Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Accounting in Business
Uploaded by
Allister Rex Camanse0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesOriginal Title
accounting in business
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesAccounting in Business
Uploaded by
Allister Rex CamanseCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
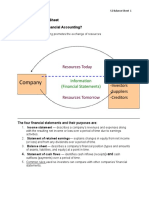
Accounting in Business:
• Accounting is the “language of business.”
• It is an information and measurement system that identifies, records and communicates
relevant, reliable and comparable information about business activities in economic terms.
• Three major accounting activities are identifying, recording, and communicating.
• Users of accounting include external users and internal users. You should be able to provide
examples of both.
• Opportunities in accounting are abundant but can generally be categorized into financial,
managerial, taxation, and other accounting related jobs.
• Ethics in accounting have been in the spotlight lately.
• GAAP – Generally Accepted Accounting Principles are the rules that we will follow throughout
the semester. FASB sets both broad and specific principles. SEC establishes reporting
requirements for publicly held companies. The IASB identifies preferred accounting practices for
international issues.
Accounting Principles:
• The cost principle – Accounting information should be based on actual cost, which is
measure on a cash or equal to cash basis.
• The revenue recognition principle – provides guidance on when a company should
recognize or record revenue.
• Matching principle – A company must record its expenses incurred to generate revenue
in the same period.
• Full disclosure principle – Details must be reported so that user’s decisions can be
informed.
Fundamental Accounting Equation
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
Things of Value Debt Owner’s Claims
Resources owned by a Company Creditors’ Claims on Assets Net Assets
Yield future benefits Payables Residual Equity
- Owed to others Assets - Liabilities
Common:
Cash Accounts Payable Contributed Capital
Accounts Receivable Wages Payable Common Stock
Prepaids Notes Payable Retained Earnings
Property and Equipment Taxes Payable Net Income
- - Dividends
You might also like
- Synthesis ReviewerDocument10 pagesSynthesis ReviewerStela Marie CarandangNo ratings yet
- Company Outsiders: Resources TodayDocument20 pagesCompany Outsiders: Resources TodaySarbani Mishra0% (1)
- ACCT 101 Chapter 1 HandoutDocument3 pagesACCT 101 Chapter 1 HandoutLlana RoxanneNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Accounting Notes Types of Businesses and UsesDocument4 pagesFundamentals of Accounting Notes Types of Businesses and UsesSALENE WHYTENo ratings yet
- AFM CH 2Document58 pagesAFM CH 2Birhanu MengisteNo ratings yet
- Accounting in ActionDocument42 pagesAccounting in ActionMuhammad TausiqueNo ratings yet
- Finance+Webinar 13.12.2022++updatedDocument42 pagesFinance+Webinar 13.12.2022++updatedJasmine ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Session 1 - Introduction To Accounting and Balance SheetDocument32 pagesSession 1 - Introduction To Accounting and Balance Sheethieucaiminh155No ratings yet
- FMA NotesDocument19 pagesFMA NotesLAXIANo ratings yet
- Basics of Accounting: Zafar MehsudDocument28 pagesBasics of Accounting: Zafar MehsudatifNo ratings yet
- An Intro To Bussiness AccountingDocument57 pagesAn Intro To Bussiness AccountingNadia AnuarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Accounting Accounting Concepts: & EquationDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Accounting Accounting Concepts: & Equationjoycen11No ratings yet
- 2.2 Financial StatementsDocument38 pages2.2 Financial StatementsNefarioDMNo ratings yet
- Part Two: Financial Accounting: An IntroductionDocument139 pagesPart Two: Financial Accounting: An IntroductionRobel Habtamu100% (1)
- MAF CH 2 NEWDocument58 pagesMAF CH 2 NEWAsegid H/meskelNo ratings yet
- 1.accounting in BusinessDocument11 pages1.accounting in BusinessNino GodoradzeNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Acocunting and Business Management 1 2Document14 pagesFundamentals of Acocunting and Business Management 1 2kristinekaylegusimat12No ratings yet
- Introducing Accounting in Business: ACG 2021: Chapter 1Document59 pagesIntroducing Accounting in Business: ACG 2021: Chapter 1Kelvin Jay Sebastian SaplaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Accounting in ActionDocument42 pagesChapter 1 - Accounting in ActionFify AmalindaNo ratings yet
- MBAB 5P01 - Chapter 1Document3 pagesMBAB 5P01 - Chapter 1Priya MehtaNo ratings yet
- FABM - SummaryDocument48 pagesFABM - SummaryGabriel OrpiadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 2020 StudentDocument43 pagesChapter 2 2020 StudentHương NguyễnNo ratings yet
- ACT201 Chap001 NBNDocument18 pagesACT201 Chap001 NBNAudity PaulNo ratings yet
- Act201 Ch1 NNHDocument42 pagesAct201 Ch1 NNHrahat ahmedNo ratings yet
- Component of Financial StatementDocument3 pagesComponent of Financial StatementYangEXONo ratings yet
- Session 3&4 IA 2021Document93 pagesSession 3&4 IA 2021Ashley NguyenNo ratings yet
- Class 2 PDFDocument17 pagesClass 2 PDFRajat AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Accounting in ActionDocument42 pagesAccounting in ActiondrivehaqNo ratings yet
- 01-Accounting Principles CHE40Document34 pages01-Accounting Principles CHE40Faye Blair MarkovaNo ratings yet
- Act201 Ch1 NNHDocument42 pagesAct201 Ch1 NNHTiloma M. ZannatNo ratings yet
- Act201 Ch1 NNHDocument42 pagesAct201 Ch1 NNHTiloma M. ZannatNo ratings yet
- Accounting - Instructor-1Document154 pagesAccounting - Instructor-1karimhisham100% (1)
- Trading Basics: AccountingDocument10 pagesTrading Basics: AccountingNonameforeverNo ratings yet
- Hand Out in Basic AccountingDocument32 pagesHand Out in Basic AccountingJemuell RedNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Part TwoDocument175 pagesChapter Two Part TwoWelday GebremichaelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document8 pagesLecture 2zahidabdul.4219No ratings yet
- Accrual vs. Cash AccountingDocument33 pagesAccrual vs. Cash AccountingAbhishek ShetyeNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Global Accounting StandardsDocument16 pagesBenefits of Global Accounting StandardsJones EdombingoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AccountingDocument39 pagesIntroduction To AccountingRazib KhanNo ratings yet
- Supplementary 1 - Financial StatementsDocument21 pagesSupplementary 1 - Financial StatementsQuốc Khánh100% (1)
- ACCOUNTINGDocument6 pagesACCOUNTINGFe VhieNo ratings yet
- Nature of Business and AccountingDocument3 pagesNature of Business and AccountingHailey LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Finance ShortcourseDocument46 pagesFinance Shortcoursemahendra ega higuittaNo ratings yet
- Commercial AccountingDocument16 pagesCommercial AccountingAaditya Pandey AmritNo ratings yet
- Financial Decision Making Tools: Financial Statements: Presented By: Dr. Anthony Ly B. Dagang Anthony - Dagang@lccdo - Edu.phDocument31 pagesFinancial Decision Making Tools: Financial Statements: Presented By: Dr. Anthony Ly B. Dagang Anthony - Dagang@lccdo - Edu.phmila dacarNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in FABM 3rd QuarterlyDocument4 pagesReviewer in FABM 3rd Quarterlydeivejenrych95No ratings yet
- პირველი თავი ფინანსური აღრიცხვაDocument46 pagesპირველი თავი ფინანსური აღრიცხვაninia apkhazavaNo ratings yet
- FABM PrelimDocument5 pagesFABM PrelimIvana CianeNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting and ReportingDocument24 pagesFinancial Accounting and ReportingAman JainNo ratings yet
- Financial Statements, Cash Flows, and TaxesDocument27 pagesFinancial Statements, Cash Flows, and TaxeszhengcunzhangNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AccountingDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Accountingluna dupontNo ratings yet
- Intro, Accounting Conecpts and EquationDocument30 pagesIntro, Accounting Conecpts and EquationPraween BimsaraNo ratings yet
- Topic 2Document48 pagesTopic 2Marie JulienNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Acctg NotesDocument6 pagesChapter 1 - Acctg Notesfennyl婷.No ratings yet
- Accounting Conventions and EquationDocument33 pagesAccounting Conventions and EquationanuragNo ratings yet
- L1-Introduction To AccountingDocument67 pagesL1-Introduction To AccountingSYAMIMI ANUARNo ratings yet
- Principles of AccountingDocument27 pagesPrinciples of AccountingRaahim NajmiNo ratings yet
- The Basic Accounting EquationDocument2 pagesThe Basic Accounting Equationharoun baccarNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 2Document16 pagesTopic 1 2lala lianNo ratings yet
- "The Language of Business: How Accounting Tells Your Story" "A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding, Interpreting, and Leveraging Financial Statements for Personal and Professional Success"From Everand"The Language of Business: How Accounting Tells Your Story" "A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding, Interpreting, and Leveraging Financial Statements for Personal and Professional Success"No ratings yet