Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tài liệu TT
Uploaded by
copoc419070 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views8 pagesOriginal Title
Tài-liệu-TT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views8 pagesTài liệu TT
Uploaded by
copoc41907Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
IDS (intrusion detection system)
• is a device or software application that monitors a network or systems for
malicious activity or policy violations.
• Any intrusion activity or violation is typically reported either to an
administrator or collected centrally using a security information and event
management (SIEM) system.
• A SIEM system combines outputs from multiple sources and uses alarm
filtering techniques to distinguish malicious activity from false alarms
IDS can be classified into 3 different types:
•NIDS: Network-based intrusion detection system
• HIDS: Host-based intrusion detection system
• HYBRID IDS
HIDS (Host-based intrusion detection system)
• is an intrusion detection system that is capable of monitoring and analyzing
the internals of a computing system as well as the network packets on its
network interfaces, similar to the way a network-based intrusion detection
system (NIDS) operates.
• This was the first type of intrusion detection software to have been designed,
with the original target system being the mainframe computer where outside
interaction was infrequent
IDS Detection methods
• Signature-based detection
• Statistical anomaly-based detection
•Stateful protocol analysis detection
IPS (Intrusion prevention systems)
• are network security appliances that monitor network or system activities for
malicious activity.
• The main functions of intrusion prevention systems are:
✓ to identify malicious activity
✓ log information about this activity (ghi chép)
✓ report it and attempt to block or stop it.
• are considered extensions of intrusion detection systems because they both
monitor network traffic and/or system activities for malicious activity.
IPS can be classified into four different types:
• NIPS: Network-based intrusion prevention system
• WIPS: Wireless intrusion prevention system
• NBA: Network behavior analysis
• HIPS: Host-based intrusion prevention system
IPS can be classified into four different types:
• Network-based intrusion prevention system (NIPS): monitors the entire
network for suspicious traffic by analyzing protocol activity.
• Wireless intrusion prevention system (WIPS): monitor a wireless network for
suspicious traffic by analyzing wireless networking protocols.
• Network behavior analysis (NBA): examines network traffic to identify threats
that generate unusual traffic flows, such as distributed denial of service (DDoS)
attacks, certain forms of malware and policy violations.
• Host-based intrusion prevention system (HIPS): an installed software package
which monitors a single host for suspicious activity by analyzing events
occurring within that host
IDS & IPS difference
• The main differences are
✓ unlike intrusion detection systems, intrusion prevention systems are placed
in-line and are able to actively prevent or block intrusions that are detected.
✓ IPS can take such actions as sending an alarm, dropping detected malicious
packets, resetting a connection or blocking traffic from the offending ĪP
address. (malicious)
✓ An IPS also can correct cyclic (theo chu kỳ) redundancy, check (CRC) errors
(kiêm dự chu trình) , defragment (chống phân mảnh) packet streams, mitigate
(giảm bớt) TCP sequencing issues, and clean up unwanted transport and
network layer options
Firewall
• In commercial and residential construction, firewalls are concrete or masonry
walls that/which run from the basement through the roof, to prevent a fire from
spreading from one section of the building to another.
• In aircraft and automobiles, a firewall is an insulated metal barrier that keeps
the hot and dangerous moving parts of the motor separate from the inflammable
interior where the passengers sit.
• A firewall in an information security program is similar to a building's firewall
in events specific types of information from moving between the outside world,
known as the untrusted network (for example, the Internet), and the inside
world, known as the trusted network. The firewall may be a separate computer
system, a software service running on an existing router or server, or a separate
network containing a number of supporting devices.
• In computing, a firewall is a network security system that monitors and
controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security
rules. A firewall typically establishes a barrier between a trusted internal
network and untrusted external network, such as the Internet. Firewalls can be
categorized by processing mode, development era, or structure.
Firewall
• Firewall (computing), a technological barrier designed to prevent unauthorized
or unwanted communications between computer networks or hosts
• Firewall (construction), a barrier inside a building, designed to limit the spread
of fire, heat and structural collapse
• Firewall (engine), the part of a vehicle that separates the engine compartment
from the rest of the vehicle.
****
• A firewall that protects an individual computer is called a Personal Firewall. It
is an application which controls network traffic to and from a computer,
permitting or denying communications based on a security policy. Typically it
works as an application layer firewall.
• It is useful for an individual and a family because simply they only need to
protect their own computer.
• It allows a security policy to be defined for individual computers
• Many personal firewalls are able to control network traffic allowed ne secured
computer. When an application attempts an outbound connection, the firewall
may block it if blacklisted, or ask the user whether to blacklist it if it is not yet
known
Common personal firewalls:
• Cisco Security Agent
• Microsoft Internet connection firewall
• Symantec personal firewall
****
• A firewall that is present in an enterprise network for the protection of
multiple computers is called a Network Firewall and it is classified into 4 sub
types as follow:
- Packet-filtering firewalls (stateful and nonstateful)
- Circuit-level gateways
- Application-level gateways
- NAT firewall (Network Address Translation)
• Common appliance-based network firewalls:
- Cisco PIX, Cisco ASA
- Juniper NetScreen firewall
- Nokia firewalls
- Symantec's Enterprise Firewall.
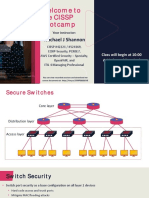
***ẢNH***
Firewall products
• Software firewalls are the firewalls which are installed in the Operating
System
• Some software firewall products are:
- SunScreen firewall
- IPF
- Microsoft ISA server
- Check Point NG
- Linux's IPTables
• Software Firewalls are responsible for more tasks than Hardware firewalls. It
operates as DNS server or DHCP server.
Firewall products
• Hardware firewalls or appliance firewalls are the firewalls which are
integrated in specialized hardwares designed for firewall only.
• Some common hardware firewall products are:
- Cisco PIX
- Cisco ASA
- NetScreen firewall
- SonicWall Appliaces
- WatchGuard Fireboxes
- Nokia firewall
- Symantec's Enterprise Firewall.
• Integrated firewalls: Besides basic functions of a firewall, it has another
function like VPN, intrusion detection and prevention, spam filtering,
antiviruses
Firewall classification based on use technology
• Personal firewalls
• Packet filters
• Network Address Translations (NAT) firewalls
• Circuit-level firewalls
• Proxy firewalls • Stateful firewalls
• Transparent firewall: trong suốt
• Virtual firewalls
Fundamental components of a firewall
A firewall consists of one or more components as follow:
•Packet Filtering - Bộ lọc gói tin
• Application Gateway - Cổng ứng dụng
• Circuit Level Gate - Cổng mạch
Some firewall architectures
• Packet filtering Router
• Dual – homed Host • Screened Host
• Screened Subnet Host
- Use Bastion Host
- Put internal router external router together
- Put Bastion host and external router together put sth together
Common personal firewall features: (advatages)
• Block or alert the user about all unauthorized inbound or outbound connection
attempts.
• Allows the user to control which programs can and cannot access the local
network and/or Internet and provide the user with information about an
application that makes a connection attempt.
• Hide the computer from port scans by not responding to unsolicited network
traffic.
• Monitor applications that are listening for incoming connections. • Monitor
and regulate all incoming and outgoing Internet users.
• Prevent unwanted network traffic from locally installed applications.
• Provide information about the destination server with which an application is
attempting to communicate.
• Track recent incoming events, outgoing events, and intrusion events to see
who has accessed or tried to access your computer.
• Blocks and prevents hacking attempt or attack from hackers.
Firewalls help protecting internal network from hackers, however
firewall do have some limitations.
• If the system has been compromised by malware, spyware or similar
software, these programs can also manipulate the firewall, because both are
running on the same system. It may be possible to bypass or even completely
shut down software firewalls in such a manner.
• A firewall can't notify, if it has been incorrectly configured.
• Firewall may limit access from the Internet, but it may not protect your
network from wireless and other access to your systems.
• Firewalls and Virtual Private Networks are not the only solution to secure
private documents and emails that are either sent within an organization or to
other business contacts that are outside the organization.
• The alerts generated can possibly desensitize users to alerts by warning the
user of actions that may not be malicious.
• Software firewalls that interface with the operating system or with other
firewalls or security software at the kernel mode level may potentially cause
instability and/or introduce security flaws.
