheetDocument3 pagesPPF Worksheetsnsmiddleschool2020No ratings yet
- CEIT3771 06 Nor 2019Document4 pagesCEIT3771 06 Nor 2019kuazikua hondjeraNo ratings yet
- Form 9 AK Economics Sept 2023Document12 pagesForm 9 AK Economics Sept 2023xxzsandeepNo ratings yet
- What Are The Fundamental Economic Problems?Document11 pagesWhat Are The Fundamental Economic Problems?Anonymous XIDvTPdNNo ratings yet
- CA Foundation Eco & BCK English BookDocument179 pagesCA Foundation Eco & BCK English BookRaghav SomaniNo ratings yet
- Skans Chapter Wise Economics McqsDocument41 pagesSkans Chapter Wise Economics Mcqsahsanchoudharyat007No ratings yet
- CA Foundation Economics Question Paper With Answer Nov 2019Document11 pagesCA Foundation Economics Question Paper With Answer Nov 2019malkitsingh8742No ratings yet
- Econ140 ch1 A-AcademyDocument7 pagesEcon140 ch1 A-AcademyMohamed AlhawajNo ratings yet
- Macroecononics Unit1 Basic Economic ConceptDocument75 pagesMacroecononics Unit1 Basic Economic ConceptChanel CocoNo ratings yet
- MIcro Economics Important Questions 1Document21 pagesMIcro Economics Important Questions 1btsqueen62No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Micro EconomicsDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Micro Economicsshashikumar shashiNo ratings yet
- Work Book-Economics-Grade-11 - 12Document31 pagesWork Book-Economics-Grade-11 - 12Abubeker Abdullahi100% (1)
- Eco Chapter 1Document8 pagesEco Chapter 1SITI NUR HAZIQAH HAMIDONNo ratings yet
- Holiday HWDocument4 pagesHoliday HWPriya srikotiNo ratings yet
- Economics and BCK QUESTION PAPERDocument8 pagesEconomics and BCK QUESTION PAPERnashwauefaNo ratings yet
- Economics PT-1 Section A AnswersDocument5 pagesEconomics PT-1 Section A AnswersJANARTHANAN MNo ratings yet
- ECO & BCK - OrginalDocument18 pagesECO & BCK - OrginalKanchan AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Bannari Amman Institute of TechnologyDocument8 pagesBannari Amman Institute of TechnologyJANARTHANAN MNo ratings yet
- Sec-B2 2022Document3 pagesSec-B2 2022Sanchari DasNo ratings yet
- Form 9 AK Economic Applications Sep 2023Document17 pagesForm 9 AK Economic Applications Sep 2023xxzsandeepNo ratings yet
- Economics 9 .......... (Cambridge) : Monthlytest - October 2020Document4 pagesEconomics 9 .......... (Cambridge) : Monthlytest - October 2020Mohamed MubarakNo ratings yet
- 2021S P42Document4 pages2021S P42Bijaya PandayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document22 pagesChapter 1Farah FarhathunNo ratings yet
- Economics Class 12 Notes, Ebook - Solved Questions For Board Exams - Free PDF DownloadDocument100 pagesEconomics Class 12 Notes, Ebook - Solved Questions For Board Exams - Free PDF DownloadRobo Buddy100% (1)
- Net BookDocument17 pagesNet BookMaina SaikiaNo ratings yet
- WBUT Values & Ethics Paper - 2011Document4 pagesWBUT Values & Ethics Paper - 2011Sourav PandaNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics: Sample Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument6 pagesMicroeconomics: Sample Multiple-Choice Questionskunalshah81No ratings yet
- Mock Test 2 - Business EconomicsDocument9 pagesMock Test 2 - Business Economicsrishjain1118No ratings yet
- AP Economics Study GuideDocument5 pagesAP Economics Study GuideArjun GourishettyNo ratings yet
- CUET-Economics - Practice-Paper (Sscstudy - Com)Document6 pagesCUET-Economics - Practice-Paper (Sscstudy - Com)singhrekha9958No ratings yet
- Economics by Ragan 14th Edition Chapter 24 Test BankDocument57 pagesEconomics by Ragan 14th Edition Chapter 24 Test BankTeodor SaucaNo ratings yet
- Add Less To The Output Than Previous Units of Labour. (B)Document10 pagesAdd Less To The Output Than Previous Units of Labour. (B)Samuel FabiyiNo ratings yet
- Intro To Economics (AK) (CLASS XII) (CBSE)Document12 pagesIntro To Economics (AK) (CLASS XII) (CBSE)Mark GhoshNo ratings yet
- Today Economics Ca Foundation QPDocument4 pagesToday Economics Ca Foundation QPAparnaNo ratings yet
- 760oswaal Case-Based Questions Economics 12th (Issued by CBSE in April-2021)Document4 pages760oswaal Case-Based Questions Economics 12th (Issued by CBSE in April-2021)Tanishq TayalNo ratings yet
- ECONOMICS SS2 2nd TERM NOTES 2021-22 - 2Document64 pagesECONOMICS SS2 2nd TERM NOTES 2021-22 - 2isaac bakare100% (1)
- SQP-2 EconomicsDocument6 pagesSQP-2 EconomicsAsha BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan May 21, 2023Document23 pagesAdobe Scan May 21, 2023ksumit52225No ratings yet
- Principles of Economics Question PaperDocument130 pagesPrinciples of Economics Question PaperEmmanuel Kwame Ocloo50% (2)
- Micro CH - 1 SPCC - PDFDocument34 pagesMicro CH - 1 SPCC - PDFNamandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 01 Aug 2022Document13 pagesAdobe Scan 01 Aug 2022Siddharth SinghNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics: Dr. Ahmed Said AhmedDocument18 pagesMicroeconomics: Dr. Ahmed Said Ahmedmariam raafatNo ratings yet
