Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Batch-7 Bme Fap Word
Uploaded by
official67050 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views5 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views5 pagesBatch-7 Bme Fap Word
Uploaded by
official6705Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
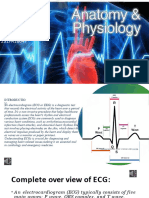
INTRODUCTION atria (the upper chambers of
the heart). Here's a detailed
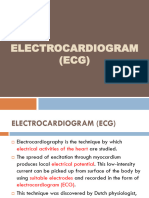
An electrocardiogram (ECG or
explanation of the P wave:
EKG) is a diagnostic test that
records the electrical activity
of the heart over a period of
1. *Atrial Depolarization*:
time.
It’s a non-invasive procedure
The P wave signifies the
that helps healthcare
spread of electrical impulses
professionals assess the
through the atria, initiating
heart's rhythm and electrical
their contraction. It starts at
conduction system. ECGs are
the SA node (sinoatrial node),
commonly used to diagnose
the heart's natural pacemaker
various heart conditions, such
and propagates through both
as arrhythmias, myocardial
atria, causing them to
infarction (heart attacks), and
contract and push blood into
abnormal heart rhythms. The
the ventricles.
test involves placing
2. Characteristics*:
electrodes on the skin, which
The P wave is typically a
detect the electrical impulses
small, rounded, and upright
produced by the heart and
deflection on the ECG tracing.
display them as waves on a
Its duration is usually less
monitor or paper printout.
than 0.12 seconds.
Understanding ECGs is crucial
The amplitude (height) of the
for diagnosing and managing
P wave is usually less than 2.5
heart-related issues , making
mm in the limb leads and less
it an essential tool in
than 1.5 mm in the precordial
cardiology and emergency
(chest) leads.
medicine.
3. *Significance*:
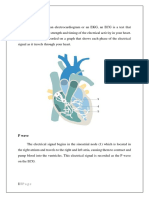
P-WAVE The morphology and duration
of the P wave provide
The P wave is the first
valuable information about
deflection seen on an
the integrity of the atria and
electrocardiogram. (ECG) and
the conduction pathway from
represents atrial
the SA node to the AV node.
depolarization, which is the
Changes in the P wave
electrical activity associated
morphology or duration may
with the contraction of the
indicate abnormalities such as
atrial enlargement, atrial A normal Q wave is often
fibrillation, atrial flutter, or considered to be less than
other atrial arrhythmias. 0.04 seconds in duration and
4. *Clinical Implications*: less than one-third the height
A tall, peaked P wave (>2.5 of the R wave in the same
mm) may suggest right atrial lead.
enlargement. An abnormal or pathological
A broadened P wave (>0.12 Q wave may indicate
seconds) may indicate myocardial infarction (heart
conduction delays within the attack) or other conditions
atria. that cause significant damage
Absent P waves may suggest or scar tissue formation in the
atrial standstill or complete myocardium (heart muscle).
heart block Pathological Q waves are
typically deeper (>1 mm or
Q-WAVE:
>25% of the R wave
Let's have complete on explanation amplitude) and wider (>0.04
of the Q wave seconds) compared to normal
1. *Definition*: Q waves.
In the context of a myocardial
The Q wave is the first negative infarction, pathological Q
deflection following the P wave in waves often develop in the
the QRS complex of an ECG. leads facing the area of
It represents the initial infarction, reflecting
depolarization of the permanent damage to the
interventricular septum, which myocardium.
occurs as the electrical impulse 4. *Interpretation*:
travels from the atria through the
AV node to the bundle of His and The presence of pathological
then to the bundle branches. Q waves, along with other
ECG changes such as ST-
2. *Characteristics*: segment elevation or
The Q wave is typically small depression, T-wave inversion,
and narrow, with a duration and clinical symptoms, can
of less than 0.04 seconds. aid in diagnosing acute
3. Clinical Significance*: myocardial infarction.
However, it's important to
consider the clinical context,
patient history, and additional ventricles, resulting in the
diagnostic tests (such as characteristic waveform seen
cardiac enzymes and imaging on the ECG.
studies) when interpreting Q
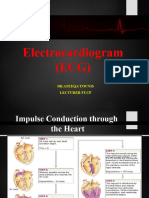
QR INTERVAL
waves.
The QT interval is a
QRS WAVE: measurement on an
The QRS complex is a key electrocardiogram (ECG)
component of (ECG) and that represents the time
between ventricular
represents ventricular
depolarization and
depolarization, which is the
repolarization. It's measured
electrical activity associated from the start of the QRS
with the contraction of the complex to the end of the T
ventricles (the lower wave. The QT interval can
chambers of the heart). be used to approximate the
time taken for the cardiac
1. Definition*:
ventricles to contract and
The QRS complex is the relax. The QT interval
second major deflection seen varies with heart rate, and is
on an ECG tracing, following typically reported adjusted
for heart rate (QTc) via
the P wave.
Bazett's formula.
It consists of three distinct
The QT interval includes the
waves: Q wave, R wave, and S QRS complex, the ST
wave, though the Q or S segment, and the T wave. It
waves may be absent in some encompasses the time from
leads. the beginning of ventricular
depolarization to the end of
2. *Sequence of Ventricular
ventricular repolarization,
Depolarization*: and therefore includes all of
The QRS complex represents the electrical events that
the rapid depolarization of take place in the ventricles.
the ventricles, leading to their PR SEGMENT
contraction and subsequent
ejection of blood into the The PR segment on an
pulmonary artery and aorta. electrocardiogram (ECG)
The depolarization begins at represents the flat, baseline
the interventricular septum portion betweenthe end of
and spreads through the the P wave and the beginning
of the QRS complex. It interval can be associated
reflects the time it takes for with an increased risk of
the Electrical impulse to arrhythmias. Monitoring the
travel through the AV node QT interval is important in
and reach the bundle of His. assessing cardiac
The PR segment should be repolarization and the
isoelectric, indicating a potential for certain drug-
resting state before induced arrhythmias.
ventricular depolarization
CONCLUSION
begins with the QRS
complex. The conclusion of an
ST SEGMENT electrocardiogram (ECG)
The ST segment on an interpretation typically
electrocardiogram (ECG) is summarizes the findings of
the flat, isoelectric section the test. It may include
following the QRS complex information about the heart
and preceding the T wave. It rate, rhythm, presence of any
represents the time between abnormalities such as
ventricular depolarization and arrhythmias, conduction
repolarization. Changes in abnormalities, ischemic
the ST segment can indicate changes, or structural
myocardial injury or abnormalities. However, it's
ischemia. Elevation or important to note that the
depression of the ST segment interpretation and conclusion
may be indicative of of an ECG should be done by
conditions like a heart attack a qualified healthcare
or angina. professional
QT INTERVAL BATCH-7
The QT interval on an
electrocardiogram (ECG) is
231FA16011
the duration from the
beginning of the QRS complex
231FA16019
to the end of the T wave. It
represents the total time for 231FA16033
ventricular depolarization and
repolarization. Prolongation 231FA16047
or shortening of the QT
You might also like
- ECG Interpretation Cheat SheetDocument14 pagesECG Interpretation Cheat Sheetrenet_alexandre75% (4)
- EKG Study GuideDocument45 pagesEKG Study GuideBrawner100% (6)
- ECG/EKG Interpretation: An Easy Approach to Read a 12-Lead ECG and How to Diagnose and Treat ArrhythmiasFrom EverandECG/EKG Interpretation: An Easy Approach to Read a 12-Lead ECG and How to Diagnose and Treat ArrhythmiasRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Electrocardiography ECGDocument60 pagesElectrocardiography ECGSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Basic Ecg: in The Eyes of NURSEDocument112 pagesBasic Ecg: in The Eyes of NURSESam jr TababaNo ratings yet
- Principles of ECGDocument11 pagesPrinciples of ECGDeinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- 12 Lead EKG Interpretation Part 1Document7 pages12 Lead EKG Interpretation Part 1Nuru99100% (1)
- Kuliah Ekg UnswagatiDocument75 pagesKuliah Ekg UnswagatiiikNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Prevention Is Better Than CureDocument8 pagesHypertension: Prevention Is Better Than CureAnneliesDillenNo ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookFrom EverandEKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookNo ratings yet
- CONCEPT - QuestionsDocument2 pagesCONCEPT - Questionsgreen_archerNo ratings yet
- Defibrillation ChecklistDocument4 pagesDefibrillation ChecklistCzarina100% (1)
- Clinical Demonstration: Topic: Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document24 pagesClinical Demonstration: Topic: Electrocardiogram (ECG)soniya josephNo ratings yet
- ECG InterpretationDocument11 pagesECG InterpretationAndrea AndradaNo ratings yet
- 231FA16011 231FA16019 231FA16033 231FA16047: Done by BATCH-7 (BME-32)Document16 pages231FA16011 231FA16019 231FA16033 231FA16047: Done by BATCH-7 (BME-32)official6705No ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document25 pagesElectrocardiogram (ECG)Laraib KanwalNo ratings yet
- The Electrocardiogram: Normal Conduction PathwayDocument16 pagesThe Electrocardiogram: Normal Conduction PathwayFourth YearNo ratings yet
- FAP PPT Batch-7Document16 pagesFAP PPT Batch-7official6705No ratings yet
- E Lectrocardiography ECG: Practical Physiology 2020-2021 LabDocument8 pagesE Lectrocardiography ECG: Practical Physiology 2020-2021 LabBushra AlkaqaniNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAMDocument50 pagesELECTROCARDIOGRAMamitava2010No ratings yet
- Comparison of PSD of Normal and Abnormal ECGsDocument5 pagesComparison of PSD of Normal and Abnormal ECGsEduardoHernandezNo ratings yet
- 01 - Basic Principles of ECG Analysis - UpToDateDocument22 pages01 - Basic Principles of ECG Analysis - UpToDateElmer MoscosoNo ratings yet
- ElectrocardiogramSignalAnalysis-An OverviewDocument5 pagesElectrocardiogramSignalAnalysis-An OverviewLejla AkšamovićNo ratings yet
- 12IJDocument5 pages12IJRishi CRMNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 5 PDFDocument50 pagesLab Exercise 5 PDFE1- Villapaz, Aiemarie R. (Aie)No ratings yet
- Aaa Ejempl TraductDocument8 pagesAaa Ejempl TraductJm GamaNo ratings yet
- NEONARYTDocument28 pagesNEONARYToctaviena zakariaNo ratings yet
- Ecg 1Document198 pagesEcg 1hibaNo ratings yet
- ECG Tutorial - Basic Principles of ECG Analysis - UpToDateDocument17 pagesECG Tutorial - Basic Principles of ECG Analysis - UpToDateImja94No ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Dysrhythmias and Conduction Problems DysrhythmiasDocument15 pagesManagement of Patients With Dysrhythmias and Conduction Problems DysrhythmiasRoyce Vincent TizonNo ratings yet
- Ecg SignalDocument6 pagesEcg SignalShubham RajpootNo ratings yet
- ECG (Electrocardiogram) Tracings: Capitol University College of NursingDocument5 pagesECG (Electrocardiogram) Tracings: Capitol University College of NursingRiel TumandaNo ratings yet
- Premature Atrial Complexes: Feature Description DurationDocument3 pagesPremature Atrial Complexes: Feature Description DurationRicky Marion ManaloNo ratings yet
- 118 Skills Lab-Week 2-ECG TakingDocument8 pages118 Skills Lab-Week 2-ECG TakingKeisha BartolataNo ratings yet
- Ecg ProcedureDocument5 pagesEcg ProcedureLungu AdrianNo ratings yet
- Ecg Interpretation Review PDFDocument21 pagesEcg Interpretation Review PDFMark FernandezNo ratings yet
- ElectrocardiogramDocument3 pagesElectrocardiogramgaratoh099No ratings yet
- SPDX Electrocardiography-EcgDocument6 pagesSPDX Electrocardiography-Ecgdumppotato24No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document29 pagesUnit 1SasikumarNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Feature Extraction of ECG Signal For Myocardial Ischemia DetectionDocument5 pagesAnalysis and Feature Extraction of ECG Signal For Myocardial Ischemia DetectionerpublicationNo ratings yet
- ECG FinalDocument128 pagesECG FinalErikaNo ratings yet
- What Is An ECG?Document23 pagesWhat Is An ECG?Karan PrabaNo ratings yet
- Green Orange Blue Creative Healthcare Facility PresentationDocument31 pagesGreen Orange Blue Creative Healthcare Facility Presentationshreyamukherjee3009No ratings yet
- Basic Ecg: Internal Medicine Cardiology Critical Care SpecialistDocument128 pagesBasic Ecg: Internal Medicine Cardiology Critical Care SpecialistEzraManzanoNo ratings yet
- ECG InterpretationDocument5 pagesECG InterpretationjenNo ratings yet
- ECG DurationsDocument2 pagesECG Durationscnshariff@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Ecg Interpretation ReviewDocument15 pagesEcg Interpretation ReviewFrechel Ann Landingin PedrozoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 7.2 - ElectrocardiogramDocument2 pagesExercise 7.2 - ElectrocardiogramKevin F. CortesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ECGDocument39 pagesIntroduction To ECGSingey LhendupNo ratings yet
- Ecg PreparationDocument15 pagesEcg PreparationErika Danalle ArceoNo ratings yet
- CardiovascularDocument30 pagesCardiovasculartiago alvesNo ratings yet
- Section 1. ECG Basics 1. TP Segment.: ECG Reviews and Criteria Brugada SyndromeDocument183 pagesSection 1. ECG Basics 1. TP Segment.: ECG Reviews and Criteria Brugada SyndromeTiến HàNo ratings yet
- Ecg 2Document106 pagesEcg 2hammad992No ratings yet
- KULIAH ECG Dinkes PurworejoDocument69 pagesKULIAH ECG Dinkes PurworejoSofian PalupiNo ratings yet
- How Procedure Is Performed: ElectrocardiogramDocument10 pagesHow Procedure Is Performed: ElectrocardiogramJonathan AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Basic ECG InterpretationDocument62 pagesBasic ECG Interpretationmohannadalkwiese3No ratings yet
- Answer NDocument1 pageAnswer NJ tanieeNo ratings yet
- KULIAH ECG Dinkes PurworejoDocument69 pagesKULIAH ECG Dinkes PurworejoVella NurfatimahNo ratings yet
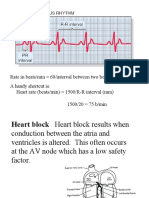
- Rate in Beats/min 60/interval Between Two Beats in Seconds A Handy Shortcut Is: Heart Rate (Beats/min) 1500/R-R Interval (MM) 1500/20 75 B/minDocument37 pagesRate in Beats/min 60/interval Between Two Beats in Seconds A Handy Shortcut Is: Heart Rate (Beats/min) 1500/R-R Interval (MM) 1500/20 75 B/minLuis AlayoNo ratings yet
- QRS ComplexDocument7 pagesQRS Complexchiusavi77No ratings yet
- DYSRHYTMIASDocument16 pagesDYSRHYTMIASVictor StevenNo ratings yet
- 5 - EcgDocument37 pages5 - EcgMonika MeriyaNo ratings yet
- 2 Rotary People of Action - Information About NischalDocument13 pages2 Rotary People of Action - Information About NischalRajendra LamsalNo ratings yet
- Calcium Channel Blockers inDocument15 pagesCalcium Channel Blockers inAnonymous NeRC5JYiSNo ratings yet
- Levine Sign - Google SearchDocument1 pageLevine Sign - Google SearchMathan KarthikNo ratings yet
- Acyanotic Congenital Heart Disease With Increased Pulmonary Blood FlowDocument9 pagesAcyanotic Congenital Heart Disease With Increased Pulmonary Blood Flowdrhomiedan100% (1)
- Hypertensionandheart Failure: Jeremy Slivnick,, Brent C. LampertDocument11 pagesHypertensionandheart Failure: Jeremy Slivnick,, Brent C. LampertFannyNo ratings yet
- Early Mobilization Reduces Delirium After Coronary Artery Bypass Graft SurgeryDocument6 pagesEarly Mobilization Reduces Delirium After Coronary Artery Bypass Graft SurgeryevaNo ratings yet
- Cord Pulmonar CronicDocument11 pagesCord Pulmonar CronicroxanachiticNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System (CVS) - Ii: MBBS Year-3 (Academic Year 2020-2021)Document10 pagesCardiovascular System (CVS) - Ii: MBBS Year-3 (Academic Year 2020-2021)FarsibalooNo ratings yet
- Approach To Syncope On Electrophysiologist PerspectiveDocument21 pagesApproach To Syncope On Electrophysiologist PerspectiveVarissara SinkajarernNo ratings yet
- Word EndnoteDocument2 pagesWord Endnotegreeen.pat6918No ratings yet
- Beta Blocker AgentsDocument28 pagesBeta Blocker Agentskuncupcupu1368No ratings yet
- Nclex ExamDocument18 pagesNclex Examwaqas_xsNo ratings yet
- Ecg - Basics For The Anesthesiologists: Dr.K.M.LakshmanarajanDocument145 pagesEcg - Basics For The Anesthesiologists: Dr.K.M.LakshmanarajanKM Lakshmana RajanNo ratings yet
- IPPDocument77 pagesIPPshanifNo ratings yet
- Stemi Pathway: Record TimeDocument2 pagesStemi Pathway: Record TimeOlga Jadha CasmiraNo ratings yet
- Kewenangan Klinis SP - JPDocument3 pagesKewenangan Klinis SP - JPVania Lystia TantraNo ratings yet
- Frederik H Verbrugge Natriuretic Response ToDocument12 pagesFrederik H Verbrugge Natriuretic Response ToErick Rivera SainzNo ratings yet
- CABG ConduitDocument15 pagesCABG ConduitSundaresan SankarNo ratings yet
- ESC Congress 2020: The Digital ExperienceDocument9 pagesESC Congress 2020: The Digital ExperienceMeatus AcusticusNo ratings yet
- Digoxin ToxicityDocument25 pagesDigoxin ToxicitywasimNo ratings yet
- PhDthesisAASL PDFDocument168 pagesPhDthesisAASL PDFmuhammad alamNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ArrestDocument19 pagesCardiac ArrestHaimelien De LimosNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument3 pagesTetralogy of FallotJohn Mark PocsidioNo ratings yet
- BNP & Nt-Pro BNPDocument7 pagesBNP & Nt-Pro BNPyehezkieldwardNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrest Pada Setting Icu: Pembimbing: Dr. Tommy Nugroho, SpanDocument38 pagesCardiac Arrest Pada Setting Icu: Pembimbing: Dr. Tommy Nugroho, SpanYeltserNo ratings yet
- Neonatal ShockDocument91 pagesNeonatal ShockCapricious BibekNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Therapy For Rate and Rhythm Control For Atrial Fibrillation in 2017Document8 pagesPharmacological Therapy For Rate and Rhythm Control For Atrial Fibrillation in 2017UCI CONTINGENCIANo ratings yet