Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Strategic management
Uploaded by
loriemiepCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Strategic management
Uploaded by
loriemiepCopyright:
Available Formats
Week 1
Chapter 1: EVOLUTION OF BUSINESS POLICY AND STRATEGY
In the world of business, there is so-called Business Policies. These are set of rules that guide the decisions and
actions of the members of the organization. This may be informal or in writing coming in the form of operational
manual, personnel handbook, and memoranda. Business Policies also are set of rules that guide the conduct of the
business in pursuit of profit and other objectives of the business organization.
❖ Concept of Strategy
Strategy- referring to top management’s plan to attain outcomes consistent with the organization’s mission and
goals. (Wright, Kroll, and Parnel)
- Characterized as operational level referring to it as a set of competitive moves and business
approaches that management is employing to run the company. (Thompson and Strickland)
- Largely treated as semantic issue. (Jeffrey Bracker)
- Greek word “stratego” referring to a “general”
“to plan the destruction of one’s enemies through effective use of resources” 2
Categories:
1. Intended Strategy- refers to original staregy that management plans and intends to implement
2. Realized Strategy- refers to actual and eventual strategy that management actually implements. Characteristics of
Strategy:
a. Traditionally meant to be a grand plan made in the light of what is believed an adversary might or might not do.
b. Derives its relevance given from the existence competition in business.
c. Done on the presumption of the existence of a negative scenario.
d. Connotes general program of action and deployment of emphasis and resources to attain comprehensive
objectives.
e. Involves determination of the basic long-term goals and objectives of an enterprise, and the adoption of courses
of action and the allocation of resources necessary to carry out those goals.
f. A decision about how to use available resources to secure a major objective in the face of obstruction.
g. Implies action and guides decision-making, spelling out directions to be taken.
h. Strategy may, in some extreme or necessary cases, exist without a policy.
Strategy VS. Policy
STRATEGY POLICY
Exist without the established business policy Exist amidst the absence of business strategy
Operational in nature Directional in nature
Maybe informal and not necessarily written Formal or written
and often confidential
✓ Policy- viewed as internal matters that guide the operationalization of the business organization. (Please
click and see the
link)https://youtu.be/F2_EsTP_WuU
What is the nature of Strategic Management?
✓ Integrating the concept of strategy into the mainstream of the management system is what matters most in
the terms of giving directions that promises delivering profit expectations. (Please click and see the
link)https://youtu.be/_BajRnOCSKk
What is Strategic Management?
According to:
a. Stahl and Grigsby: Referring to the entire process of strategic decision-making that relates to its
environment, guide internal activities, and determines the long-term performance of the organization.
b. Wheelen and Hunger: A set of managerial decisions and actions that determine the long-run
performance of the organization.
c. Williamson, Jenkins, et al: Framework that evolves around the idea of shaping the destiny of an
organization.
d. Wright, Kroll, and Parnell: Consists of managerial decisions and actions that help to ensure that the
organization of formulates and maintains a beneficial fit with its environment.
Strategic Management Page 1 of 5
Week 1
Steps that Top Management Should Accomplish:
1. Analyze the opportunities and threats or constraints that exist in the external envi.
2. Analyze the organization’s strengths and weaknesses in its envi.
3. Establish the org.’s mission and develop the goals.
4. Formulate the strategies that will match the org.’s strengths and weaknesses with the
environment’s opportunities and threats.
5. Implement strategies.
6. Engage in the strategic control activities to ensure that the org.’s goals are attained. General
Strategic Orientation of Competing firm:
a. Defender. This type includes companies with limited product line that focus on improving the efficiency of their
existing operation.
b. Prospectors. Type of companies includes firms with fairly broad product lines that focus on product innovation
c. Analyzers. Includes business organizations that operate in at least two different product-market areas, one
stable and one variable.
d. Reactors. Includes companies that lack a consistent strategy-structure-culture relationship. Their responses to
environmental pressures tend to be piecemeal strategic changes.
Strategy VS. Tactics
Tactics- are more operational and done in context with or as a support activity or operation to achieve a strategy.
