Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Online Food Delivery App Foodie
Online Food Delivery App Foodie
Uploaded by
Dr. A. Haja Abdul KhaderOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Online Food Delivery App Foodie
Online Food Delivery App Foodie
Uploaded by
Dr. A. Haja Abdul KhaderCopyright:
Available Formats
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.
net/publication/353474489
Online Food Delivery App ‘Foodie’
Article · July 2021
DOI: 10.51201/JUSST/21/07200
CITATIONS READS
11 13,274
3 authors, including:
Muskan Jain
Raisoni Group of Institutions
4 PUBLICATIONS 18 CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE
All content following this page was uploaded by Muskan Jain on 12 May 2022.
The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file.
Journal of University of Shanghai for Science and Technology ISSN: 1007-6735
Online Food Delivery App ‘Foodie’
Hemant Kumar1, Muskan Jain2, Manpreet Singh Bajwa 3
1,2
Student, 3Assistant Professor
1, 2
Faculty of Engineering and Technology,
SGT University, Gurugram, India
1
iihemantbhagat@gmail.com, 2imuskan.jain22@gmail.com, 3manpreet_feat@sgtuni
versity.org
Abstract:The purpose of this thesis is to build an online food ordering application
named “FOODIE”. Our research also includes the “satisfaction of consumers by using
online food services”. It will deal with consumer behaviour & helps to analyse their
perceptions & will also help us to understand consumer equilibrium. Through these
platforms, sharing one’s experience with others has become so easy, in the form of
reviews, be it regarding a product brought or any kind of service availed.
Keywords:Online food ordering, Mobile Application, Foodie, Customer
Satisfaction
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of mobile technology, mobile application is connecting every
field all together. Therefore, food industry is using this technology in connecting with
vast public through online food ordering. Online food ordering may be a process that
delivers food from local restaurants and other food co-operatives through a mobile
application or an internet site. This type of food delivery is gaining popularity with more
and more people especially the younger generation turning to mobile food ordering apps,
thereby changing the way food is delivered and picked up [1]. Customers prefer using the
food ordering app as they will generate an order without having to elucidate it to a special
person and have the food delivered at his doorstep. Moreover, online payment makes this
process easier and faster. Some popular online food ordering companies are “Swiggy”,
“Zomato”.
Popular machine learning algorithms like Decision Tree were applied over a dataset of
lakhs of records. For the customer, this application provides a view of food information
like category, name, image, price, description etc. on the application. For the
administrator in any particular restaurant, this application offers a series of operations to
add, update, delete and query the information of food, food order, customer and
employees. The typical mechanism behind food delivery is as follows: the user on the
food delivery application chooses a restaurant to order food from, checks the menu list,
select food to order and proceed to payment. Once payment is done, an employee i.e., the
rider nearby the location picks food from the restaurant and delivers to the user’s home
[2]. This also increases employability as a platform is provided to deliver food to the
houses.
The basic features that are needed by the customers in an application are making order,
food review, order history, restaurant profile, profile setting, order status, and track order.
Volume 23, Issue 7, July - 2021 Page -761
Journal of University of Shanghai for Science and Technology ISSN: 1007-6735
The features that are needed in website for restaurant are: restaurant profile, order
(incoming, dispatched), menu (modification, availability), and courier [3].
2. Related work
The journey of food delivery services came when the term ‘Dabbawalas’ was used to
service where lunches were packed and sent through rail or bicycle to the working
professionals in Mumbai, India. Then, with the development in technology and in the
world of mobile phones and internet, the first food delivery service was given in 1995 by
“World Wide waiter” (Waiter.com) in northern California where the restaurants had
partnered with the services to take their offline menus in online world. Now, most of the
countries have their own online food ordering applications which connect small
restaurants to the consumers sitting at home and either they do not have the time or the
transport to go to these restaurants. Also, some people just avoid going out to these
crowded places and prefer eating at home. The past work present discussed the use of
mobile application with internet of things, and cloud computing for different purposes
which also includes food delivery. In this system, application focuses on targeted
audience, and the users enter their data through login, then the data is processed, and the
users utilize the facilities available [4]. These mobile applications are made by developers
using different platforms, languages: Java, and SQL, for developing front end: Android
Studio Development Kit, and back end: MySQL Server, Wamp Server [5].
The food delivery platforms are reviewed by the consumers on the basis of star rating [6]
which depends on various factors like customer satisfaction, timely delivery, and the
customers intention to use it again in future [7]. A study in [8] compares the popularity of
online food delivery apps- Zomato, Swiggy and uber eats based on the delivery services
provided. It is not necessary that a particular application is popular worldwide, popularity
changes with the location, and perception of the consumers [9]. The paper [8] concluded
that Zomato is the most successful online food delivery platform in Ludhiana, India. E-
payment is also an important factor deciding the user’s preference of choosing a platform
over many other platforms. The paper [10] tells all the important factors that affect the
adoption of food delivery apps. The paper also surveys about the age group, gender, and
the marital status of the customers that prefer ordering food at home and concludes that
around 59% of the people like eating at home rather than dining out. The paper [11]
builds a food ordering application for Tom Yum Thai Oy, a Thai restaurant in Vaasa.
The table below has different food delivery platforms used in different countries:
Table 1. Different Food Delivery Apps
S. Fooddelivery Year of Country of origin Reference
No services foundation
1 Zomato 2008 Delhi, India 12
2 Swiggy 2014 Bangalore, India 13
3 Uber eats 2014 San Francisco, 14
California, U.S.
4 Food Panda 2012 Singapore 15
5 GoFood 2018 Indonesia 16
Volume 23, Issue 7, July - 2021 Page -762
Journal of University of Shanghai for Science and Technology ISSN: 1007-6735
6 GrabFood 2012 Singapore 17
7 GrubHub 2004 Chicago, Illinois 18
8 Faasos 2011 Pune, India 19
9 DoorDash 2013 Palo Alto, 20
California, U.S.
10 Super meal 2012 Birmingham, UK 21
11 Seamless 1999 New York, U.S. 22
12 Deliveroo 2013 London, England, 23
UK
13 Dunzo 2014 Bengaluru, India 24
14 Potafo 2017 Kozhikode, India 25
15 Postmates 2011 San Francisco, 26
California, U.S.
16 Just eat 2001 Kolding, Denmark 27
17 Square Eats 2020 Botswana, Africa 28
18 Ele.me 2008 China 29
19 iFood 2011 São Paulo, State of 30
São Paulo, Brazil
20 Demae-Can 1999 Japan 31
3. Objective
The main objective of the paper is to provide an online food delivery app “FOODIE”
which can serve the society with an added advantage by ordering from two or more places
if in the same route or within 5-6 km range, and the customer can only register once using
Aadhar verification and secure log-in, it makes the web portal safe for transactions. Also,
to eliminate the wait time, the users can book a table at the restaurant of their choice with
just a few taps.
The purpose of this invention is to provide profit in terms of Stakeholders [32], easy in
terms of the app user, diverse options for ordering food, improvising in Delivery
mechanism to solve the hectic situation created by single place, single order criteria.
The app is very much easy to use as all it requires is an internet connection, just log in to
the web-portal/app and the user can order from multiple locations and can also order for
more than one location in one time. With the services, responsibilities come hand-in-
hand, it is very important to know the satisfaction of the customers in terms of using the
services, timely delivery, their intention to use the app again. So, our paper includes “the
satisfaction of customers” which also makes the business profitable as customer
satisfaction is directly proportional to the recommendation a restaurant gets every time a
customer checks the reviews. If the previous customer is satisfied and gives good reviews
then only the next customer thinks of ordering from the same, if not the customer has
Volume 23, Issue 7, July - 2021 Page -763
Journal of University of Shanghai for Science and Technology ISSN: 1007-6735
many other options to go to. So, it is very important to satisfy the customers to make
one’s name in the market.
4. Technology Used
In a food ordering mobile application different algorithm are used for different purposes.
All the data related to the customers, meals, list of restaurants are processed using
machine learning algorithms. With help of AI and machine learning: Gradient Boosting
Decision Trees, the sequence in which the notification of the orders sent to the delivery
person is improved. The decision tree algorithm and the random forest algorithms helps
by classifying the restaurant into different groups based on the reviews obtained by the
customers on the basis of the services provided [33]. Also, AI and ML helps connect the
customers to the right restaurants without letting them roam around for the perfect meal
and increase the efficiency of the food delivery operations. Therefore, AI & ML
implementation can foster Real-time, micro-optimization of dynamic demand-supply,
millions of times every day which can result in grow in online delivery business in order
value by 200%. Some AI-driven kiosks apps use Facial recognition to give a personalised
experience to customers, speeds up selection and ordering process and decreases wait
time.
Machine learning is used in 3 main areas on the food delivery business:
1. Route planning for deliveries
2. Sales forecasts and amount to food to be prepared (avoid waste)
3. Product suggestion
• Route Planning’s ML applications goal is to achieve reduced delivery times and costs.
Usually, neural networks that work with past data as input and suggest best fit
scenarios for new routes.
• Sales forecasts ML applications goal is to reduce costs and inefficiencies in the
supply chain level. It uses as input sell-in and sell-out information, price, price
elasticity, market demand data proxies to generate production and stock quantity
suggestions to maximize sell-out while reducing cost and avoiding food waste.
• Product suggestion ML applications goal is, well, to suggest food that you might like
to order based on preferences, on-site navigation, previously ordered items and more.
The final goal of these applications of course is to sell more.
Cloud computing can also play vital role in food industry in areas like Customer
Relationship Management, Customer Service and Supply Chain Management [34]. By
using cloud computing, the food service providers ensure the delivery of the right product
in the right place at the right time as it connects people and companies in real-time and for
making food service provider’s work easier.
Apart from these technologies, the food delivery application is developed using different
platforms, for both front and back end. For front end, programming languages like C++,
Java is used for android/apple mobile phones. To make work easy some cross platform
applications are developed using different frameworks to help make apps that can work
on different platforms. Some of the framework’s present are PhoneGap, jQuery Mobile,
AngularJS, and Ajax. These frameworks help in improving the app quality, the cost for
app development is comparatively low, and the targeted audience is large as it combines
multiple platforms [35].
Volume 23, Issue 7, July - 2021 Page -764
Journal of University of Shanghai for Science and Technology ISSN: 1007-6735
After the development of the application, one of the factors which plays a very important
role in the success of the online food delivery application is different payment methods
[36]. Customer Convenience, secured payment architecture, Strategy for referral coupon,
different Payment preference of the customers, and various Discount by Portals all comes
under e-payment systems and result in increase in volume in sale.
Table 2. Technologies used
Objective C
Swift
Programming Languages
Java
Kotlin
PhoneGap
jQuery Mobile
Frameworks
AngularJS
Ajax
HTML5
CSS3
Web development
JavaScript
XML
PHP
Data scripting
MySQL
Xcode
IDE
Android Studio
Cloud Storage Amazon S3
Mongo DB
Database
Redis
Google Analytics
Utilities
Visual Website Optimizer
Mixpanel
Analytics Google Analytics
Keen.io
Gmail
Email
AWS
Cloud
Deployment platforms iOS
Android
MD5 encryption (Message Digest
Data Encryption algorithm 5)
SSL (secure socket layer)
5. Customer Satisfaction
With the covid-19 outbreak, lockdown restrictions do not allow people to enjoy dine- in
services in the restaurants which affected the world’s economy and restaurant sales
[37][38] but online food delivery services provided non- contact delivery prepared food
Volume 23, Issue 7, July - 2021 Page -765
Journal of University of Shanghai for Science and Technology ISSN: 1007-6735
and thus enabled the food providers to keep operating. The online ordering of food has
greatly influenced and changed the way of people’s eating habits and preferences while
ordering food online [39]. Every customer has their own preference, for some timely
delivery is important, for others payment options or quality of food is important. The
main factors influencing the consumers to order food online are: short delivery time,
convenient, easy accessibility, very flexible, different mode of payments, and promotions/
offers [40].
