Professional Documents
Culture Documents
VT Graphs
VT Graphs
Uploaded by
Tarun Kumar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views6 pagesOriginal Title
vt graphs
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views6 pagesVT Graphs
VT Graphs
Uploaded by
Tarun KumarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Edexcel GCE
Core Mathematics M1
Velocity-Time
Graphs
‘Materials required for examination
Mathematical Formulae (Green) Nil
Advice to Candidates
‘You must ensure that your answers to parts of questions are clearly labelled.
‘You must show sufficient working to make your methods clear to the Fxaminer. Answers
without working may gain no credit.
Figure 1
véms’),
i \
i 1
' 1
' 1
' 1
' t
i '
' i
I t
3 7 ts)
Figure 1 shows the speed-time graph of a cyclist moving on a straight road over a 7 s period. The
sections of the graph from ¢= 0 to ¢= 3, and from ¢= 3 to 1= 7, are straight lines. The section
from ¢=3 to £7 is parallel to the taxis.
State what can be deduced about the motion of the eyelist from the fact that
(@) the graph from = 0 to 1=3 is a straight line,
co)
(b) the graph from ¢=3 to ¢= 7 is parallel to the taxis.
@
(©) Find the distance travelled by the cyclist during this 7 s period.
@
ay Constant acceleration
b) Constertr velocity
en under greek
co) olistance = ar
2. A small ball is projected vertically upwards from ground level with speed u m s", The ball takes
4 sto return to ground level.
(@) Draw, in the space below, a velocity-time graph to represent the motion of the ball during the
first 4s,
@
(®) The maximum height of the ball above the ground during the first 4 s is 19.6 m. Find the
value of u,
®
eal
v a oe
4
° Seer aeeel >
é os)
; ropa = distance)
b/ uxt 2176 & (Area ander 9
2
A car moves along a horizontal straight road, passing two points A and B. At A the speed of the
car is 15 ms. When the driver passes A, he sees a warning sign W ahead of him, 120 m away.
He immediately applies the brakes and the car decelerates with uniform deceleration, reaching W
with speed 5 ms". At W, the driver sees that the road is clear. He then immediately accelerates
the car with uniform acceleration for 16 s to reach a speed of Vm s (V> 15). He then maintains
the car at a constant speed of Vm s". Moving at this constant speed, the car passes B after a
further 22 s.
(@) Sketch, in the space below, a speed-time graph to illustrate the motion of the car as it moves
from Ato B.
@)
(6) Find the time taken for the car to move from A to B.
®
‘The distance from A to Bis | km.
(©) Find the value of V.
(5)
\ ©
j2o =
to = 10k
ez42
12% \e+OO = SOsecect*
oo
iu \oou
S sot BAYxLe + OAV =
ia aoe 28S
v
eee mov = BHO
Ve aBms
Se
x ee
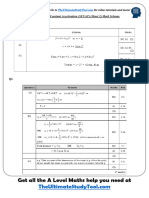
4, A car is moving along a straight horizontal road. At time t = 0, the car passes a point A with
speed 25ms', The car moves with constant speed 25m" until t = 10s. The car then
decelerates uniformly for 8 s. At time ¢ = 18 s, the speed of the car is Vm s"' and this speed is
‘maintained until the car reaches the point B at time = 30 s.
(@ Sketch a speed-time graph to show the motion of the car from A to B.
@
Given that AB = 526 m, find
() the value of V,
®
(c) the deceleration of the car between t= 10s and t= 18s.
‘ ®
ies
os }——_
- = ESS HeCeenEeE
v
eit ‘0 7 i j ci tls)
bi one © BO + lo+1F x@S-v)
Sao = Bev + 14las—~)
Date Soyii we oo (te
{7e = Vev
vetdims' ;
SS [occeteraion = godient ]
- e AY
Me ea! 7 pi a
8 if a
5. A car is moving along a straight horizontal road. The speed of the car as it passes the point A is
25 ms" and the car maintains this speed for 30 s. The car then decelerates uniformly to a speed
of 10 m s*, The speed of 10 m s* is then maintained until the car passes the point B. The time
taken to travel from A to B is 90 s and AB = 1410 m.
(@) Sketch a speed-time graph to show the motion of the car from A to B.
®
(6) Calculate the deceleration of the car as it decelerates from 25 m sto 10 ms
@
as
1 ——+
ae fara pe CH y
30 38 as
I4lO0> Foo + BOtE x 15
SIO € Bose Kis
66> sore
& = 38
b ie hange “AY
decelerahon - Changt "2
cnenge “M&S
eee
a 1S.
g
2187s ms
NzisKs4 6
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Screenshot 2023-12-25 at 6.31.40 PMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2023-12-25 at 6.31.40 PMTarun KumarNo ratings yet
- AdnaceDocument11 pagesAdnaceTarun KumarNo ratings yet
- Ticket Tarun Aggarwal BR 1093285355Document2 pagesTicket Tarun Aggarwal BR 1093285355Tarun KumarNo ratings yet
- Day 2Document4 pagesDay 2Tarun KumarNo ratings yet
- Constant AccelationDocument7 pagesConstant AccelationTarun KumarNo ratings yet
- CS3Document1 pageCS3Tarun KumarNo ratings yet
- Reciprocal Linear HandoutDocument4 pagesReciprocal Linear HandoutTarun KumarNo ratings yet
- Equation of A Line - Practice QuestionsDocument10 pagesEquation of A Line - Practice QuestionsTarun KumarNo ratings yet