- Most Imp 499 MCQs On Economics.Document43 pagesMost Imp 499 MCQs On Economics.Rahul Kumar DabotraNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument4 pagesEconomicsMohamed MubarakNo ratings yet
- TiktoktoktikDocument34 pagesTiktoktoktikabhinav4090tiNo ratings yet
- Economics Sm2Document150 pagesEconomics Sm2Senthil Kumar GanesanNo ratings yet
- Business Economics ICFAIDocument20 pagesBusiness Economics ICFAIDaniel VincentNo ratings yet
- Model Exam - Economics - AAUDocument20 pagesModel Exam - Economics - AAUrami assefa91% (11)
- Adobe Scan Apr 25, 2021Document3 pagesAdobe Scan Apr 25, 2021Anusha ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Ca 4 68Document18 pagesCa 4 68aanjnay1234No ratings yet
- Election and Representation Part 2Document37 pagesElection and Representation Part 2aanjnay1234No ratings yet
- Summits 2021-22Document3 pagesSummits 2021-22aanjnay1234No ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document8 pagesAssignment 1aanjnay1234No ratings yet
- Science 1Document4 pagesScience 1aanjnay1234No ratings yet
- PU Mock 5 - QDocument8 pagesPU Mock 5 - Qaanjnay1234No ratings yet
- Legal - 2Document5 pagesLegal - 2aanjnay1234No ratings yet
- CLAT 2023 Current Affairs Repository QuestionsDocument172 pagesCLAT 2023 Current Affairs Repository Questionsaanjnay1234No ratings yet
- Ashiq Sulthan V State of KeralaDocument6 pagesAshiq Sulthan V State of Keralaaanjnay1234No ratings yet
- Mock PU-1 2023 - QDocument9 pagesMock PU-1 2023 - Qaanjnay1234No ratings yet
- TP 2019 6 SCC 512 518 Aanjnay1234 Gmailcom 20240302 073410 1 7Document7 pagesTP 2019 6 SCC 512 518 Aanjnay1234 Gmailcom 20240302 073410 1 7aanjnay1234No ratings yet
- The Law and The LawyersDocument21 pagesThe Law and The Lawyersaanjnay1234No ratings yet
- Africa's Cities Opening Doors To The WorldDocument166 pagesAfrica's Cities Opening Doors To The WorldjeuneafriqueNo ratings yet
- All India Cantoment FedreationDocument5 pagesAll India Cantoment FedreationRavi SolankiNo ratings yet
- Salary Survey (Hong Kong) - 2022Document7 pagesSalary Survey (Hong Kong) - 2022Nathan SmithNo ratings yet
- Maula vs. Ximex, GR No. 207838, January 25, 2017Document1 pageMaula vs. Ximex, GR No. 207838, January 25, 2017Affle John LeonorNo ratings yet
- Atlanta: The Phoenix CityDocument4 pagesAtlanta: The Phoenix CitydwitunggalNo ratings yet
- Adv. Mgt.Document7 pagesAdv. Mgt.Anwar ParvezNo ratings yet
- POEA Approved Job Orders PlumbersDocument2 pagesPOEA Approved Job Orders PlumbersxerdomsNo ratings yet
- RFBT - Chapter 2 - Labor StandardsDocument6 pagesRFBT - Chapter 2 - Labor Standardslaythejoylunas21No ratings yet
- Resilience and Health Promotion in High-risk Professions: A Pilot Study of Firefighters in Canada and the United Kingdom Leigh Blaney, Vancouver Island University, Canada Vivienne Brunsden, Nottingham Trent University, United KingdomDocument12 pagesResilience and Health Promotion in High-risk Professions: A Pilot Study of Firefighters in Canada and the United Kingdom Leigh Blaney, Vancouver Island University, Canada Vivienne Brunsden, Nottingham Trent University, United KingdomIoana ElenaNo ratings yet
- Leases Tutorials Street V MountfordDocument3 pagesLeases Tutorials Street V Mountfordeasonkok22No ratings yet
- Management Controll System BookDocument192 pagesManagement Controll System Bookmathrix01No ratings yet
- Club Management Dhos-C1Document27 pagesClub Management Dhos-C1Mademozel MichaeNo ratings yet
- Job Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment (Villorente & Torres, 2018)Document26 pagesJob Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment (Villorente & Torres, 2018)Nicodeo Vicente IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Testing Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory of MotivationDocument15 pagesTesting Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory of MotivationMesa AprilzmesamayNo ratings yet
- 134) Gutierrez vs. DBM (G.R. No. 153266, March 18, 2010)Document24 pages134) Gutierrez vs. DBM (G.R. No. 153266, March 18, 2010)Carmel Grace KiwasNo ratings yet
- Job Application Letter Sample With No ExperienceDocument7 pagesJob Application Letter Sample With No Experiencebcr1xd5a100% (1)
- Policy Brief On Women S Entrepreneurship PDFDocument36 pagesPolicy Brief On Women S Entrepreneurship PDFKunal ObhraiNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Employee Stock Option PlansDocument41 pagesAccounting For Employee Stock Option Plansamit debnathNo ratings yet
- 49 - 50 - 19 Finance Regular Ad JA JMDocument6 pages49 - 50 - 19 Finance Regular Ad JA JMchiranjeevi kindinlaNo ratings yet