As to: Strategy Tactics
Level of Conduct Developed at the highest levels Employed at related to lower
of management levels of
management
Regularity Continuous and Irregular Determined on a
periodic cycle with fixed
time schedule
Subjective Values Strategic decision-making is Tactical decision-making is
heavily weighed not heavily weighed
Range of Alternatives greater Lesser
Uncertainty Much greater in both Knowing the result first
formulation and
implementation
Nature of Problems Strategic problems are Structured and often
generally unstructured and repetitive
tend to be one of a kind
Information Needs Requires large amount of Rely more heavily on
information internally generated data
Time Horizon Intended to, and do last for Covers a short duration
long periods of time
Reference Original in the sense that it is Formulated within and in
the source of origin for the pursuit of strategies
development of tactics
Details Broad Fewer
Type of personnel Most part formulated by Large number of managers
involved management and staff and
employees
Ease of Evaluation Easier to measure the Not Easy
effectiveness and
efficiency
Context of Point of View Formulated from corporate Developed principally
viewpoint from a functional point of
view
Importance Highest importance in the org Considerably less
significant
(Please click and see the link for further comprehension)
https://youtu.be/ASjjmU_7nGk
Strategic Management Page 2 of 5
Week 1
https://youtu.be/-5Qv30004CM
Bases of Policies and Strategies
a. Legal Mandate-refers to formulating policies on the basis of the provisions of the charter or legal basis for
creation or existence of the business organization including the applicable provisions of laws and policies or
pronouncement of the government and its statutory or regulatory bodies.
b. Vision and Mission statement-essentially refers to the leadership bias as well as sense of direction and mission
for which the organization emanates from its founders and the previous or incumbent leaders or managers of the
organization.
c. Specific Objectives- are corporate objectives purposely developed for the organization and for its members or
employees at large to pursue
d. Programs and Policies- are specific programs set forth by the organization’s policy makers in pursuit of short
and long-term goals given certain considerations at hand.
Approaches to Identifying Policies and Strategies
1. Policy/Strategy Profile
2. Gap Analysis
3. Competitive Strategy Analysis
Outcome
Profit maximizing
Classical Evolutionary
Processes Emergent
Deliberate
Systematic Processual
Plural
Figure 1. Generic Perspective of Strategy
*Search about it (Source: Whittington 2001)
Developing Policy and Strategy
a. Top-Bottom Approach. Initiatives in developing policies and strategies come from the top management with
rank and file tasked to implementing or following the policies and strategies.
b. Bottom-Top Approach. Policy and strategy initiatives emanate from the bottom or rank-and-file from which top
management develops concrete policies and strategies for the lower-ranked employees to observe or follow.
c. Top-Bottom-Top. Policy and strategy initiatives are taken by the top management then filtered down to lower-
ranked personnel for consultations then returned back to the top management for refinement
(Please click and see the link: https://youtu.be/7xXzEhnjJD4)
: https://youtu.be/lO9u5pA6Rns
How to make strategic decision-making?
a. Rare. Strategic decisions are unusual and typically have no precedent to follow.
b. Consequential. Strategic decisions should commit substantial resources and demand a great deal of commitment
from people at all levels.
c. Directive. Strategic decisions set precedents for lesser decisions and future actions throughout the organization.
Process:
1. Evaluate current performance results in terms of (a) ROI, Profitability, and so forth, (b) current mission,
objectives, strategies, and policies.
2. Review corporate governance, that is, the performance of the firm’s BOD and Top Management.
3. Scan and assess external environment to determine the strategic factors that pose Opportunities and Threats.
4. Scan and Assess the internal corporate environment to determine the strategic factors that are Strengths and
Weaknesses.
5. Analyze strategic SWOT factors to pinpoint problem areas, and review and revise the corporate mission and
objectives as necessary.
6. Generate, evaluate, and select the best alternative strategy in the light of the analysis conducted in Step 5.
Strategic Management Page 3 of 5
Week 1
7. Implement selected strategies via programs, budgets, and procedures.
8. Evaluate and implement strategies via feedback systems and control of activities to ensure their minimum
deviation from plans.
