0% found this document useful (0 votes)
247 views13 pagesMechatronic System Design Process Guide
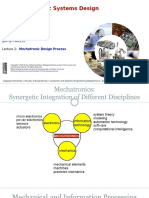
The document outlines the mechatronic design process, which takes a synergistic and iterative approach integrating different engineering disciplines. It describes the key stages as defining objectives and specifications, analyzing and designing the system concurrently through modeling and simulation, then building and testing a prototype.
Uploaded by
mxolisi.dhlamini95Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
247 views13 pagesMechatronic System Design Process Guide
The document outlines the mechatronic design process, which takes a synergistic and iterative approach integrating different engineering disciplines. It describes the key stages as defining objectives and specifications, analyzing and designing the system concurrently through modeling and simulation, then building and testing a prototype.
Uploaded by
mxolisi.dhlamini95Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd