Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(01-22) Geotechnical Engineering - Set 3
Uploaded by
Ram CaniculaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(01-22) Geotechnical Engineering - Set 3
Uploaded by
Ram CaniculaCopyright:
Available Formats
Review Innovations CE Review for Apr 2024 – Geotechnical Engineering 3
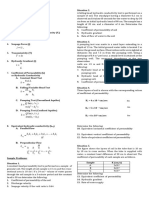
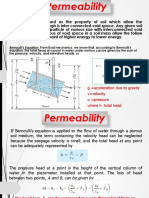
Flow of Water thru soil Situation 2.
A falling head hydraulic conductivity test is performed on a
1. Discharge (Q) sample of soil. The standpipe having a diameter 0.2 cm is
Q = Av = kiA observed and it takes 60 seconds for the water to drop by 50
cm from an initial hydraulic head of 90 cm. The sample has a
2. Discharge Velocity (V) length of 20 cm, and a diameter of 4 cm. Determine the
v = ki following:
4. Coefficient of permeability of soil
3. Seepage Velocity or Interstitial Velocity (V s) 5. Hydraulic gradient
v ki
vs = = 6. Rate of flow of water in the soil
n n
Situation 3.
4. Seepage Force (j) A pumping test was made in a sand layer extending to a
j = i w depth of 15 m. The initial ground water table is located 2 m
below the ground surface. Observation wells were sighted at
5. Transmissivity (T) distances 3m and 7.5 m from the pumping well. Using a
T = kt discharge of 0.4 m3 per hour, a steady level is attained at the
pumping well. The measured drawdowns at the two
6. Hydraulic Gradient (i) observation wells are 1.5 m and 0.35 m respectively.
h Determine the following:
i=
L 7. Hydraulic head at the observation well farther from
pumping well.
7. Coefficient of Permeability (k) 8. Hydraulic head at the observation well nearer from
or Hydraulic Conductivity
pumping well.
A. Constant Head Test
9. Coefficient of permeability of the soil.
Vol L
k=
Aht Situation 4.
B. Falling/Variable Head Test Three layers of soil is shown with the corresponding values
aL h1 of coefficient of permeability.
k= ln
At h2 K1 = 4 x 10 –3 cm/sec 3m
C. Pumping Test (Unconfined Aquifer)
Q ln(r1 / r2 ) 4m
k= K2 = 5 x 10 – 3 cm/sec
(h12 − h2 2 )
D. Pumping Test (Confined Aquifer)
Q ln(r1 / r2 ) K3 = 6 x 10-3 cm/sec 5m
k=
2 t (h1 − h2 )
Determine the following:
8. Equivalent hydraulic conductivity (k eq) 10. Equivalent horizontal coefficient of permeability
A. Parallel Flow 11. Equivalent vertical coefficient of permeability
h1k1 + h2 k2 + h3k3 + ... + hn kn 12. Ratio of equivalent coefficient of permeability
keq =
H
B. Perpendicular Flow Situation 5.
H The figure shows the layers of soil in the tube that is 10 cm
keq = by 10 cm in cross section. When the tube is supplied with
h1 h2 h3 h
+ + + ... + n water, a constant head difference of 30 cm is observed. The
k1 k2 k3 kn
coefficient of permeability of each sample are as follows.
Sample Problems:
Sample K (cm/s)
Situation 1. A 2 × 10-3
A constant-head permeability test is performed on a sample B 3 × 10-3
of granular soil. The length of soil sample is 15 cm and the C 4 × 10-3
cross-sectional area is 10 cm2. If a 24 cm3 volume of water
Determine the following:
passes through the soil sample in a 3-minute period and the
13. Equivalent coefficient of permeability
constant head is 30 cm determine the following:
1. Coefficient of permeability of the soil 14. Hydraulic gradient
2. Discharge velocity 15. Rate of water supply
3. Seepage velocity if the void ratio is 0.64
Manila/Cebu/Baguio FB: @ReviewInnovationsOfficial Davao FB: Review Innovations Davao Branch
(02) 8735-9161 0919-227-9194 (082) 221-1121 0930-256-0998
Review Innovations CE Review for Apr 2024 – Geotechnical Engineering 3
Situation 9.