Modalities in Strategic Decision by Mintzberg
a. Entrepreneurial Mode
b. Adaptive Mode
c. Planning Mode
d. Logical Mode
Role of Board of Directors
a. Monitor. BODs can keep abreast of the developments inside and outside the corporation, bringing to
management’s attention development it might have overlooked.
b. Evaluate and Influence. Examine management’s proposals, decisions, and actions, agree or disagree with them,
give advice and offer suggestions, and outline alternatives.
c. Initiate and Determine. BOD can delineate a corporation’s mission and specify strategic options to its
management.
References:
Orcullo Jr., N, (2007), Fundamentals of Strategic Management, Rex Book Store
Pereda, R., et. Al, (2015), Strategic Management, Unlimited Books Library Services & Publishing Inc.
*Note: Prepare for an assessment next meeting. God bless and stay safe!
Strategic Management Page 4 of 5
You might also like
- Concepts of Policy and StrategyDocument3 pagesConcepts of Policy and StrategyDenise Cruz64% (11)
- SM Short MaterialDocument11 pagesSM Short MaterialK.v. PriyankcaNo ratings yet
- MBA204 - Strategic Management Establishing Business DirectionDocument41 pagesMBA204 - Strategic Management Establishing Business DirectionChristian Dominic MarayagNo ratings yet
- The Purpose of Strategic and Business AnalysisDocument26 pagesThe Purpose of Strategic and Business Analysismarinelle gonzalesNo ratings yet
- ICAB Advance Level Strategic Business Management Study Manual Theory & ModelDocument638 pagesICAB Advance Level Strategic Business Management Study Manual Theory & ModelOptimal Management SolutionNo ratings yet
- strategicDocument5 pagesstrategicragojo.khristelleayla.cruzNo ratings yet
- BA 316 Notes For Chapter 1 and 2Document7 pagesBA 316 Notes For Chapter 1 and 2PremiumNo ratings yet
- Strama - PrelimDocument4 pagesStrama - PrelimMeybilene BernardoNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Rev 1Document6 pagesStrategic Management Rev 1RIJJIE Y�IGO DEVERANo ratings yet
- Business Policy and Strategy: Presented By: Jerissa Joy TaongDocument16 pagesBusiness Policy and Strategy: Presented By: Jerissa Joy TaongJerissa Joy TaongNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document6 pagesLesson 1not funny didn't laughNo ratings yet
- New WordDocument6 pagesNew WordAdetunji TaiwoNo ratings yet
- Copy of Copy of Copy of SM - Lec7Document40 pagesCopy of Copy of Copy of SM - Lec7Kanak ThackerNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management GuideDocument168 pagesStrategic Management GuideShriram DawkharNo ratings yet
- 402 - Strategic Management Short Notes Dr. K JAYANTHDocument16 pages402 - Strategic Management Short Notes Dr. K JAYANTHJ.M Sai TejaNo ratings yet
- Business Policy & Strategic Management PDFDocument132 pagesBusiness Policy & Strategic Management PDFUdit VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Business Policy and Strategic MGT Block - 1Document46 pagesBusiness Policy and Strategic MGT Block - 1abdikarimNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Strategy Implementation: Basic Types of Organizational StructureDocument3 pagesThe Nature of Strategy Implementation: Basic Types of Organizational StructureXNo ratings yet
- Nature of Strategic Management Strategic Management Is The Art and Science of Formulating, Implementing andDocument15 pagesNature of Strategic Management Strategic Management Is The Art and Science of Formulating, Implementing andArya ManaloNo ratings yet
- Strategic Formulation & ImplementationDocument26 pagesStrategic Formulation & ImplementationNaman KhudasiaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Business Policy and StrategyDocument10 pagesEvolution of Business Policy and StrategyKim Carlo F. Tangian100% (3)
- Chart BookDocument217 pagesChart BookSimran RanaNo ratings yet
- MGT 490 - Strategic Management: Lecture SlidesDocument20 pagesMGT 490 - Strategic Management: Lecture SlidesBarkat UllahNo ratings yet
- Issues in Strategic ImplementationDocument3 pagesIssues in Strategic ImplementationHasan shaikh0% (1)
- Slides-Week 01-02Document19 pagesSlides-Week 01-02Chi StiNo ratings yet
