0% found this document useful (0 votes)
309 views14 pagesXL3525 Pulse Width Modulator Overview
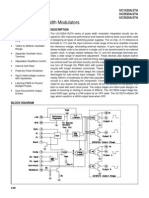
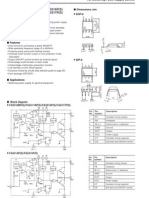
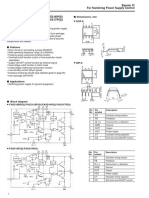
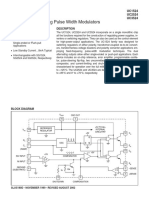
The document describes a pulse width modulator integrated circuit. It provides details on the device's features such as an on-chip voltage reference and soft start circuitry. The document also includes pin connections, a functional block diagram, specifications and recommended operating conditions.
Uploaded by
Jose HernandezCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
309 views14 pagesXL3525 Pulse Width Modulator Overview
The document describes a pulse width modulator integrated circuit. It provides details on the device's features such as an on-chip voltage reference and soft start circuitry. The document also includes pin connections, a functional block diagram, specifications and recommended operating conditions.
Uploaded by
Jose HernandezCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd