Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Receivable Financing - Notes
Uploaded by
TEOPE, EMERLIZA DE CASTROCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Receivable Financing - Notes
Uploaded by
TEOPE, EMERLIZA DE CASTROCopyright:
Available Formats
Receivable Financing
Receivable Financing - financial flexibility or capability of an entity to raise money out of its receivables
Common Forms of Receivable Financing
1. Pledge of Accounts Receivable
2. Assignment of Accounts Receivable
3. Factoring of Accounts Receivable
4. Discounting of Notes Receivable
Pledge of Accounts Receivable
- no journal entry is necessary with respect to the pledged accounts receivable
- it is sufficient the disclosure is made in the note to financial statement “The Note Payable to bank matures on December
31, 2020 and is secured by Accounts Receivable with face value of 1,000,000.”
Assignment of Accounts Receivable
- more formal type of pledging of accounts receivable
- specific accounts are assigned (compare to pledging in which all accounts are pledged as collateral)
Features of Assignment of Accounts Receivable
1. Assignment may be done
a. Non-notification Basis - usually the case, customers are not informed that their accounts have been assigned
b. Notification Basis - customers are notified to make their payment directly to the assignee
2. The bank or a finance entity evaluates the entity’s accounts receivable lends only a percentage of the face of the
accounts assigned for factors such as sales discount, sales returns and allowances and uncollectible accounts; Percentage
may be 70%, 80% or 90% depending on the quality of the accounts
3. The assignee usually charges a fee for the assignment - Service Charge or Finance Charge
Presentation of the Assigned Accounts
Accounts Receivable has two classifications:
a. Accounts Receivable - Unassigned
b. Accounts Receivable - Assigned
For the disclosure in the notes:
Accounts Receivable - Assigned xx
Less: Note Payable - Bank (xx)
Equity in assigned accounts xx
Factoring of Accounts Receivable
- sale of accounts receivable on a without recourse, notification basis
- the entity sells accounts receivable to a bank or finance entity called Factor
- the entity transfers ownership of the accounts receivable to the Factor compare to assignment where the entity still
retains ownership of the accounts receivable
Types of Factoring Accounts Receivable
1. Casual
Journal Entry
Cash xx
Allowance for doubtful accounts xx
Loss on factoring xx
Accounts receivable xx
2. Factoring as a continuing agreement
Journal Entry
Cash xx
Commission expense xx Factoring fee for credit approval
Receivable from factor xx Factor’s Holdback - Usually to cover sales return and allowances
Accounts receivable xx
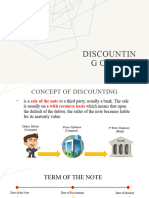
Discounting of Notes Receivable (Note is Negotiable)
Parties involved in Discounting Notes Receivable
1. Maker - the one liable to pay the Payee (Notes Payable is the account in his Balance Sheet)
2. Payee - the one entitled to receive the payment from Maker (Notes Receivable is the account in his Balance Sheet)
3. Endorser - the Payee who endorses the Notes Receivable to bank or finance company
4. Endorsee - the bank or finance company
Types of Endorsement
1. With Recourse - the endorser shall pay the endorsee if the maker dishonors the note (refuses to pay the endorsee)
- there is a contingent liability or secondary liability for the endorser
2. Without Recourse - endorser avoids future liability if the maker refuses to the endorsee on the maturity date
In the absence of any evidence to the contrary, endorsement is assumed to be with recourse.
Computations
Maturity Value xx (Principal + Interest)
Less: Discount (xx) (Maturity Value x Discount Rate x Discount Period)
Net Proceeds xx
Interest = Principal x Interest Rate x Term of the Note
Discount Period = Term of the Note – Expired Period
- also the unexpired period
Compare Net Proceeds vs Carrying Amount of Note (Principal + Accrued Interest)
- If Carrying Amount of Note is higher, there is loss on discounting (usually the case)
- If Net Proceeds is higher, there is gain on discounting
Journal Entry if Discounting is Without Recourse (with loss on discounting)
Cash xx
Loss on note receivable discounting xx
Notes receivable xx
Interest income xx
Journal Entry if Discounting is With Recourse
1. Conditional Sale (with loss on discounting)
Cash xx
Loss on note receivable discounting xx
Notes receivable discounted xx
Interest income xx
The account Note Receivable Discounted is deducted from the total notes receivable when preparing the statement of
financial position with disclosure of the contingent liability.