- Chapter One - Introducing The Practice of StrategyDocument4 pagesChapter One - Introducing The Practice of Strategystanely ndlovuNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Process Key StepsDocument9 pagesStrategic Management Process Key StepsMayuri MahadikNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Components of The Strategic Management ModelDocument7 pagesDiscuss The Components of The Strategic Management ModelGovinda BiswasNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Introduction To StrategyDocument21 pagesModule 3 - Introduction To StrategyIslam GayaNo ratings yet
- BPSM 1 Introduction Prof. SangitaDocument34 pagesBPSM 1 Introduction Prof. Sangitasantoshnagane72No ratings yet
- Strategic Management - PresentationDocument27 pagesStrategic Management - Presentationmenchong 123No ratings yet
- Stages of Strategic Management: Strategy FormulatonDocument3 pagesStages of Strategic Management: Strategy FormulatonEliy NaziraNo ratings yet
- Strategic - Management - Marathon - Revision NotesDocument40 pagesStrategic - Management - Marathon - Revision NotesAshmi UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Normann: Strategy Is The Art of Creating ValueDocument13 pagesNormann: Strategy Is The Art of Creating ValueSharath NairNo ratings yet
- Strategic Information Systems: Gaining Competitive AdvantageDocument50 pagesStrategic Information Systems: Gaining Competitive AdvantageLamees RababahNo ratings yet
- 46774bosinter p7 Secb Cp3Document24 pages46774bosinter p7 Secb Cp3Karthik AnnaduraiNo ratings yet
- CHapter 1Document30 pagesCHapter 1cddr257vxzNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Strategic Management Unit 1Document17 pagesIntroduction To Strategic Management Unit 1Hujjat UllahNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management GuideDocument7 pagesStrategic Management GuideAnooja SajeevNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management 1 Topics 1 and 2Document5 pagesStrategic Management 1 Topics 1 and 2veronicaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document29 pagesChapter 1JulianNo ratings yet
- Business Policy & Strategy Notes (2019) (Vi - Sem - BMS - SSCBS - Du)Document62 pagesBusiness Policy & Strategy Notes (2019) (Vi - Sem - BMS - SSCBS - Du)Sanya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.Document24 pagesChapter 1.20BBA29 DUBEY ADITYA ManasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 HandoutsDocument5 pagesChapter 1 HandoutsKathleen Ariola100% (1)
- Strategic Management Chapter Summary and HighlightsDocument7 pagesStrategic Management Chapter Summary and HighlightsNerizza SomeraNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument138 pagesStrategic ManagementVinay BhandariNo ratings yet
- CBMEC-Module 1Document16 pagesCBMEC-Module 1JE JE GAGATAMNo ratings yet
- 1 - Strategic Management Inputs and CompetitivenessDocument17 pages1 - Strategic Management Inputs and CompetitivenessAnn BalmesNo ratings yet
- Assignment Unit - 1 Strategic Management and Business Policy Submitted To Alfishaman Submitted by Bhavna PathakDocument13 pagesAssignment Unit - 1 Strategic Management and Business Policy Submitted To Alfishaman Submitted by Bhavna PathakBhavnaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Module ExplainedDocument18 pagesStrategic Management Module ExplainedRhea PelayoNo ratings yet
- ElegantDocument19 pagesElegantsonia khatibNo ratings yet
- ICAB Advanced Level Strategic Business Management Study Manual Chapterwise Model, Diagram, Formula & FigureDocument134 pagesICAB Advanced Level Strategic Business Management Study Manual Chapterwise Model, Diagram, Formula & FigureOptimal Management Solution100% (1)
- Course Code: 546 Course: Strategic Management Seminar Student: Mercy Katini Shallo STUDENT NO: BUS-3-6149-3/2009 Lecturer: C. NyamongoDocument26 pagesCourse Code: 546 Course: Strategic Management Seminar Student: Mercy Katini Shallo STUDENT NO: BUS-3-6149-3/2009 Lecturer: C. NyamongoMaria Maganda MalditaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: Key ConceptsDocument30 pagesStrategic Management: Key ConceptsShelly SinghalNo ratings yet
- 2232.presentation On Strategic ManagemntDocument16 pages2232.presentation On Strategic ManagemntRahul BansalNo ratings yet
- The One Page Strategic PlanDocument4 pagesThe One Page Strategic PlanHervidal PisciottiNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument5 pagesStrategic ManagementSumedh DiweNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Concepts for Organizational SuccessDocument50 pagesStrategic Management Concepts for Organizational SuccessPayal RathodNo ratings yet