A firewall is used to
• Prevent the Passage of Unwanted Content
• Prevent Unauthorized Remote Access
• Prevent Indecent Content
• Guarantee Security Based on Protocol and IP Address
• Protect Seamless Operations in Enterprises
•Protect Conversations and Coordination Contents
• Prevent Destructive Content from Online Videos and Games
Key differences between Firewall and Antivirus
1. A firewall can be employed for software as well as hardware; antivirus can
only be applied for software.
2. Antivirus conducts screening, including identification, naming, and deletion.
Alternatively, firewall controls and processes input and output sets.
3. External attacks are only managed by Firewalls, while Antivirus manages
external and internal threats.
4. When the attack firewall is checked, certain rules are applied based on
inbound packets. In comparison, malicious files and applications corrupted by
antivirus are scanned and checked. IP spoofing and routing attacks are strategies
that may theoretically compromise the protection of the packet filters.
5. A network protocol firewall protects your device, thereby blocking
vulnerable port packets, whereas an anti-virus prevents malicious data on the
level of the file.
6. The monitoring capability of the firewall is based on a pre-defined set of
rules. Whereas the monitoring capability of antivirus is based on techniques
imposed by the manufacturer.
You might also like
- Introduction To FirewallsDocument33 pagesIntroduction To FirewallsSwathi Palle100% (1)
- Local-Iptv M3uDocument3 pagesLocal-Iptv M3uفؤاد مهندسNo ratings yet
- Common Security Attacks and Their CountermeasuresDocument46 pagesCommon Security Attacks and Their Countermeasuresdellibabu50975% (4)
- AppSec DC 2019 ASVS 4.0 FinalDocument312 pagesAppSec DC 2019 ASVS 4.0 FinalSreedhar Reddy A CNo ratings yet
- Visa Smart Debit/ Credit Transaction Flow OverviewDocument51 pagesVisa Smart Debit/ Credit Transaction Flow OverviewRabindranath Thanikaivelu100% (5)
- Gigamon Solution Overview PDFDocument46 pagesGigamon Solution Overview PDFVan NguyenNo ratings yet
- IAS Chapter 3 EditedDocument22 pagesIAS Chapter 3 Editedteshu wodesaNo ratings yet
- FirewallDocument12 pagesFirewallHarpreetNo ratings yet
- 7-Module 2-22-02-2024Document41 pages7-Module 2-22-02-2024theorphicarcaneNo ratings yet
- 4-Module - 2 Security Device Management-18!01!2024Document58 pages4-Module - 2 Security Device Management-18!01!2024shreemanjulaaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Firewalls: © N. Ganesan, PH.DDocument57 pagesIntroduction To Firewalls: © N. Ganesan, PH.DXozanNo ratings yet
- Presenters:: Behind The Firewall Its Safe:)Document25 pagesPresenters:: Behind The Firewall Its Safe:)DivayChadhaNo ratings yet
- IA 124: Introduction To IT Security: VPN & FirewallDocument30 pagesIA 124: Introduction To IT Security: VPN & FirewalljohnNo ratings yet
- Describe IT Security SolutionsDocument78 pagesDescribe IT Security SolutionsyuulooNo ratings yet
- Task 1 - SecurityDocument25 pagesTask 1 - SecurityMuheet zahidNo ratings yet
- Lect 7Document67 pagesLect 7shirto cubherNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 - Network SecurityDocument35 pagesTopic 5 - Network Securitys.l.mills86No ratings yet
- Fire Walls: Prepared by Komal BasharatDocument21 pagesFire Walls: Prepared by Komal BasharatAlina PariNo ratings yet
- Lec6 Network Security - Firewall, Proxy, DMZDocument10 pagesLec6 Network Security - Firewall, Proxy, DMZRomany MagdyNo ratings yet
- Working of A Software Firewalls 244 (EDU - ARIS.GE)Document23 pagesWorking of A Software Firewalls 244 (EDU - ARIS.GE)КобейнNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 BCSE353E ETH VL2023240100850 2023-06-03 Reference-Material-IDocument27 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 BCSE353E ETH VL2023240100850 2023-06-03 Reference-Material-Idsa dsaNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 2-Network & Internet ForensicsDocument26 pagesUNIT - 2-Network & Internet ForensicsVishwakarma UniversityNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document28 pagesPresentation 1VEnki RaoNo ratings yet