When the maker paid the endorsee on maturity date (to extinguish the contingent liability)
Note receivable discounted xx
Note receivable xx
When the maker did not pay (dishonors the note) the endorsee on maturity date
Accounts receivable xx To pay the endorsee (bank or finance company)
Cash xx
Note receivable discounted xx To cancel the contingent liability
Note receivable xx
2. Secured Borrowing (no gain or loss on discounting)
Cash xx
Interest expense xx
Liability for note receivable discounted xx
Interest income xx
When the maker paid the endorsee on maturity date (to extinguish the contingent liability)
Liability for note receivable discounted xx
Note receivable xx
When the maker did not pay (dishonors the note) the endorsee on maturity date
Accounts receivable xx To pay the endorsee (bank or finance company)
Cash xx
Liability for note receivable discounted xx To cancel the contingent liability
Note receivable xx
You might also like
- Loan Receivable and Receivable Financing PDFDocument3 pagesLoan Receivable and Receivable Financing PDFgenesis serominesNo ratings yet
- C9 Receivable Financing Discounting of Notes ReceivableDocument24 pagesC9 Receivable Financing Discounting of Notes ReceivableAngelie LaxaNo ratings yet
- Receivable FinancingDocument15 pagesReceivable FinancingArt EezyNo ratings yet
- Receivable Financing CH14 by LailaneDocument30 pagesReceivable Financing CH14 by LailaneEunice BernalNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Bonds Payable and Other ConceptsDocument6 pagesTopic 3 - Bonds Payable and Other ConceptsDustinEarth Buyo MontebonNo ratings yet
- Are Present Obligation of An Entity: As A Result of Past EventsDocument14 pagesAre Present Obligation of An Entity: As A Result of Past EventsMARY ACOSTANo ratings yet
- Receivable FinancingDocument34 pagesReceivable FinancingmaryzeenNo ratings yet
- Receivable Financing: 3. Factoring of Accounts Receivable 4. Discounting of Notes ReceivableDocument2 pagesReceivable Financing: 3. Factoring of Accounts Receivable 4. Discounting of Notes ReceivableJonathan NavalloNo ratings yet
- Receivable Financing: Pledge, Assignment, and FactoringDocument30 pagesReceivable Financing: Pledge, Assignment, and FactoringJoy UyNo ratings yet
- Discounting of NRDocument9 pagesDiscounting of NRArt EezyNo ratings yet
- PDAFDocument2 pagesPDAFMaeNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Liabilities: Characteristics of An Accounting Liability AreDocument35 pagesAccounting For Liabilities: Characteristics of An Accounting Liability Arejeanette lampitocNo ratings yet
- ACC 102 Receivable FinancingDocument5 pagesACC 102 Receivable Financingwerter werterNo ratings yet
- Current Liabilities: School of Business and AccountancyDocument4 pagesCurrent Liabilities: School of Business and AccountancyRochelle FactoresNo ratings yet
- Receivable Financing Pledge Assignment ADocument34 pagesReceivable Financing Pledge Assignment AJoy UyNo ratings yet
- 11 - Current Liabilities, Provisions and ContingenciesDocument5 pages11 - Current Liabilities, Provisions and ContingenciesSilent KillerNo ratings yet
- Factoring Accounts ReceivableDocument4 pagesFactoring Accounts ReceivableJohn MaynardNo ratings yet
- Notes PayableDocument8 pagesNotes Payablechamie143No ratings yet
- Accounting For BondsDocument11 pagesAccounting For BondsChrisus Joseph SarchezNo ratings yet
- Current LiabilitiesDocument3 pagesCurrent LiabilitiesKent Raysil PamaongNo ratings yet
- 15 Acctg Ed 1 - Receivable Financing 2Document10 pages15 Acctg Ed 1 - Receivable Financing 2Nath BongalonNo ratings yet
- 06 Receivable FinancingDocument10 pages06 Receivable Financingsharielles /No ratings yet
- Far 2Document20 pagesFar 2millescaasiNo ratings yet
- FAR - 207 Receivable FinancingDocument12 pagesFAR - 207 Receivable FinancingJai BacalsoNo ratings yet
- Total Cash Receipt From Issuance of BondsDocument11 pagesTotal Cash Receipt From Issuance of Bondskrisha milloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Bonds PayableDocument9 pagesChapter 7 Bonds PayableCarlos arnaldo lavadoNo ratings yet
- C8 Recievable Financing Pledge Assignment FactoringDocument32 pagesC8 Recievable Financing Pledge Assignment FactoringAngelie LaxaNo ratings yet
- Receivable Financing: Quick Review!Document9 pagesReceivable Financing: Quick Review!Barbie BleuNo ratings yet
- 3 ReceivablesDocument4 pages3 ReceivablesCharisse AbordoNo ratings yet
- 1 Intro To LiabilitiesDocument13 pages1 Intro To LiabilitiesPioloNo ratings yet
- Accounts ReceivableDocument5 pagesAccounts ReceivableEj BalbzNo ratings yet
- Debt Restructure - 10Document2 pagesDebt Restructure - 10Divine CarreraNo ratings yet
- Receivable Financing: Pledge of Accounts ReceivableDocument7 pagesReceivable Financing: Pledge of Accounts Receivablelouise carinoNo ratings yet
- Updates On Far QuestionsDocument3 pagesUpdates On Far QuestionsJurie BalandacaNo ratings yet
- Receivable Financing Lecture For DiscounDocument20 pagesReceivable Financing Lecture For DiscounJoy UyNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship and Financial Management Group 8Document4 pagesEntrepreneurship and Financial Management Group 8Aaron MushunjeNo ratings yet
- Module 2f DiscountingDocument16 pagesModule 2f DiscountingChen HaoNo ratings yet
- Accounts ReceivableDocument3 pagesAccounts Receivablelea atienza100% (1)
- AccountingDocument26 pagesAccountingMuhammad Jaafar AbinalNo ratings yet
- 6.b. Basic Audit Techniques: Revenue CyclesDocument27 pages6.b. Basic Audit Techniques: Revenue CyclesdewiNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Accounts Receivable Part II - 111702467Document11 pagesModule 3 - Accounts Receivable Part II - 111702467shimizuyumi53No ratings yet
- VALIX IA2 Chapter 1Document5 pagesVALIX IA2 Chapter 1M100% (1)
- Unang Pahina Far LiabilitiesDocument41 pagesUnang Pahina Far LiabilitiesNadin Olga SemiraNo ratings yet
- Pledge - : Far 6810 - Receivable FinancingDocument3 pagesPledge - : Far 6810 - Receivable FinancingKent Raysil PamaongNo ratings yet
- Unit VI (Accounting For Promissory Note)Document14 pagesUnit VI (Accounting For Promissory Note)bum_24100% (7)
- 14 Acctg Ed 1 - Receivable FinancingDocument19 pages14 Acctg Ed 1 - Receivable FinancingNath BongalonNo ratings yet
- Intermediate AccountingDocument7 pagesIntermediate Accountingjaninasachadelacruz0119No ratings yet
- 10 Receivable Financing For UploadDocument19 pages10 Receivable Financing For UploadMay Grethel Joy PeranteNo ratings yet
- 112.material For Receivable FinancingDocument8 pages112.material For Receivable FinancingJalanur MarohomNo ratings yet
- Liabilities 1 For Intermediate Accounting 2Document24 pagesLiabilities 1 For Intermediate Accounting 2Barredo, Joanna M.No ratings yet
- Cash FlowRev Students2Document25 pagesCash FlowRev Students2Luthfi AmaliaNo ratings yet
- General LedgerDocument15 pagesGeneral LedgerBanele SibiyaNo ratings yet
- 2 Adjusting Journal EntriesDocument6 pages2 Adjusting Journal EntriesJerric CristobalNo ratings yet
- Notes Receivable DiscountingDocument33 pagesNotes Receivable DiscountingKristia AnagapNo ratings yet
- Debt RestructuringDocument2 pagesDebt RestructuringVicong PogiNo ratings yet
- IllustrationDocument10 pagesIllustrationAmaris AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Receivable FinancingDocument6 pagesReceivable FinancingErla PilapilNo ratings yet
- Corporation - Transactions Subsequent To FormationDocument7 pagesCorporation - Transactions Subsequent To FormationJohncel Tawat100% (1)