For the falling head permeability test conducted below:
Length of specimen = 200 mm
30 cm Area of soil specimen = 1000 mm2
Area of standpipe = 40 mm2
Head difference at t = 0 s, h1= 500 mm
A B C Head difference at t = 180 s, h2 = 300 mm
23. Calculate the hydraulic conductivity in mm/sec
A (2.27 x 10-2 mm/sec)
15cm 20cm 25 cm
Situation 10.
Situation 6.
For the layered soil shown below.
A test is set up as shown in the figure. A cylindrical mold 4
cm in diameter is filled with silt to a height of 15 cm, whose
coefficient of permeability K1 = 1.1 × 10-2 cm/min. A second
coaxial mold is placed around the first mold to form an
annular ring whose outside diameter is 10 cm and whose
height is also 15 cm. Its thickness is negligible. The second
mold is filled with sand whose coefficient of permeability is
K2 = 8.2 × 10-2 cm/min. The test set up is a permeameter of
constant head. Water is placed in the mold and maintained 24. Estimate the ratio of equivalent hydraulic conductivity
at a level of 36 cm above the level of the outlet. (horizontal to vertical ratio) (145.4)
16. What is the total flow of water in cm3/min?
17. What is the equivalent coefficient of permeability Situation 11.
cm/min? The figure shows three layers of soil that is in a 100 mm by
18. What is the total amount of water percolated after 55 100 mm container. Water is supplied to maintain a constant-
min? head difference of 300 mm across the sample. The hydraulic
conductivities of the soils in the direction of flow through
Situation 7. them are as follows:
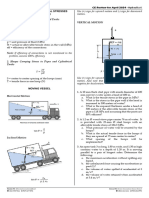
A river and a canal run parallel to each other but at different Sample K (cm/s)
elevations as shown in the figure and has been determined A 1.0 × 10-2
to exist for a 450 m length. The coefficient of permeability of B 3.0 × 10-3
the sand is 3 m per day. Determine the following: C 4.9 × 10-4
19. Hydraulic gradient 25. Estimate the discharge in the soil in cm3/hr
20. Quantity of water which flows into the canal (291.24 cm3/hr)
21. Seepage velocity if the porosity of the sand
is 0.22
Elevation = 90m
Elevation = 80m
River
Canal
Sand layer 1.5m thick
128m
Problems for Practice:
Situation 8.
For the constant head permeability test conducted below:
L = 30 cm
A = Area of Specimen = 177 cm2
Constant head difference, h = 50 cm
Water collected in a period of 5 min = 350 cm3
22. Calculate the hydraulic conductivity in cm/sec
(3.95 x 10-3 cm/sec)
Manila/Cebu/Baguio FB: @ReviewInnovationsOfficial Davao FB: Review Innovations Davao Branch
(02) 8735-9161 0919-227-9194 (082) 221-1121 0930-256-0998
You might also like
- Set 3 CE Board April 2023 - Geotechnical EngineeringDocument2 pagesSet 3 CE Board April 2023 - Geotechnical EngineeringNica SudamaNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2022 - Geotechnical Engineering - Set 3Document2 pagesCE Board Nov 2022 - Geotechnical Engineering - Set 3Dens DensNo ratings yet
- SOIL PERMEABILITY AND FLOW NETS Problem Set2Document2 pagesSOIL PERMEABILITY AND FLOW NETS Problem Set2yexui.31No ratings yet
- SM Lec 11Document14 pagesSM Lec 11haad.malik007No ratings yet
- Review-Module 23 Geo 4Document3 pagesReview-Module 23 Geo 4Ma Ella Mae LogronioNo ratings yet
- Review Module - Geotechnical Engineering (Atterberg'S Limits)Document7 pagesReview Module - Geotechnical Engineering (Atterberg'S Limits)Yang RhiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document30 pagesChapter 7Marcus NatividadesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document30 pagesChapter 7anon_749279665No ratings yet
- Review Module 23 Geotechnical Engineering 4 Part 1Document2 pagesReview Module 23 Geotechnical Engineering 4 Part 1Mark Daren Patrona RamonNo ratings yet
- G Acceleration Due To Gravity V Velocity U Pressure Where H Total HeadDocument23 pagesG Acceleration Due To Gravity V Velocity U Pressure Where H Total HeadMinhaz Khan100% (1)
- ContabilidadDocument14 pagesContabilidadMiqueas SantosNo ratings yet
- CE3410 EXP8 PartA 2023 Manual VFDocument10 pagesCE3410 EXP8 PartA 2023 Manual VFSUBHAM SAGARNo ratings yet
- Permeability & In-Situ StressesDocument23 pagesPermeability & In-Situ StressesDeep ShahNo ratings yet
- Permeability: G Acceleration Due To Gravity V Velocity U Pressure Where H Total HeadDocument22 pagesPermeability: G Acceleration Due To Gravity V Velocity U Pressure Where H Total HeadSabiha sultanaNo ratings yet
- PermeabilityDocument29 pagesPermeabilityF.a.AlfredThomNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - PERMEABILITY PDFDocument39 pagesChapter 7 - PERMEABILITY PDFVivekka Olivia JohnNo ratings yet
- PRC ReviewerDocument16 pagesPRC ReviewermaeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document13 pagesChapter 6Ma. Niña Michelle ElicNo ratings yet
- Pacure Part 3Document29 pagesPacure Part 3Annie TheExplorerNo ratings yet
- CE17 - MODULE3 - Flow of Water Through SoilsDocument12 pagesCE17 - MODULE3 - Flow of Water Through SoilsKATHLEEN CASTRONo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 ONE-DIMENSIONAL FLOW OF WATER THROUGH SOILSDocument24 pagesLesson 8 ONE-DIMENSIONAL FLOW OF WATER THROUGH SOILSNaruto UzumakiNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli's Equation: From Fluid Mechanics, We Know That, According To Bernoulli'sDocument40 pagesBernoulli's Equation: From Fluid Mechanics, We Know That, According To Bernoulli'sJami Ahmed100% (1)
- Geotech Notes SemisDocument13 pagesGeotech Notes SemisMarycorNo ratings yet
- M2 03 Constant and Falling Head TestDocument13 pagesM2 03 Constant and Falling Head TestPzynae FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- محاظرة 5 PDFDocument21 pagesمحاظرة 5 PDFنور عليNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9 Measurement of Hydraulic Conductivity of Granular SoilsDocument12 pagesExperiment 9 Measurement of Hydraulic Conductivity of Granular SoilsAllyssa SuyatNo ratings yet
- Permeability in SoilsDocument47 pagesPermeability in SoilsRusmar LaverosNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4.a. Sample ProblemsDocument6 pagesMODULE 4.a. Sample ProblemsZhebyNo ratings yet
- PERMEABILITYDocument26 pagesPERMEABILITYChristian Felix MapilesNo ratings yet
- CEC 212 PRCDocument53 pagesCEC 212 PRCZaid HabibuNo ratings yet
- Lab 12. Falling Hea Test. GP3. SE 4101Document8 pagesLab 12. Falling Hea Test. GP3. SE 4101AldinNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems (Permeability, Compaction, Compressibility)Document2 pagesPractice Problems (Permeability, Compaction, Compressibility)Hiel FuentesNo ratings yet
- Permeability Test Lab4Document6 pagesPermeability Test Lab4Chikonde ChikondeNo ratings yet
- PermeabilityDocument8 pagesPermeabilityPrashant MaliNo ratings yet
- Ce353 Part 3 Hydrology Centino Annie MaeDocument30 pagesCe353 Part 3 Hydrology Centino Annie MaeAnnie Mae CentinoNo ratings yet
- 44C PDFDocument16 pages44C PDFLokesh Yadav100% (1)
