Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gouty Arthritis
Gouty Arthritis
Uploaded by
kabbun enterprises0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesGouty Arthritis
Gouty Arthritis
Uploaded by
kabbun enterprisesCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
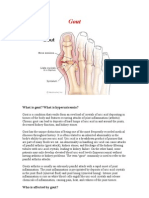
Gouty Arthritis
Gouty arthritis, commonly known as gout, is a type of
inflammatory arthritis characterized by sudden, severe
attacks of pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in
the joints, often affecting the big toe.
Types of Gouty Arthritis:
There are two main types of gouty arthritis:
1. Acute Gout
2. Chronic Gout
Cause of Gouty Arthritis:
Gout is caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the
blood, known as hyperuricemia.
Signs and Symptoms of Gouty Arthritis:
- Tenderness to touch.
- Limited range of motion in the joint.
- Fever, in some cases.
Diagnostic Findings of Gouty Arthritis:
- Elevated serum uric acid levels (>6.8 mg/dL).
- Synovial fluid analysis showing the presence of
needle-shaped rate crystals.
- Imaging studies (X-rays, ultrasound, or CT scans)
may show joint damage or the presence of tophi in
chronic gout.
Treatment or Management of Gouty Arthritis:
- Acute attacks: NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-
inflammatory drugs), colchicine, or corticosteroids to
relieve pain and inflammation.
- Lifestyle modifications: Low-purine diet, weight loss,
reduced alcohol intake.
- Medications to lower uric acid levels (urate-lowering
therapy): Allopurinol, febuxostat, probenecid.
- Avoidance of triggers: Certain foods (e.g., red meat,
organ meats, seafood), alcohol, and medications that
can increase uric acid levels.
Management of gouty arthritis aims to relieve
symptoms, prevent future attacks, and reduce the risk
of complications such as joint damage and tophi
formation. Regular monitoring of uric acid levels and
adherence to treatment are essential for effective
management.
You might also like
- Kuliah Gouty ArthritisDocument56 pagesKuliah Gouty Arthritischrysandre100% (1)
- Gout & PseudogoutDocument14 pagesGout & PseudogoutPatrick CommettantNo ratings yet
- GOUTDocument3 pagesGOUTHenry KaweesaNo ratings yet
- GoutDocument6 pagesGoutNader Smadi100% (1)
- Name: ID:: Madiha Sayed Nagy. 51859Document12 pagesName: ID:: Madiha Sayed Nagy. 51859drng48No ratings yet
- GoutDocument6 pagesGoutNhoydaleen SandovalNo ratings yet
- What Is GoutDocument11 pagesWhat Is GoutProser Faith TabaculdeNo ratings yet
- Gout In-Depth ReportDocument29 pagesGout In-Depth ReportEllen Grace CalayNo ratings yet
- GoutDocument3 pagesGoutashylajaraniNo ratings yet
- Gout Gout (Also Known As Podagra When It Involves The Big Toe) Is ADocument5 pagesGout Gout (Also Known As Podagra When It Involves The Big Toe) Is AJoanna Erika TanNo ratings yet
- Hyperurecimia and GoutDocument3 pagesHyperurecimia and GoutSunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- GoutDocument19 pagesGoutpawannnnNo ratings yet
- GoutDocument5 pagesGoutDe Sesto Rhys Carlo100% (2)
- Gouty PowerpointDocument14 pagesGouty PowerpointBSN4ANo ratings yet
- Gout Arthritis Konas IRA Palembang 2018Document48 pagesGout Arthritis Konas IRA Palembang 2018YULIANo ratings yet
- Written Report 2Document8 pagesWritten Report 2IsaacNo ratings yet
- Gout DLL ArtikelDocument74 pagesGout DLL ArtikelFawzia Haura FathinNo ratings yet
- Case Review GoutDocument21 pagesCase Review GoutLaras Bani WasesoNo ratings yet
- Notes-Management of Patients With Rheumatoid DisordersDocument6 pagesNotes-Management of Patients With Rheumatoid DisordersCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Synopsis: Urgent Action Key PointsDocument13 pagesSynopsis: Urgent Action Key PointsBlue PoopNo ratings yet
- CaseDocument66 pagesCaseJustin HannahNo ratings yet
- EtoricoxibfinalasprintedDocument4 pagesEtoricoxibfinalasprintedFarah ShaniaNo ratings yet
- The Rich Man'S DiseaseDocument9 pagesThe Rich Man'S DiseaseSixtyskillsNo ratings yet
- Capture I 1.1 Background: Vel Artiticam Vocant - The Gout That Is Called Podagra or Arthtritis') Was The DominicianDocument8 pagesCapture I 1.1 Background: Vel Artiticam Vocant - The Gout That Is Called Podagra or Arthtritis') Was The DominicianDevy Syahputri Tanjung100% (1)