- Audit of Cash - SeatworkDocument4 pagesAudit of Cash - SeatworkTEOPE, EMERLIZA DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- AR and Doubtful Accounts - NotesDocument5 pagesAR and Doubtful Accounts - NotesTEOPE, EMERLIZA DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- Corporate Liquidation - PrequizDocument2 pagesCorporate Liquidation - PrequizTEOPE, EMERLIZA DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- Business Combination Stock AcquisitionDocument2 pagesBusiness Combination Stock AcquisitionTEOPE, EMERLIZA DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- Corporate Liquidation - DiscussionDocument21 pagesCorporate Liquidation - DiscussionTEOPE, EMERLIZA DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- Partnership Liquidation AddDocument11 pagesPartnership Liquidation AddTEOPE, EMERLIZA DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- Partnership DissolutionDocument5 pagesPartnership DissolutionTEOPE, EMERLIZA DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- Partnership Dissolution Retirement of A PartnerDocument3 pagesPartnership Dissolution Retirement of A PartnerTEOPE, EMERLIZA DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- Math ExamDocument4 pagesMath ExamTEOPE, EMERLIZA DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- Media IndustryDocument16 pagesMedia IndustryTEOPE, EMERLIZA DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- BusinessDocument14 pagesBusinessTEOPE, EMERLIZA DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- ECON252 Midterm1 ExamDocument8 pagesECON252 Midterm1 ExamTu ShirotaNo ratings yet
- Financial Management For Decision Makers Canadian 2nd Edition Atrill Test BankDocument17 pagesFinancial Management For Decision Makers Canadian 2nd Edition Atrill Test Bankodiledominicmyfmf100% (28)
- Manufacturing Accounts - Extra Questions - A LevelDocument6 pagesManufacturing Accounts - Extra Questions - A LevelMUSTHARI KHANNo ratings yet
- Cara Menghitung BALANCE SHEETDocument1 pageCara Menghitung BALANCE SHEETIncesNo ratings yet
- Capital GainDocument4 pagesCapital GainqwertyNo ratings yet
- Multinational Business Finance 14th Edition Eiteman Test BankDocument36 pagesMultinational Business Finance 14th Edition Eiteman Test Bankrecolletfirework.i9oe100% (23)
- Coffey V Ripple Labs ComplaintDocument32 pagesCoffey V Ripple Labs ComplaintShaurya MalwaNo ratings yet
- Francisco Partners CaseDocument32 pagesFrancisco Partners CaseJose M Terrés-NícoliNo ratings yet
- Current AccountsDocument8 pagesCurrent AccountsAnonymous fcqc0EsXHNo ratings yet
- Eco Project Rbi 2Document19 pagesEco Project Rbi 2tusharNo ratings yet
- FIM Exercise AnsDocument6 pagesFIM Exercise AnsSam MNo ratings yet
- 349191compund Intrest Sheet-3 - CrwillDocument9 pages349191compund Intrest Sheet-3 - Crwillmadhuknl8674No ratings yet
- Mobile Banking Project 2010-2011Document74 pagesMobile Banking Project 2010-2011Nitesh Salunke67% (3)
- FCCBDocument17 pagesFCCBcoffytoffyNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10 Intermediate Acctng 1Document49 pagesCHAPTER 10 Intermediate Acctng 1Tessang OnongenNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Single EntryDocument8 pagesAccounting For Single EntryhabibahNo ratings yet
- 02 PPT Statement of Financial Position PDFDocument61 pages02 PPT Statement of Financial Position PDFRaizah GaloNo ratings yet
- 2008 TCFA Annual ConferenceDocument48 pages2008 TCFA Annual ConferenceaNo ratings yet
- Short Questions FMDocument21 pagesShort Questions FMsultanrana100% (1)
- Final Exam Engineering EconomyDocument2 pagesFinal Exam Engineering EconomyGelvie Lagos100% (2)
- The Future of MoneyDocument4 pagesThe Future of MoneyChipwalter100% (1)
- Broker 2 Broker OtherBroker ICMarketsGlobalDocument2 pagesBroker 2 Broker OtherBroker ICMarketsGlobaltravis efraimNo ratings yet
- Sample Buyer Presentation - 2Document13 pagesSample Buyer Presentation - 2mauricio0327No ratings yet
- Dornbusch 6e Chapter12Document19 pagesDornbusch 6e Chapter12kushalNo ratings yet
- Account Closure Form2 PDFDocument1 pageAccount Closure Form2 PDFdigant daveNo ratings yet
- Principles of AccountingDocument8 pagesPrinciples of AccountingDanish MuradNo ratings yet
- Pricing Fixed-Income SecuritiesDocument50 pagesPricing Fixed-Income SecuritiesyeehawwwwNo ratings yet
- FRM Practice Exam From EdupristineDocument52 pagesFRM Practice Exam From EdupristineAnish Jagdish LakhaniNo ratings yet
- Government of RajasthanDocument209 pagesGovernment of RajasthanEr Kamal SinghNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow StatementDocument1 pageCash Flow StatementYagika JagnaniNo ratings yet