Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Poster Materials - Pardin
Uploaded by
Timothy Pardin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesChemistry Poster Materials - Pardin
Uploaded by
Timothy PardinCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Chemistry Poster Materials (Timothy Pardin)
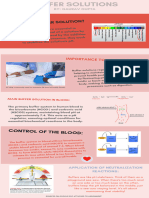
Theory (Definition of Buffer):
A buffer is a solution that resists changes in pH upon the addition of small amounts of acids
or bases. It is a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base, or a weak base and its
conjugate acid, that maintains a relatively constant pH in the presence of small amounts of
acids or bases. The weak acid and its conjugate base, or the weak base and its conjugate acid,
form a buffer system that neutralizes the added acid or base, preventing a significant change
in pH.
Application of Buffer:
Buffers are widely used in various applications, including in the field of chemistry, biology,
and pharmaceuticals. They are essential in maintaining the pH of biological fluids, such as
blood and urine, within a narrow range, ensuring proper functioning of the body. In the
pharmaceutical industry, buffers are used in the production of drugs to control the pH of the
solution during the manufacturing process. They are also used in the food industry to
maintain the pH of food products and to prevent spoilage.
Use of Pictures or Icons Related to the Theory:
Text Citation and Bibliography:
- "Buffers" by Robert W. Taft, Jr. in "Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry" (John Wiley &
Sons, Inc., 2001).
- "Buffers" by David J. C. Macnicol in "Encyclopedia of Food Science and Technology"
(Academic Press, 2001).
- "Buffer Systems" by David J. C. Macnicol in "Encyclopedia of Food Science and
Technology" (Academic Press, 2001).
References:
- https://www.coursehero.com/file/82802015/Buffers-Particulate-Diagram-Posters-1docx/
- https://www.microchemicals.com/technical_information/wet_etching.pdf
- https://chemistry.as.virginia.edu/how-prepare-and-present-scientific-poster
- https://www.flinnsci.com/products/chemistry/student-laboratory-kits/
- https://us.vwr.com/store/product/8866376/anatomy-of-an-atom-poster
You might also like
- Buffers and PHDocument29 pagesBuffers and PHp bergerNo ratings yet
- Understanding PH and BufferDocument2 pagesUnderstanding PH and BufferRyan Carlo Conde100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Solutions For Oral Administration-2 PDFDocument31 pagesPharmaceutical Solutions For Oral Administration-2 PDFHanaa Abo Sweirh100% (1)
- The Alkaline Diet Made Easy: Reclaim Your Health, Lose Weight & Heal NaturallyFrom EverandThe Alkaline Diet Made Easy: Reclaim Your Health, Lose Weight & Heal NaturallyNo ratings yet
- Factors That Influence Microbial Growth in FoodDocument72 pagesFactors That Influence Microbial Growth in FoodIrham Ibrahim100% (1)
- AHCC: The Medical Breakthrough in Natural ImmunotherapyFrom EverandAHCC: The Medical Breakthrough in Natural ImmunotherapyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Buffers in Pharmaceutical SystemsDocument2 pagesBuffers in Pharmaceutical SystemsRenAria6918No ratings yet
- Importance of BuffersDocument7 pagesImportance of BuffersAsad AzizNo ratings yet
- PH Measurement and Importance of ItDocument9 pagesPH Measurement and Importance of ItIsabel Sofia Corredor MendezNo ratings yet
- Understanding PH KopyasıDocument22 pagesUnderstanding PH KopyasıturanozanmcfNo ratings yet
- Lecture5 Pharmaceutics (Buffer Partition)Document6 pagesLecture5 Pharmaceutics (Buffer Partition)haroon41No ratings yet
- Buffers Solutions in Biological EnvironmentsDocument3 pagesBuffers Solutions in Biological Environmentsfaizshaikh4No ratings yet
- Buffers in Our Daily LifeDocument4 pagesBuffers in Our Daily LifeClement CharlesNo ratings yet
- PH, Buffer & Isotonic SolutionsDocument33 pagesPH, Buffer & Isotonic SolutionsrajendraNo ratings yet
- PH Maintenance in Cell Culture Media - Aiswariya S ADocument21 pagesPH Maintenance in Cell Culture Media - Aiswariya S AAiswariya S ANo ratings yet
- Buffer System - Group 3Document5 pagesBuffer System - Group 3Rameen QadirNo ratings yet
- Significance of Buffer in Living OrganismDocument1 pageSignificance of Buffer in Living OrganismJohn Jill T. VillamorNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical ExcipientsDocument69 pagesPharmaceutical ExcipientsDeepankar SutradharNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1 Write Up of Product Development - 2Document11 pagesAssignment - 1 Write Up of Product Development - 2Pooja GhongadeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Buffers in The BloodDocument8 pagesChemical Buffers in The BloodMaedaah ShuaibNo ratings yet
- ACID and BASESDocument24 pagesACID and BASESlaurence gonzalesNo ratings yet
- What Is PH - Growth TechnologyDocument4 pagesWhat Is PH - Growth TechnologydewanibipinNo ratings yet
- Adolfocasestudy 4Document3 pagesAdolfocasestudy 4api-302022851No ratings yet
- Chem 41 Lab Formal Report 01 - Preparation of Buffers & Amino Acids As AmpholytesDocument13 pagesChem 41 Lab Formal Report 01 - Preparation of Buffers & Amino Acids As AmpholytesFaith VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- Biological Buffers - Lena Al-GharrasDocument16 pagesBiological Buffers - Lena Al-GharrasLena GHNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab 1Document2 pagesBiochem Lab 1Binoy SerinoNo ratings yet
- Buffers Solution & Its Applications: Abuzar KhalidDocument8 pagesBuffers Solution & Its Applications: Abuzar Khalidabuzar khalidNo ratings yet
- Buffered and Isotonic Solutions: A (Salt) (Acid) A ADocument2 pagesBuffered and Isotonic Solutions: A (Salt) (Acid) A AMary Loise LimaNo ratings yet
- The Role of Dissolution Testing in Complementary and African Traditional Medicines: Development of Methods and ApplicationsDocument21 pagesThe Role of Dissolution Testing in Complementary and African Traditional Medicines: Development of Methods and ApplicationsPriyanshu JainNo ratings yet
- Adolfocasestudy 5Document3 pagesAdolfocasestudy 5api-302022851No ratings yet
- 3.Ph Partition TheoryDocument36 pages3.Ph Partition Theoryamk_19No ratings yet
- Precentation MedicalDocument14 pagesPrecentation MedicalOwais KhanNo ratings yet
- Buffers BiochemistryDocument11 pagesBuffers Biochemistryairheadguy819No ratings yet
- QUIZ Compressed-1.pdf - BIOCHEMISTRY LAB MODULE 1 PH OF...Document91 pagesQUIZ Compressed-1.pdf - BIOCHEMISTRY LAB MODULE 1 PH OF...B-Panganiban, Cyrus SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Find Out All You Need To Know About Measuring PH in Acidified FoodsDocument24 pagesFind Out All You Need To Know About Measuring PH in Acidified Foodsqaiser khanNo ratings yet
- G.Chemistry Exp.7Document5 pagesG.Chemistry Exp.7sayar.emre888No ratings yet
- BactocidDocument18 pagesBactocidsunilbiotech.indNo ratings yet
- Buffer in Biological & Pharmaceutical SystemsDocument28 pagesBuffer in Biological & Pharmaceutical Systemshamam salih badriNo ratings yet
- Bio Seience (Unit-1)Document14 pagesBio Seience (Unit-1)EZHIL NNo ratings yet
- Food Additives Research Paper PDFDocument4 pagesFood Additives Research Paper PDFtxdpmcbkf100% (1)
- BufferDocument26 pagesBufferAlia RizanNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Biological Buffer Preparation: For Weighing, PH Measurement and PipettingDocument20 pagesA Guide To Biological Buffer Preparation: For Weighing, PH Measurement and PipettingWagner ProchnowNo ratings yet
- Buffers and PH Adjusting AgentsDocument8 pagesBuffers and PH Adjusting AgentsJoão SantosNo ratings yet
- FahimsDocument7 pagesFahimsMohammad Fahim NurNo ratings yet
- DR Selim ResearchDocument19 pagesDR Selim ResearchnourhanNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 6 PH Partition and Effectof Dosage FormDocument21 pagesLECTURE 6 PH Partition and Effectof Dosage FormNimra WNo ratings yet
- AcidifiersDocument17 pagesAcidifiersKarim Khalil100% (3)
- GR 12 A6 - 7 Add NotesDocument3 pagesGR 12 A6 - 7 Add NotesShaimaa SalamaNo ratings yet
- HEPES2Document8 pagesHEPES2Yuliana MuharramiNo ratings yet
- The Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS) : From Theory To Application To Product DevelopmentDocument25 pagesThe Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS) : From Theory To Application To Product DevelopmentDede PriyantiNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry LN03Document16 pagesBiochemistry LN03Rahaf Al-muhtasebNo ratings yet
- Buffer Solutions AssignmentDocument1 pageBuffer Solutions Assignmentggupta132007No ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Determination of PHDocument5 pagesExperiment 1 Determination of PHRoselle AbrazaldoNo ratings yet
- BABE OverviewDocument20 pagesBABE OverviewIndraAzaNo ratings yet
- The Role of PH in Food ScienceDocument9 pagesThe Role of PH in Food Sciencepushpinder paulNo ratings yet
- Food & Nutrition Europe: PreservativesDocument14 pagesFood & Nutrition Europe: PreservativesuploaderdownloaderNo ratings yet
- Pengembangan Farmasetik Bentuk Sediaan Cair (Larutan)Document40 pagesPengembangan Farmasetik Bentuk Sediaan Cair (Larutan)niantri laiaNo ratings yet
- CoatingDocument105 pagesCoatingFaress RabiNo ratings yet