- Surface Additives GuideDocument61 pagesSurface Additives GuideThanh VuNo ratings yet
- Cost Sheet of HPCLDocument18 pagesCost Sheet of HPCLDeejay ChinmayNo ratings yet
- Flash 29f800Document48 pagesFlash 29f800savidhamNo ratings yet
- Jagirdari SystemDocument10 pagesJagirdari Systemdevang guptaNo ratings yet
- Build a 3D Printer Extruder Using a Hot Glue GunDocument12 pagesBuild a 3D Printer Extruder Using a Hot Glue GunJuan Andrés Hdez SuárezNo ratings yet
- TARPfinal PDFDocument28 pagesTARPfinal PDFRakesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Business Finance Week 2 2Document14 pagesBusiness Finance Week 2 2Phoebe Rafunsel Sumbongan Juyad100% (1)
- Network N10 007 Exam ObjectivesDocument19 pagesNetwork N10 007 Exam Objectivessalah_elgazzarNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 18: ElectronicsDocument18 pagesChapter # 18: ElectronicsShahzad AslamNo ratings yet
- A European Call Option Gives A Person The Right ToDocument1 pageA European Call Option Gives A Person The Right ToAmit PandeyNo ratings yet
- 1 Million Email Subscriber PlaybookDocument29 pages1 Million Email Subscriber PlaybookGabriel Ramos100% (4)
- Assign Controlling Areas and Company Codes for Optimal Cost AccountingDocument4 pagesAssign Controlling Areas and Company Codes for Optimal Cost Accountingatsc68No ratings yet
- The Weird Trading Trick That Wins Big and Wipes Out Losses: Hughes Optioneering Team RevealsDocument27 pagesThe Weird Trading Trick That Wins Big and Wipes Out Losses: Hughes Optioneering Team RevealsE TrialNo ratings yet
- Digitech's s100 ManualDocument24 pagesDigitech's s100 ManualRudy Pizzuti50% (2)
- Falk Series C, E, F, G, J, P, Q, S, Y Gear Drives - Service ManualDocument4 pagesFalk Series C, E, F, G, J, P, Q, S, Y Gear Drives - Service ManualJorge Iván Carbajal100% (1)
- Sample Whistle Blower PolicyDocument2 pagesSample Whistle Blower Policy4geniecivilNo ratings yet
- Continuous Filters: - Proven Technology With The Latest InnovationsDocument12 pagesContinuous Filters: - Proven Technology With The Latest InnovationsabdelrhmanNo ratings yet
- Nurarihyon No Mago Season 3 Sub Indo PDFDocument3 pagesNurarihyon No Mago Season 3 Sub Indo PDFLgn StruggleNo ratings yet
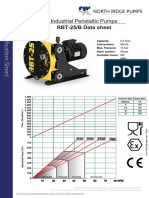
- RBT-25/B Spec SheetDocument2 pagesRBT-25/B Spec SheetSrpskiNo ratings yet
- How To Remove Letters From Stringsnumberscells in ExcelDocument1 pageHow To Remove Letters From Stringsnumberscells in ExcelharshilNo ratings yet
- Sample Midterm Test: Business EconomicsDocument5 pagesSample Midterm Test: Business EconomicsLaura BencsesNo ratings yet
- COM-BLD SSR24 Installation ManualDocument94 pagesCOM-BLD SSR24 Installation ManualAelfwine EinshpiedNo ratings yet
- Cometa vs. CA 351 Scra 294Document20 pagesCometa vs. CA 351 Scra 294albemartNo ratings yet
- Hotel Room Booking System Use-Case DiagramDocument5 pagesHotel Room Booking System Use-Case DiagramCalzita Jeffrey0% (1)
- Process Flow Diagram (For Subscribers Who Visits Merchant Business Premises)Document2 pagesProcess Flow Diagram (For Subscribers Who Visits Merchant Business Premises)Lovelyn ArokhamoniNo ratings yet
- Topic No-11 AIRCRAFT OXYGEN REQUIREMENTDocument9 pagesTopic No-11 AIRCRAFT OXYGEN REQUIREMENTSamarth SNo ratings yet
- Creating and Opening WorkbooksDocument20 pagesCreating and Opening WorkbooksCon SiosonNo ratings yet
- Aurdrea Weiman Resume1 1Document1 pageAurdrea Weiman Resume1 1api-321906932No ratings yet
- MCIAA Tax Exemption CaseDocument4 pagesMCIAA Tax Exemption CaseJep Echon TilosNo ratings yet
- Chap 01-Introduction To AccountingDocument56 pagesChap 01-Introduction To AccountingJean CoulNo ratings yet
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)From EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewFrom EverandGenerative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0From EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Sales Pitch: How to Craft a Story to Stand Out and WinFrom EverandSales Pitch: How to Craft a Story to Stand Out and WinRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Artificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (104)
- Lean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in Your Corporation, 2nd EdFrom EverandLean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in Your Corporation, 2nd EdRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (17)
- Elevate: The Three Disciplines of Advanced Strategic ThinkingFrom EverandElevate: The Three Disciplines of Advanced Strategic ThinkingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Blue Ocean Strategy, Expanded Edition: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition IrrelevantFrom EverandBlue Ocean Strategy, Expanded Edition: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition IrrelevantRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (387)
- Your Creative Mind: How to Disrupt Your Thinking, Abandon Your Comfort Zone, and Develop Bold New StrategiesFrom EverandYour Creative Mind: How to Disrupt Your Thinking, Abandon Your Comfort Zone, and Develop Bold New StrategiesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- SYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsFrom EverandSYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (48)
- Amp It Up: Leading for Hypergrowth by Raising Expectations, Increasing Urgency, and Elevating IntensityFrom EverandAmp It Up: Leading for Hypergrowth by Raising Expectations, Increasing Urgency, and Elevating IntensityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (50)
- How to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffFrom EverandHow to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (61)
- The Toyota Way (Second Edition): 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest ManufacturerFrom EverandThe Toyota Way (Second Edition): 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest ManufacturerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (121)
- Small Business For Dummies: 5th EditionFrom EverandSmall Business For Dummies: 5th EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Systems Thinking: A Guide to Strategic Planning, Problem Solving, and Creating Lasting Results for Your BusinessFrom EverandSystems Thinking: A Guide to Strategic Planning, Problem Solving, and Creating Lasting Results for Your BusinessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (80)
- Impact Networks: Create Connection, Spark Collaboration, and Catalyze Systemic ChangeFrom EverandImpact Networks: Create Connection, Spark Collaboration, and Catalyze Systemic ChangeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Tax-Free Wealth: How to Build Massive Wealth by Permanently Lowering Your TaxesFrom EverandTax-Free Wealth: How to Build Massive Wealth by Permanently Lowering Your TaxesNo ratings yet
- HBR Guide to Setting Your StrategyFrom EverandHBR Guide to Setting Your StrategyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on AI, Analytics, and the New Machine AgeFrom EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on AI, Analytics, and the New Machine AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (69)
- 2022-2023 Price Action Trading Guide for Beginners in 45 MinutesFrom Everand2022-2023 Price Action Trading Guide for Beginners in 45 MinutesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- The Digital Transformation Playbook: Rethink Your Business for the Digital AgeFrom EverandThe Digital Transformation Playbook: Rethink Your Business for the Digital AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- Power and Prediction: The Disruptive Economics of Artificial IntelligenceFrom EverandPower and Prediction: The Disruptive Economics of Artificial IntelligenceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (38)
- How to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffFrom EverandHow to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Jim Collins' Good to Great Why Some Companies Make the Leap ... And Others Don’t SummaryFrom EverandJim Collins' Good to Great Why Some Companies Make the Leap ... And Others Don’t SummaryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Red Team: How to Succeed By Thinking Like the EnemyFrom EverandRed Team: How to Succeed By Thinking Like the EnemyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (15)
- The 10X Rule: The Only Difference Between Success and FailureFrom EverandThe 10X Rule: The Only Difference Between Success and FailureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (289)
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't (Rockefeller Habits 2.0 Revised Edition)From EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't (Rockefeller Habits 2.0 Revised Edition)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)