- Accra Business School: MSC Human Resource ManagementDocument9 pagesAccra Business School: MSC Human Resource ManagementBenjamin OpokuNo ratings yet
- STE Handbook 2011.12Document186 pagesSTE Handbook 2011.12Jamie_L_JenkinsNo ratings yet
- QuingDocument48 pagesQuinglulughoshNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document5 pagesTutorial 1MiyukiNo ratings yet
- BLUM vs. Zamora - DigestDocument2 pagesBLUM vs. Zamora - DigestBigs BeguiaNo ratings yet
- Domestic Auto PartsDocument4 pagesDomestic Auto PartsEmmely Morales LunaNo ratings yet
- PNG Employment Act 1978Document68 pagesPNG Employment Act 1978Meyvin AriroNo ratings yet
- Principles of Safety ManagementDocument70 pagesPrinciples of Safety ManagementOmar Siddiqui0% (1)
- Question Paper - Final Examination - Introduction To BusinessDocument13 pagesQuestion Paper - Final Examination - Introduction To BusinessKavitha SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Egov Excel TemplateDocument6 pagesEgov Excel Templatekimberly garcesNo ratings yet
- The Perceived Effects of Cyberbullying in Adulthood in The WorkplaceDocument135 pagesThe Perceived Effects of Cyberbullying in Adulthood in The WorkplaceRana Sikandar100% (2)
- Financial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassFrom EverandFinancial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassNo ratings yet
- The War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesFrom EverandThe War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Narrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsFrom EverandNarrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (94)
- The Meth Lunches: Food and Longing in an American CityFrom EverandThe Meth Lunches: Food and Longing in an American CityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- A History of the United States in Five Crashes: Stock Market Meltdowns That Defined a NationFrom EverandA History of the United States in Five Crashes: Stock Market Meltdowns That Defined a NationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- University of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingFrom EverandUniversity of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (97)
- The Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaFrom EverandThe Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaNo ratings yet
- These are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaFrom EverandThese are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- This Changes Everything: Capitalism vs. The ClimateFrom EverandThis Changes Everything: Capitalism vs. The ClimateRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (349)
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyFrom EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (228)
- Look Again: The Power of Noticing What Was Always ThereFrom EverandLook Again: The Power of Noticing What Was Always ThereRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Principles for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailFrom EverandPrinciples for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (237)
- The Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationFrom EverandThe Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (46)
- Economics 101: How the World WorksFrom EverandEconomics 101: How the World WorksRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (34)
- The Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumFrom EverandThe Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (12)
- Economics 101: From Consumer Behavior to Competitive Markets—Everything You Need to Know About EconomicsFrom EverandEconomics 101: From Consumer Behavior to Competitive Markets—Everything You Need to Know About EconomicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Finance Curse: How Global Finance Is Making Us All PoorerFrom EverandThe Finance Curse: How Global Finance Is Making Us All PoorerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Second Class: How the Elites Betrayed America's Working Men and WomenFrom EverandSecond Class: How the Elites Betrayed America's Working Men and WomenNo ratings yet
- The Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetFrom EverandThe Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetNo ratings yet
- Anarchy, State, and Utopia: Second EditionFrom EverandAnarchy, State, and Utopia: Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (180)
- Vulture Capitalism: Corporate Crimes, Backdoor Bailouts, and the Death of FreedomFrom EverandVulture Capitalism: Corporate Crimes, Backdoor Bailouts, and the Death of FreedomNo ratings yet
- The New Elite: Inside the Minds of the Truly WealthyFrom EverandThe New Elite: Inside the Minds of the Truly WealthyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)