- Arthritis DR SalmanDocument41 pagesArthritis DR SalmanSaliha AkramNo ratings yet
- Hyperuricemia XXXX XXXXX XxjeuneDocument32 pagesHyperuricemia XXXX XXXXX XxjeuneOziq Juga ReMa-eNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Physical Therapy Interventions For Gout Arthritis - Single Case Study ReportDocument11 pagesEffectiveness of Physical Therapy Interventions For Gout Arthritis - Single Case Study ReportLoubna AdnaneNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Gout EnglishDocument8 pagesJurnal Gout EnglishPutri ArtikaNo ratings yet
- Pemicu 4 Putu GOUTDocument31 pagesPemicu 4 Putu GOUTTirtha MaharaniNo ratings yet
- NCP Nursing Care Plan For Gout Gouty ArthritisDocument4 pagesNCP Nursing Care Plan For Gout Gouty ArthritisFatima Qaushar Manam100% (2)
- Joint Pain - ClassDocument88 pagesJoint Pain - ClassPrecious ChaiNo ratings yet
- GoutDocument2 pagesGoutTeodora PetcuNo ratings yet
- Dhaneshwar Prasad Yadav Junior InternDocument15 pagesDhaneshwar Prasad Yadav Junior InternJanak KcNo ratings yet
- GoutDocument12 pagesGoutEarle Jimenez Niervo RN100% (1)
- GoutDocument7 pagesGoutTharen OfficialNo ratings yet
- GoutDocument15 pagesGoutRatih PurwaningsihNo ratings yet
- sID2018 04 25 - 101056Document37 pagessID2018 04 25 - 101056Kate KateNo ratings yet
- MSK Lecture DR - Ba 2014 15Document55 pagesMSK Lecture DR - Ba 2014 15marina_shawkyNo ratings yet
- Lect # 2 Care of Patients With Gout and Paget's DiseaseDocument21 pagesLect # 2 Care of Patients With Gout and Paget's DiseaseShayan ShayanNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy: Jagir R. Patel Assistant Professor Dept. PharmacologyDocument45 pagesPharmacotherapy: Jagir R. Patel Assistant Professor Dept. PharmacologybikeyNo ratings yet
- What Is It?Document3 pagesWhat Is It?putrielindaNo ratings yet
- Chapter VI - Bone Pathology: Arthritis & GoutDocument4 pagesChapter VI - Bone Pathology: Arthritis & GoutIndranil SinhaNo ratings yet
- A2 Group 3 GOUTDocument83 pagesA2 Group 3 GOUTArt Buenaventura0% (1)
- All About Gout: A Patient Guide To Managing GoutDocument8 pagesAll About Gout: A Patient Guide To Managing Goutmath_mallikarjun_sapNo ratings yet
- Got ADocument5 pagesGot AViribu GaliciaNo ratings yet
- L Joint Pain Mine Updated 22-23 V2Document61 pagesL Joint Pain Mine Updated 22-23 V2swing.sujuNo ratings yet
- Gouty ArthritisDocument12 pagesGouty ArthritisManoj KandoiNo ratings yet
- 2033 Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument48 pages2033 Rheumatoid Arthritisdinaarzina100% (1)
- Diabetic Foot, Diabetic Foot Ulcer & Diabetic Foot Care: Prepared by Munirah Supervised by DR NaqibDocument49 pagesDiabetic Foot, Diabetic Foot Ulcer & Diabetic Foot Care: Prepared by Munirah Supervised by DR NaqibAfifah SelamatNo ratings yet
- Bone andDocument33 pagesBone andSuci MayveraNo ratings yet
- Disorder of Musculo - System. LeatestDocument178 pagesDisorder of Musculo - System. LeatestCheru TecheNo ratings yet
- ARTHRITISDocument42 pagesARTHRITISYvonneNo ratings yet
- Report On OA and GoutDocument11 pagesReport On OA and GoutZnieh ZniehNo ratings yet
- Acutely Swollen JointDocument7 pagesAcutely Swollen JointHossein VakiliNo ratings yet
- Osh State UniversityDocument14 pagesOsh State Universitykhuzaima9No ratings yet
- Lapkas Dalam Reumatologi Heri EnglishDocument21 pagesLapkas Dalam Reumatologi Heri EnglishHera HeraNo ratings yet
- Anti GoutDocument41 pagesAnti GoutGareth BaleNo ratings yet
- TODADocument1 pageTODAkabbun enterprisesNo ratings yet
- Full Presidential SystemsDocument6 pagesFull Presidential Systemskabbun enterprisesNo ratings yet
- Budget Plan Science 5 Third Quarter: No. of Days EnhancementDocument2 pagesBudget Plan Science 5 Third Quarter: No. of Days Enhancementkabbun enterprisesNo ratings yet
- Science Investigatory Project: Prepared By: Maria Aleli R. Martinez Isabela West District I Grade VDocument10 pagesScience Investigatory Project: Prepared By: Maria Aleli R. Martinez Isabela West District I Grade Vkabbun enterprisesNo ratings yet