Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hardware
Hardware
Uploaded by
Jay Estrella0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views20 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views20 pagesHardware
Hardware
Uploaded by
Jay EstrellaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 20
FINE A. Quito
Fes
PHILIPPINE ORTHOPEDIC CENTER
‘Nursing Training & Research Department
‘Ma, Clara St,, cor. Banawe, Quezon City
ORTHOPEDIC HARDWARE
Principles in the Management of Fracture: (4 R’s)
1, RECOGNITION - Involves history taking skills of nurses to assess the type of fracture and its
‘manifestations specifically the signs and symptoms.
2, REDUCTION/RETENTION ~ Putting back the bone to its proper alignment. It is categorized
into two:
a) Close Reduction ~ manual manipulation of the bone back to its proper alignment
b) Open Reduction — surgical intervention in aligning the bone back to its normal form
3. RETENTION/IMMOBILIZATION ~ Maintaining the alignment of the fractured bone using
immobilization gadgets such as Cast, Traction, External Fixators and Orthopedic Braces.
REHABILITATION ~ Putting and helping the patient achieve the optimum level of functioning
after having the Retention Phase,
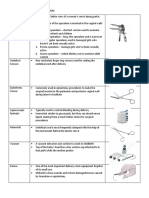
Common Orthopedic Hardware and Internal Fixators & Its Uses:
caster poner tee therapeutic
| effect for Osteomyel
Provides prophylactic
me effect in plating, IMN,
s a and other types of
3 Internal and External
Fixators)
BONE DRILL & DRILL BIT
‘For boring hole through the one!
8. RE
“To hold rod in place during
instrumentation specially
for Scoliosis
OSTEOTOMES (CHISEL)
*Used for obtaining bone
chips for spinal fusion
“Used for scraping
dead/necrotic bone tissues
INTRO 2019- HARDWARE
CERCLAGE WIRE
* For fracture of the
patella, used in Tension
Band Wiring
LUQUE ROD &
HARRINGTON ROD
* Instrumentation for Scoliosis
INTRMEDULLARY
NAIL EXTRACTOR
* For removal of IM
Nailing
HEMOVAC/BAROVAC DRAIN
** For collection of drainage under
negative pressure
GIGLI SAW
* To cut bones during amputation
CRUTCHFIELD,
TONG
* Applied at
Parietal area for
cervical traction
‘SKIN STAPLER application
*To hold skin
edges together
post operatively
INTRAMEDULLARY
NAIL (1M) with
WIRE CUTTER LOCKING SCREW
: 7 * For fracture of
To cut wires
the middle 3“ or
Distal Femur
INTRO 2019— HARDWARE
INTRAMEDULLARY
__RONGEUR IL nl
- * For cutting * For fracture of
bone chips the tibia
INTRAMEDULLARY
NAIL (1M) with
LOCKING SCRI
* For fracture of
Distal Tibia
PLATE
* For fracture of Proximal
BONE PLATES
* For long bone Tibia
fractures and not
comminuted in
appearance
:INMANN PIN
* Used for long
bones
COMPRESSION PLATE &
ip ‘SCREWS
* For Compression Hip iit
Screw Fixations ; ¢ +
. ROGER ANDERSON
= larochrtrc 05, HOGER ANDERSON
os trochanteric Fracture of (RAEF)
| the Femur, * For comminuted
= fracture of the long,
bone
NNTRD 2019- HARDWARE
BIPOLAR HIP
PROSTHESIS with
BIPOLAR HIP. ACETABULAR CAP
PROSTHESIS * For total hip
* For partial hip replacement
replacement arthroplasty (THRA)
arthroplasty (PHRA)
For total knee s
replacement arthroplasty SPACER ANTIBIOTIC
__ * For degenerative knee * Replacement of
Joint diseases, fracture of infected hip prosthesis
the distal femur and
proximal part of the tibia,
and rheumatoid arthritis
of the knees
HYBRID EXTERNAL
FIXATOR
* For peri-articular
fracture of the ankle or
knee joint, or near the
joints
* For comminuted
fracture, non-union,
mal-union and for
bone growth &
lengthening
INTRO 2019 - HARDWARE
Common Examples of External Fixators attached to actual patients:
*ANNING EXTERNAL FIXATOR
* For fracture of the knee joint, distal part of
femur extending to the proximal part of the
tibia/fibula
DELTA FRAME
* For fracture of the peri-articular area of wel
the joint, proximal portion of the tibia
DELTA FRAME
* Applied with short leg
posterior mold and
rested/placed on a Bohler
Braun Splint J
INVERTED DELTA DELTA FRAME DEN
FRAME HAM (ANKLE BRIDGE)
* applied when there “The frame is
is severe soft tissue extended to the ankle
involvement that can
interfere the insertion
of pins
to give way to soft.
tissue granulation and
healing
INTRO 2018 HARDWARE
QUADRILATERAL
EXTERNAL FIXATOR
* For fracture of the
middle 3" of tibia
fibula, comminuted
ROGER ANDERSON EXTERNAL FIXATOR
[RAEF)
* For comminuted fracture of the long bone
* Can be used both on upper and lower
extremity)
(COMMON SURGERY ABBREVIATIONS:
1. ACL—Anterior Cruciate Ligament
2. ADSF— Anterior Decompression Spinal Fusion
3. AEA—Above Elbow Amputation
4. AKA-Above Knee Amputation
5. BKA—Below Knee Amputation
6. BG—Bone Grafting
7. CHSF— Compression Hip Screw Fixation
8 CSTR—Complete Soft Tissue Release
9. CW-Cerclage Wiring
10. DCS — Dynamic Compression Screw
11. FTSG — Full Thickness Skin Grafting
12. HRI Harrington Rod Instrumentation
13. IMN~ Intra Medullary Nailing
14. ORSF— Open Reduction Screw Fixation
15. ORIF - Open Reduction Internal Fixation
16, PLBG ~ Postero-Lateral Bone Grafting
17. PMR~ Posterior Medial Release
18. PHRA/PHRP — Partial Hip Replacement Arthroplasty/Prosthesis
19. PSF = Posterior Spinal Fusion
20. PSTR- Postero Soft Tissue Release
21. PSR~ Progressive Surgical Release
22, RAEF ~ Roger Anderson External Fixation
23. ROI— Removal of Implant
24, RFS — Rush Frozen Section
25. CHSF — Compression Hip Screw Fixation
26. STSG — Split Thickness Skin Grafting
rao 2019- HARDWARE
27, $51—Segmental Spinal Instrumentation
28, TBW- Tension Band Wiring
29. TAR-Tendon Achilles Repair
30, THRP — Total Hip Replacement Prosthesis
31, VDO- Varus Derotation Osteotomy
COMMON ANESTHESIA ABBREVIATIONS:
PN OVEN
ABPB — Axillary Brachial Plexus Block
SAB — Subarachnoid Block
GETA~General Endotracheal Anesthesia
GOTA— General Orotracheal Anesthesia
GA-General Anesthesia
SA~Spinal Anesthesia
CLEA — Continuous Lumbar Epidural Block
‘SCBPB — Supraclavicular Brachial Plexus Block
: Republi of the Philippines
A ME Department of Health
PERLIPPINE ORTHOPEDIC NTL Elvira A.Quiton RH, MAN
Maria Clara cor. Banawe St conte No 01747
Quezon City
oar a ears Order-Uiseuss the importance of Doctor's order
2. Inform the patient about the need & purpose of the procedure.
3. Preparation: .
a, Identify the different parts of the orthopedic bed.
b. Assemble the needed equipments: Thomas splint & Pearson Attachment
Medial side (lower portion) lateral side
Medial upright upper portion
~ Know the affected extremity
+* Where to stand on the demo side-leok for the last pulley and siand on the side.
4, Mount the Thomas and Pearson on the rest splint:
5 Principles in the application of the slings to be emphasized
a. Not tostight Not to loose
b. One (1) inch distance in between the slings to promote aeration or
ventilatton
Popliteal and Heel portion should be free from any sling.
Smooth and right side should come in contact with the patient’s ski n>)
©. Two (2) longer and wider slings for the thigh portion and the dseee () for,
he leg area
How (0 apply sling? — start from the redial side to the lateral side , socure
both ends together, fan fold nicely on the lateral aspect arid secure with the pin
or clip. Observe the principle of not too tight not too loose and avoid hitting
the patient’s extremity with the pin.
The tic rope should be attach on the medial aspect to the lateral aspect,
5. Insertion of the apparatus under the affected extremity.
Three (3) manpower needed:
a. to insert the whale apparatus under the affected extremity.
b. Manual Traction to be seleased after the completion of the traction weight
on the 3" pully,
c. To lift the affected extremity —
- simultaneously at the count of three (3)
* Instruction to the patient
Hold on the trapeze, flex the unaffected Jeg athe count of three (3), the three.
' (3) manpower to do their work simultaneously.
6, «Application of Traction weight
* Rope to be attached to the Steinmman’s pin holder to run along the 3 pulley
and attach the prescribed weight,
Check the principles of sling application, and make the necessary adjustments,
also check the alignment.
7. Apply suspension Traction
* One (1) end of the thigh rope should be attached ‘o the latera
Bids al aspect of the
ischial ring with a slip knot
eo * Attach suspension rope on the mid’ part of the thigh rope, to the first pulley
insert suspension weight, hang it on the first pulley pass it on the second (2)
fi pulley under the rest splint. Club hitch knot on the Thomas splint And another
club hitch knot on the Pearson, closc it with a knot to socure it,
* Be sure to maintain the traction rope inside, and the suspension wight should
be outside
8 Remove the rest splint
9. Apply faot support
10. Check the principles of traction, Emphasizing the five (5) principles of traction
and discuss the nursing care.
Swing the patient to and fro , side (o side to heck the. efficiency of t:dction.
a. patient should be on a dorsal recumbent position.
ge +b. Line. of pull should be in line with the deformity. Positioning of a diagonal
bar and Positioning ofa pulley. First pulley should be in fine with the
thigh, 2" pulley should be in line with the knee or screw, 3" pulley should
be in line with the 1 and 2™ pulley.
c. Traction should always be continuous, emphasize the importance of
manual traction.
d. Avoid friction — rope should be running along he grove of he pulley, knots
should be away from he pulley. Weight should be hanging fre¢ly. Observe
for wear and tear of ropes and bags.
¢. Provide counter traction — Patient's body weight will serve as counter
traction.
REMOVAL OF TRACTION
. Apply test splint,
. .Hang suspension weight qn the first pulley.
Complete removal of suspension weight — remove the knot on the Pearson and
Thomas.
4. Manual traction on the steinmman’s pin holder, remove the traction weight on the
third pulley, secure the traction rope on ‘he rest splint another on the Thomas and
Pearson attachment
NURSING CARE OF PATIENTS WITH TRACTION
1. Assessment — assess the patient as to level of understanding, consciousness.
2. Provision of general comfort:
a. Skin care — head to toe, focus on the sponging of the allected cxtremity.
HOW TO SPONGE?
- 2 basins with face towels and soap.
- Remove sling one by one and sponge.
- Remove the foot support and*sponge.
b. Changing of Linen
c. Provide bedpan as needed. Serve bedpan on the unaffected side, provide
pillow at the back and provide privacy :
d, Perineal Care. 4
3. Potential Complications:
a. Upper Respiratory — PNEUMONIA - bronchial taping and deep
breathing. |
b. Bedsore - good perineal care, proper skin care turning Jeft-buttocks once
ina while.
c. Urinary and Kidney problem — good perineal care, increase fluid inteke.
d. Bowel complication — fear of apparatus, no privacy, lack of fluids,
perineal care.
¢. Pin site infection — observe for s/sx of infection, losing pin tract, pus
coming out, foul-smelling, fever.
Elvira A. Quiton Ris, MAN
Lic, No. 0137247 *
- aseptic technique and proper referral to DIC.
Deformity ~ contracted knee, atrophy, foot drop, joint contractures.
4. Provision of exercises
a ROM exercises with the use of trapeze
b. Deep breathing exercises
Static quadriceps exercises, alternate contraction and relaxation of
quadriceps muscles.
d. Toes pedal exercises
Nutritional status — depending on the status of patient
Psychological aspect ~ fear of unknown, fear of death, fear of the Se fear
of losing job, financial fear. «
7. Provision of supportive therapy — offer book to read, something to listen radio or
tv, discover interest.
8. Spiritual aspect — know his religion, encourage relatives to give spiritual,
communication, visiting, chaplain,
9. Diversional Activities — divert attention.
&.
ey
lic. No, 0937217...
MENTS ie Be ‘ANCE "SKELETAL TR*OTION |
a
wiNDY MATERUL
yextiiorepic WURSIN
a".
ast SruNnT
CORD ‘eae
ile
OVERHRAD
TIKAPEZE
WEIGIT TEACTIO nx
SUSFENTION Weil. AAG
STEIN MANS
PIN NOLDER
BALAN anes : KIRSCHNERS WIRE
— FRACTURE BOARD hover
4 VERTICAL, BARS
Z HORIZONTAL BARS ‘ Foot BOARD
1 PIAGONAL BAR :
2 STRAIGHT o CROSS BAR
1 CURNE BAR
HENRY L. MENDOZA, LMT, EMT, RN, MA
CLINICAL INSTRUCTOR : oy
ha Be RGA SEDI UD. Ea A CGon Rs, WAY
Ue No 017217
tf
1. Definition of Traction
Traction is the act of pulling and drawing which is
A associated with counter-traction.
Patients’ body weight acts as a counter-traction.
II. Indications. or purposes of traction;
1. For immobilization -
2. To prevent and correct deformity -
3. For support 2
4, To veduce muscle pain and spasm
5. To reduce fracture
6. To maintain good alignment
IIL. Three general classifications of tract
nianner of application, ;
1, Manual traction - traction applied to the body by
the hands of the operator,
fo Skeletal traction - {traction applied to the bones with
tion according to the
--—.. the use of piris, wires and tones. .
5. Skin TRatrion
1 he i Ue He jhe use C
: Hess ve DH ESSE
: ATERIALS
: re - [BRUANCE SKELETAL FRACTION]
eRe Len
ny
rot
> VINKE-Skull CAL eR 7 CRU THY I OVERHEAD
7 FOR CERVICAL Sine 70R Ceeulihe ONE Te SERA ATION | |
7 Skldat troche 1 Slut (pati ix OF Humerus — < |
foam fraction > non-adhesive
1 mocigiea buck tension - hip and Femar
Elvira A. Quilon Rit, MA‘
ee oe Lic, No. 0137217
{| wlide > qrendeltnbarg
rauees > hip and
nes RM pen
¢ |Hammock suspension] va
jock suspension Headhalter. cervical ;
- fracture of the pelvis. ne ae ASA i
Malgaigne igne fracture. spine, oo ie lor amgeont
WEN RE adlusrr contin us sn >
(5 bo rane pebcee]
SURGICAL NEC
~ affections of lumbar spine
OF HUMERU S Fon Lambo sa i in
nakave Ken “Gare ve
I SSS
300T OT CAsT\ yas
eee eees pee pete */
i wal ea
~I
— al Sse =e
contracture of hip and knee,
WoT
Ty Tr -b v
v.-0f
by Elvira A. Quion Rls, MAN
er BRAC BS Ue Mo 0137217
weakened muscles;
P
: i
¢ BRACES - are mechanical support for
Joints and bones in rehabilitation as supporting body
‘weight; to control involuntary movements, to prevent
5, and to correct deformities.
osns:
‘a. immobilization
b control involuntary movement
support i! ; ‘
permit patients to walk with and without fatigue
prevent and correct deformity
iplittain body alignment
AL iN
ail gc
‘ShapLBanfo-sptinn\ OPPENHEIMER
per’pheral nerve injury SPLINT
|Shantz Colfar
~ affection of the cervical spine
- affection of the cctvico-thoraco
lumbar spine
ong leg Brace:
Ui ilateral long leg Brac:
~ indicated for post-polio
7 ole of the lumbar spine Dennis broune Splint
“lume sacra) indi ibfo
~ Lowi Boek, pal - indicated for clubfoot.
Fox Stou108i Sa
Ny HENRY L. MENDOZ
. A, LMT,
cuiNcaL nisrRuctOR AN
(‘Milwaukee Bracel- for scoliosis
Cc Te ?
iy
fadial
per helmer -
Elvira A. Quivi ii, tals
c | Lic. No, 0137217
FOUR POSTER BRALE
FOR CERVICAL SPINE
SOML-Steano epper dhercce ee
ie (4 BRA UG]
OCR EATO. (HAUDIGULAR PAUADELI BRA
HENRY L. MENDOZA, LNT, EMT, RN, MAN
CLINICAL. INSTRUCTOR
ATLANTA BRA CE
Uk Pla FOR LEGG CALVE
PERTHESE DISEASE
Tyamamord} FoR SCoLJosis
TE~bebw
ROGER ANDERSON EXTERNA TIYATOR
Fon Comminurel Fy
for the lone Bones TOWERS EXTERNAL FIXATOR
TOR MANDIBIE
sw dire 7 Wgft awa
anit
>
P CH STS Elvira A Quion RI, MAN
- Lic. Mo. 0137217
ee me a :
CAST: form of support obtained as a gypsum rendered
snhydrous by calcination, when mixed with water it
anhyd: :
swells, sets and forms rapidly a hard cement.
Purposes:
1, for immobilization ;
2. prevent and correct deformity
3. for support « .
4, for clevation
. 5. obtaining a mold of a limb to serve as a model for
sd, making artificial limb.
ThA 4 SOATT 9
TANGLKG ase
oitD
ranging cast
fracture of the shaft of humerus
[Body cast\, lower lunibar spine.
~ affection of the cervical spine
re
ee - wrist and fingers with infec-
ae le : tion, gpea wounds and gwelline
; ee Gox
7 ISACC } affections of the wrist and fingers
6
— i : ee
— et Arreetiod 2 panic sa
for scoliosis
A LACC } affections of radius ulna and wist it
: ]
FY agg
anne ort
Cenrrerk Sfmt
ng arm posterior mold
B28 ~ fox the affection of radius and
meu 3 ulna with infection,
oper wounds and swelling
Ate Oe
. °
mh i Proms -unaa € Caurus
~ Foe ni Arénd 1. os
sens ‘
Fuenster or munster cast! ;
= Fanerva cast]
+ fracture of radi ;
radius ulna with
- upper dprsal and cervical spine.
callus formation,
—
Evra A. Quion Rt, AN
Lic, No. 0137217
hip spica - affection of hips and femur
a, We thay + Nfowe
BVA + gubal nwo open
c. double ~ prth hy o£ domme
4
(is LATERAL
Ye, ost Fa arrecrinse hy en CA LUS Feeasarird
sella cl
Quadrilateral cast, og
ischial weight bearing cast fracture
ail 7 OA LURE FoRMarD Nn
Pe een
? pantaon cast/- pelvis fracture
q~ eS
Boor LAST
fas ing cast]
> affection of ankles
c
COUNs FORMATION
rotator splint DigtAL Bad Fumun.
P-8ad TibIAG EibuLA
~ for patient who undergone hip operation
to maintain the internal rotation jf
0
Elvira A Quiton Rli, MAN
Lic, No. 0137217
SLCG- ankle and toes
ENRY L. iENDOZA, LMT, EMT, RN, MAN
CLINICAL INSTRUCTOR
\SLPM| affections of the ankle
and toes with infections,
worn 1B
oplehcn 4 Fam Fimak
ous be 20 JIRCULAR CAST
LLP affections of tibie-fibula
With infections,
wounds and swelling care
wounds and swelling. oe
~ upper portion of the mee and shoulder
joint.
patellar tendon Dearing cast
~ allections of tiblay bul,
with callus formation (
h sugar tong}
eee
- affection of the upper portion of the hutnerus
Saf eas>
ie " re
and shoulder joint with infection, open and swelling, Inder casi affection of patella
s ylinder mold } affection of patella with sweeling
ns sy
z emp Reoure
‘ ig | pacar ee
EBRTE aA or abduction splint ~ D/3rd of tibia fibule w/ callus
~ heck of the humerus formation
aoe .
If
Jaen CONAN GoplamoaV ere = por spine done drill ~ more note
© anttenal pixalor urges rill bit. punneet din bore un
Samp > if alttady’ ampututel — tone peste
ha Clap pk wre ~ For the ote a Mine Pam gem -and HDI
M1 shin ctapler hole in Bane cement Dad fan naliast
Ore T-plale + '
Povgcur - removal o Eira Aiton, i plate + proxima
rerohic ee Orthopade Hardware tile Vébms > Plat * act!
7 | 1. RAEF (Roger Ande
Fixator) anyeleeram
2. Delta Frame External Fixator w, My _| Forn fx of proximal/ distal tibi dye incerted
- ternal Fixator.” longec Yeinen_| Por 6c of femur extended to ti pine cana
Extemal Fixator For pelvic affection
a : _._____| Ex: hip dislocati 2
7) 5. Hybrid Lxtermal Pixator w/ ing For periarticular-fx of the ankle or knee «
joint :
> | CUSF (Compression Hip Screw For intertrochanteric fx of femur - common! on sider people
Fixation) : ——-_.
¢ | 7. Buttress Plate/T-plate ___| Proximal 3” of tibia 7
-| 8. XPinning/ ee _| Bor supracondylar fx ofthe humeri
~ | 9. HIRT (Harrington Rod Instrumentation) _ | For scoliosis 7
7 \10. Luque Rod —__| For scoliosis = tetera cvvatwe op spine [irale)
_ | HL. THRA (Total Hip Replacement
Replacement of femoral ead, necks neck and | OARTICUATI
acetabulum Sew fin the join
For replacement of femoral ret und neck
Arthroplasty) =
12. PHRA (Partial Hip Replacement
Arthroplasty) oe
~ (13 IMN (Intra Medullary Nailing)
~ (41MIN Extractor, i ~ | Used for removal of IMN
— | 15. Spacer Amibiotic Replacement for infected hip prosthesis
16. Hemovac. For collection of drainage under negative |
a __| pressure
| Por amputation - (gical veneval oF a per
For osteomyelitis (Therapeutic Sifect)
For plating, IMN, and all types of internal |
a = and extemat fixator (Prophylactic effect)
19. Tower External Pixator/ Interdenatal | For fx of the mandible
“| Wiring fae =o
20. TBW (Tension Bond Wiring) with the | For fk of the patella
_use of eerclage wire
[ 21. Total Kuce Arthroplasty/ Prosthesis | For fi
< component
thritis bone
spine affection —
Fx of middle 3” of femur _— lacking “secew
.
a mur and hips for Woshners wire
- [Por fx of carpals, metacarpils Hor chilaien
25. Osteotome (Chisel) ~ ber grorting | Used for obtaining bone chips for spinal
~ | egucer zation - - Gequesttomy - fasion quptat er dude,
__cequetiiui\~ déad pone _ | Used for scraping (dead arneciptic bone) | uy gjpow aepe
| 26, llizaroy External Fixator - pont gop Corcamiminied er one
m4 fon union, Malunion, jen
eu = 17.20 - £40 -ercig
{____Terms_ ‘
L.ADSF (Anterior Decompression Spinal £25 -mi
usion __ as
- cist formation : | Frogessive desirucion of he anteior TAB surgery
and kyphosis
2 Sequestrum
4, Sequestrectomy
5. Debridement =
6. Alas
LA
wiving - vertical (connect upp”
inter dental wiring - ver fico! ard jouw ice)
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- NDT Lec Group ReportingDocument16 pagesNDT Lec Group ReportingJay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Nutri Lab Group Report 2Document18 pagesNutri Lab Group Report 2Jay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Nutri Lab Group ReportDocument14 pagesNutri Lab Group ReportJay Estrella100% (2)
- Poc Final List Todo Na ToDocument5 pagesPoc Final List Todo Na ToJay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- NDT Lab PrelimDocument11 pagesNDT Lab PrelimJay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- MCN Lec Antepartal To Ob ClassificationDocument11 pagesMCN Lec Antepartal To Ob ClassificationJay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- MCN Rle Instruments and Setting Up of DR TableDocument4 pagesMCN Rle Instruments and Setting Up of DR TableJay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Pharma-Drug Actions of The Body-PRELIMSDocument5 pagesPharma-Drug Actions of The Body-PRELIMSJay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Prelim Care of Mother Child Adolescent Lec TransesDocument9 pagesPrelim Care of Mother Child Adolescent Lec TransesJay Estrella50% (2)
- Pharmacology PrelimDocument11 pagesPharmacology PrelimJay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Leopold's ManeuoverDocument3 pagesLeopold's ManeuoverJay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Perineal Care MCN RleDocument3 pagesPerineal Care MCN RleJay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Prelim Ncm109aDocument19 pagesPrelim Ncm109aJay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- 6 BASIC NUTRIENTS NDT Lec Sep15Document7 pages6 BASIC NUTRIENTS NDT Lec Sep15Jay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Cmca Rle L1 DocumentationDocument23 pagesCmca Rle L1 DocumentationJay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- PRELIM-BASIC FOREIGN LANGUAGE Slides 31-61Document5 pagesPRELIM-BASIC FOREIGN LANGUAGE Slides 31-61Jay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Bed Bath and ShampooingDocument1 pageBed Bath and ShampooingJay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- PRELIM-NCM109 B-Oxygen AdministrationDocument10 pagesPRELIM-NCM109 B-Oxygen AdministrationJay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Cmca Rle L5 PrelimsDocument8 pagesCmca Rle L5 PrelimsJay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- PRELIM-NCM109 B-Specimen CollectionDocument6 pagesPRELIM-NCM109 B-Specimen CollectionJay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Prelim-Ncm109 B-NSD SetDocument1 pagePrelim-Ncm109 B-NSD SetJay EstrellaNo ratings yet