- Soilmech Ps4 TemplateDocument15 pagesSoilmech Ps4 Templateyexui.31No ratings yet
- Exp-6 Permeability by Varying HeadDocument12 pagesExp-6 Permeability by Varying HeadanonymousNo ratings yet
- ECG426 - Week 3 - I - PermeabilityDocument25 pagesECG426 - Week 3 - I - PermeabilityNur SyahiraNo ratings yet
- Fluid 2011Document10 pagesFluid 2011fatin AmiraNo ratings yet
- Constant Head Permeability TestDocument14 pagesConstant Head Permeability Testfuji0% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydralauics Engineering (Qwoa)Document11 pagesFluid Mechanics and Hydralauics Engineering (Qwoa)Kip ClayNo ratings yet
- Topic 5:water in Soil: Geotechnic Mardiha MokhtarDocument87 pagesTopic 5:water in Soil: Geotechnic Mardiha MokhtarEizln HqmNo ratings yet
- Groundwater-Permeability: Civl3501 - Soil MechanicsDocument51 pagesGroundwater-Permeability: Civl3501 - Soil MechanicsBazimya DixonNo ratings yet
- X. FLOW OF WATER THROUGH SOIL IIDocument2 pagesX. FLOW OF WATER THROUGH SOIL IIodilonrempillo.26No ratings yet
- 2007E&EGsPiezoconeDissipation PDFDocument12 pages2007E&EGsPiezoconeDissipation PDFAnonymous 6vZfB9pfzaNo ratings yet
- Module 15 Geotech PermeabilityDocument4 pagesModule 15 Geotech PermeabilityMark NatividadNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering Technology Civil Engineering Department Soil LaboratoryDocument14 pagesFaculty of Engineering Technology Civil Engineering Department Soil LaboratoryAnas Abu-shawishNo ratings yet
- Engineering Properties of Soils and Materials PermeabilityDocument8 pagesEngineering Properties of Soils and Materials PermeabilitySridevi GudaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 - Steady Flow in Open ChannelsDocument26 pagesLecture 11 - Steady Flow in Open ChannelsNawaz441No ratings yet
- Groundwater Hydrology Dr. Phil BedientDocument21 pagesGroundwater Hydrology Dr. Phil BedientSaurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Conductivity and SeepageDocument6 pagesHydraulic Conductivity and SeepageSheenaNo ratings yet
- Yield From An Aquifer Using Dupuit's Theory (Thiem's Formula)Document21 pagesYield From An Aquifer Using Dupuit's Theory (Thiem's Formula)abdulrehman khushik100% (1)
- Permeability - Simple ProblemDocument11 pagesPermeability - Simple ProblemDhananjay ShahNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydralaucis (Qwawh) PDFDocument12 pagesFluid Mechanics and Hydralaucis (Qwawh) PDFMohammed AnwhazNo ratings yet
- Permeability LessonsDocument13 pagesPermeability LessonsHiel FuentesNo ratings yet
- ENB272 - LN - Week 4 - Permeability - 6 Slides Per Page - GrayDocument9 pagesENB272 - LN - Week 4 - Permeability - 6 Slides Per Page - GrayfrasermcNo ratings yet
- Tutorial#5Document2 pagesTutorial#5M FazilNo ratings yet
- Part Ni JanmarDocument31 pagesPart Ni JanmarRam CaniculaNo ratings yet
- Assumption LogDocument1 pageAssumption LogRam CaniculaNo ratings yet
- (01-29) Hydraulics 6Document2 pages(01-29) Hydraulics 6Ram CaniculaNo ratings yet
- (01-25) Hydraulics 3Document2 pages(01-25) Hydraulics 3Ram CaniculaNo ratings yet
- April 2024 Refresher - MSTE 6 - BWDocument2 pagesApril 2024 Refresher - MSTE 6 - BWRam CaniculaNo ratings yet
- Strategi Pengembangan Objek Wisata Hutan Mangrove Lantebung Di Desa Lantebung Kelurahan Bira Kecamatan Tamalanrea Kota MakassarDocument11 pagesStrategi Pengembangan Objek Wisata Hutan Mangrove Lantebung Di Desa Lantebung Kelurahan Bira Kecamatan Tamalanrea Kota MakassarSuhartati KuntariNo ratings yet