- Firewall: Kriptografi & Keamanan JaringanDocument32 pagesFirewall: Kriptografi & Keamanan JaringangibrandNo ratings yet
- Module-1: Information Security DevicesDocument52 pagesModule-1: Information Security DevicessendhilksNo ratings yet
- CyberSecurity Short Course - Week 3Document46 pagesCyberSecurity Short Course - Week 3tapera_mangeziNo ratings yet
- 2a Firewall and IDS IPS Basics - OdpDocument18 pages2a Firewall and IDS IPS Basics - OdpGraham-Douglas Sphinx IbanimiNo ratings yet
- Firewall Final Firewalls-3Document67 pagesFirewall Final Firewalls-3rahulNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument9 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemKRRISH MAHESHWARINo ratings yet
- Netwok CDocument36 pagesNetwok CMohammad Jakirul IslamNo ratings yet
- Configuration PresentationDocument17 pagesConfiguration PresentationAbhishek kumarNo ratings yet
- Inbound 3532013927060021662Document34 pagesInbound 3532013927060021662vasquezjade03No ratings yet
- Firrewall and Intrusion Prevention SystemDocument23 pagesFirrewall and Intrusion Prevention Systemfatima gullNo ratings yet
- Grade 10-12 - Week 5Document4 pagesGrade 10-12 - Week 5Oliver C Silvano100% (1)
- Cyber Security III Server Management and Firewalls: Dr. Smita KacholeDocument56 pagesCyber Security III Server Management and Firewalls: Dr. Smita KacholeSmita Saudagar100% (1)
- Firewall 2012 MARCHDocument30 pagesFirewall 2012 MARCHArshpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Research On Computer Security Based On Firewall: Prepared byDocument10 pagesResearch On Computer Security Based On Firewall: Prepared byأفنان النزيليNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Firewall Security Policies Using Linux Iptables, UFW, FirewalldDocument11 pagesDesign and Implementation of Firewall Security Policies Using Linux Iptables, UFW, FirewalldUjjwal pandeyNo ratings yet
- Firewall Security GuideDocument14 pagesFirewall Security GuideAshu BhallaNo ratings yet
- U2 - M2 - FIREWALL - Security TechnologyDocument59 pagesU2 - M2 - FIREWALL - Security TechnologyGarvitJainNo ratings yet
- Cips 2012 0012Document68 pagesCips 2012 0012Pravin ChallawarNo ratings yet
- 08-CH09-CompSec2e-ver02 Firewalls PDFDocument33 pages08-CH09-CompSec2e-ver02 Firewalls PDFNikunj PatelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Network Security TechniquesDocument37 pagesLecture 3 - Network Security TechniquesHenry ChipindaNo ratings yet
- Ai - PPT - 33 && 38Document8 pagesAi - PPT - 33 && 38GokussjNo ratings yet
- Firewall: Research On Computer Security Based OnDocument16 pagesFirewall: Research On Computer Security Based Onأفنان النزيليNo ratings yet
- Introduction To FirewallsDocument76 pagesIntroduction To FirewallsLalmohan KsNo ratings yet
- Unit-II 7033 - Additional NotesDocument32 pagesUnit-II 7033 - Additional NotesHari RNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document27 pagesUnit 519wj-1236 tejaswiNo ratings yet
- IPS and IDSDocument6 pagesIPS and IDSTitto Thomas100% (1)
- NIS Question BankDocument5 pagesNIS Question BankSuman ThakurNo ratings yet
- Firewall Apr2004Document21 pagesFirewall Apr2004SunNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To FirewallsDocument21 pagesAn Introduction To Firewallscci_491934037No ratings yet
- Unit-4 Info SecuDocument8 pagesUnit-4 Info Secuworkwithasr04No ratings yet
- IPSecDocument4 pagesIPSecAryan PanchalNo ratings yet
- 18 DataCenter Security OverviewDocument22 pages18 DataCenter Security Overviewrnaveed01No ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemsDocument29 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemsDrushti DesaiNo ratings yet
- Endpoint Security and Analysis: Common Type Found in 2016Document10 pagesEndpoint Security and Analysis: Common Type Found in 2016Playing PurposesNo ratings yet
- Firewall ConfigurationDocument11 pagesFirewall ConfigurationjenalyncomedialanojanNo ratings yet
- CISSP Session 03Document85 pagesCISSP Session 03wfelicescNo ratings yet
- How Firewalls Work: Access Is Called Firewall. A Private Network Created Using World Wide Web SoftwareDocument2 pagesHow Firewalls Work: Access Is Called Firewall. A Private Network Created Using World Wide Web SoftwareAssuNo ratings yet
- Web Engineering: Assignment No 3: FirewallDocument9 pagesWeb Engineering: Assignment No 3: FirewallTabish NomanNo ratings yet
- Network Firewall 4Document8 pagesNetwork Firewall 4earl bagainNo ratings yet
- Secure Hash Standard (SHS) : FIPS PUB 180-4Document35 pagesSecure Hash Standard (SHS) : FIPS PUB 180-4Bruno GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Goolge Dork Usage Vulns Dbs WebcamsDocument8 pagesGoolge Dork Usage Vulns Dbs WebcamsGabrihel Mendieta0% (1)
- DDoS Quick GuideDocument5 pagesDDoS Quick GuideANIMESH301No ratings yet
- The Kleopatra HandbookDocument37 pagesThe Kleopatra HandbookJose Luis Zorita MoralesNo ratings yet
- Work Security - DigitalSignature - Kerberos - X.509Document60 pagesWork Security - DigitalSignature - Kerberos - X.509Abdul Rasheed Mohamed AliNo ratings yet
- Package Digest R SoftwareDocument15 pagesPackage Digest R SoftwareViorel AdirvaNo ratings yet
- University QuestionsDocument24 pagesUniversity QuestionsVasantha KumariNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity For Kids Volume 2Document16 pagesCybersecurity For Kids Volume 2Ammar HassanNo ratings yet
- Date: Grade/Section: Teacher: Subject: Activity NoDocument10 pagesDate: Grade/Section: Teacher: Subject: Activity Noarlyn villanuevaNo ratings yet
- P79 Gen121 Gen403Document2 pagesP79 Gen121 Gen403monalika7deshmukhNo ratings yet
- Download full chapter Information Technology For Management Driving Digital Transformation To Increase Local And Global Performance Growth And Sustainability 12Th Edition Turban pdf docxDocument54 pagesDownload full chapter Information Technology For Management Driving Digital Transformation To Increase Local And Global Performance Growth And Sustainability 12Th Edition Turban pdf docxchristopher.marlow821No ratings yet
- Module Code & Module Title CC5004NI Security in ComputingDocument49 pagesModule Code & Module Title CC5004NI Security in ComputingRoshik GamingNo ratings yet
- Ebook The CISO Guide To SAP Cybersecurity RisksDocument21 pagesEbook The CISO Guide To SAP Cybersecurity RisksIncresol asptaxNo ratings yet
- Template SE Testcases DocumentDocument2 pagesTemplate SE Testcases DocumentPavanpraneetha KunukuNo ratings yet
- CompTIA SecurityPlus AcronymsDocument4 pagesCompTIA SecurityPlus AcronymsYaseen GNo ratings yet
- 1 AISS13 Pre Release PDFDocument3 pages1 AISS13 Pre Release PDFTalluri PaulNo ratings yet
- GSM SecurityDocument20 pagesGSM SecurityAnand PrakashNo ratings yet
- Fact BookDocument83 pagesFact Bookamie indraNo ratings yet
- Hacking SimplifiedDocument17 pagesHacking Simplifiedsamarth kariaNo ratings yet
- Configuración VPN Site To Site Juniper CiscoDocument5 pagesConfiguración VPN Site To Site Juniper CiscoAntonio PeredaNo ratings yet
- CS 502Document46 pagesCS 502Ur MnNo ratings yet
- Crowdstrike Huge Fan of Your Work Intelligence ReportDocument16 pagesCrowdstrike Huge Fan of Your Work Intelligence ReportTEL FET100% (1)
- Saracevic Adamovic Bisevac 86Document20 pagesSaracevic Adamovic Bisevac 86Tudor MicuNo ratings yet
- VPN QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesVPN Questionnaire黃木子No ratings yet
- LICENCIASDocument5 pagesLICENCIASFerDD2No ratings yet
- ISEHV7 Course CalendarDocument15 pagesISEHV7 Course CalendarAppin NitinNo ratings yet