- Lecture PF3105 Week04 PaperDocument4 pagesLecture PF3105 Week04 PaperKerie ThamNo ratings yet
- GREAT Workshop ReportDocument45 pagesGREAT Workshop ReportRoy Perez SalazarNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - 5: Plant ProgressDocument4 pagesWeek 1 - 5: Plant ProgressMariacherry MartinNo ratings yet
- Of The Month Is Live. 100+ Subjects. Participate Now!: Sanfoundry Certification ContestDocument4 pagesOf The Month Is Live. 100+ Subjects. Participate Now!: Sanfoundry Certification ContestBaydaa QaidyNo ratings yet
- Animals - ListeningDocument3 pagesAnimals - ListeningAneczka18No ratings yet
- Discursive EssayDocument6 pagesDiscursive Essayovexvenbf100% (2)
- Heatco 2014Document139 pagesHeatco 2014simogeoNo ratings yet
- Global Cities: HumanitiesDocument3 pagesGlobal Cities: Humanitiespratik bapechaNo ratings yet
- Users Perception of Environmental Sanitation Exercise in Selectedmarket in Nigeria CitiesDocument5 pagesUsers Perception of Environmental Sanitation Exercise in Selectedmarket in Nigeria Citiesfagbemi KayodeNo ratings yet
- Animal Diversity 7th Edition Hickman Test BankDocument10 pagesAnimal Diversity 7th Edition Hickman Test BankmaryjohnsonjkcadytnqeNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering: Final Year Project ProposalDocument4 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering: Final Year Project ProposalKingNo ratings yet
- Soal Bahasa Inggris PAS GANJIL 2022-2023Document10 pagesSoal Bahasa Inggris PAS GANJIL 2022-2023Satrio Budi Yudistira77No ratings yet
- 5-Airport Drainage EtcDocument65 pages5-Airport Drainage EtcAbraham yudhaNo ratings yet
- Water Bath Instruction ManualDocument2 pagesWater Bath Instruction ManualLoreto CarrascoNo ratings yet
- Acer MV 10 MSDSDocument5 pagesAcer MV 10 MSDSWahyu BtNo ratings yet
- Dear EarthDocument2 pagesDear Earthapi-524267960No ratings yet
- NOTES OF DEVELOPMENT Class X CBSEDocument2 pagesNOTES OF DEVELOPMENT Class X CBSETanisha RawatNo ratings yet
- Earth's Resources: 6 GradeDocument13 pagesEarth's Resources: 6 GradeJordyn IzenstarkNo ratings yet
- Skillful LS2 Unit Tests Answer KeyDocument20 pagesSkillful LS2 Unit Tests Answer KeyLam Hồ ThanhNo ratings yet
- B. EIA Presentation - For PCO - Updated - 06nov2020 - WebinarDocument96 pagesB. EIA Presentation - For PCO - Updated - 06nov2020 - Webinarrandell vasquezNo ratings yet
- Artículo Final - ENDOPARASITES IN FECES OF Dasyprocta Punctata FROM ARMENIA CITYDocument17 pagesArtículo Final - ENDOPARASITES IN FECES OF Dasyprocta Punctata FROM ARMENIA CITYALEXNo ratings yet
- Year 6 - Autumn Term 1: English HomeworkDocument16 pagesYear 6 - Autumn Term 1: English HomeworkNeil WatermanNo ratings yet
- Protective Equipment Cidex OPA Solution: Clean InstrumentsDocument1 pageProtective Equipment Cidex OPA Solution: Clean Instrumentsfagopag160No ratings yet
- Vulnerability - 2Document44 pagesVulnerability - 2Jaine LuzNo ratings yet
- G8 - T3, Week 3, Day 3Document19 pagesG8 - T3, Week 3, Day 3Mouza Mubarak Sultan Mohammed Al KhailiNo ratings yet
- BiomuriDocument14 pagesBiomuriDanielaNo ratings yet
- Environmental LawDocument6 pagesEnvironmental LawAbhinav KumarNo ratings yet
- Group Members: Andile Sibanda Takunda Chikohwa Byron Mawoyo Lebani Dube Donovan MoyoDocument15 pagesGroup Members: Andile Sibanda Takunda Chikohwa Byron Mawoyo Lebani Dube Donovan MoyoSambiri PisiraiNo ratings yet
- Talaandig EducationDocument19 pagesTalaandig EducationCathy GabroninoNo ratings yet