6. Proposed System
The app, FOODIE focuses only on delivery, so that the registered restaurants can promote
their offers and meals without bothering the delivery of the orders as Foodie will not take
any 'MINIMUM ORDER' tag on offer or meal as they are fulfilling the end consumers
demand by delivering food from the local restaurants, whereas in apps like 'Food Panda'
the restaurants decide 'minimum order amount' to order as they have to deliver the order
to the end consumer by their own-selves or a customer has to go and pick up the food
once it's prepared at the restaurant.
The application charges a certain amount of fee from the restaurateurs to get their
restaurants listed on the mobile app for promotion or new meals or new nearby options.
When the user places an order, a notification is sent to the restaurateur, the nearest
delivery person, and the platform owner. By collaborating at every stage with a powerful
algorithm, all the three stakeholders: The Restaurant Owners, The Platform Owner, and
The Delivery Professionals maintain the smooth functioning of the platform for the users.
The app Foodie will not own any restaurant or chain of delivery services. It coordinates
with the third party to plan supply for the demand that arises.
6.1. Features
• Food ordering: Allowing the users to order their food on-the-go from two different
restaurants.
• No minimum order: The customer does not have to a minimum amount to order from
a restaurant.
• Table Booking: Enables the users to book a table at the listed restaurant of their
choice with just a few taps and the wait time at the restaurant is eliminated.
• Explore Places: Offering the discovery and guide to the user for exploring nearby
restaurants with pictures, reviews and map locations.
• One Many Schemes: Ordering from two places at the same time and with the
powerful algorithm of Single Source Shortest Path will include the Pickups as Red
and If all pickups are done than the order is ready to go and will not find out the
single source path from that node to Delivery location
• Time-saving, the invention is capable of reducing the processing time to half of the
existing rate with diverse options for food, as food ordering not limited to just one
restaurant at a time.
• Online payments, online payments facilitate the flow of the money in the right
direction, a step forward to corruption-free India.
• Eco-friendly, the process proposed saves unnecessary wastage of paper of making
every document digitally.
• A user-friendly interface makes it easy to clear all doubts at one doorstep.
• Aadhar verification and secure log in the password makes the web portal safe to use
in terms of online tractions and fund transfer.
Volume 23, Issue 7, July - 2021 Page -766
Journal of University of Shanghai for Science and Technology ISSN: 1007-6735
• Less use of the renewable source of energy and have a big task performed in lesser
time.
Table 2. Existing Applications
S.no Existing Drawbacks in existing Overcome
state of art state of art
1 Food Min Order No Min Order
Panda
2 Zomato Single restaurant Can order from two
orderingmechanism, places or more if in the
one user can register same route OR within 5-
multiple times using 6 km range, a user can
multiple numbers, User register only once, User-
Interface not good friendly User Interface
3 Uber eats Fake complaints Complaint registration
leading to loss of the with proper proof, user
company, one user can can register only once
register multiple times
using multiple
numbers
6.2. Advantages
• Opened 24/7
• Save time and money
• Reduce costs
• Hits the target market
• Online delivery mechanism
• Food can be ordered from multiple sources
• Paper wastage is reduced
• Route optimization is attained
• Multiple payment methods- cash on delivery, credit/debit cards, google pay
• Helps in building up a social community for new food joints
• Live tracking available
• A win-win situation for all stakeholders
Volume 23, Issue 7, July - 2021 Page -767
Journal of University of Shanghai for Science and Technology ISSN: 1007-6735
Figure 1. Working of food delivery apps
Volume 23, Issue 7, July - 2021 Page -768
Journal of University of Shanghai for Science and Technology ISSN: 1007-6735
Figure 2. The mechanism from user end
References
1. Rahman H. (2019), A Review of the Usable Food Delivery Apps, International Journal of Engineering
Research & Technology (IJERT) ISSN: 2278-0181 Vol. 8 Issue 12, December-2019.
DOI: 10.17577/IJERTV8IS120052
2. M. Li, J. Zhang and W. Wang, "Task Selection and Scheduling for Food Delivery: A Game-Theoretic
Approach," 2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), pp. 1-6.
DOI: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2018.8647947
3. Ricky M.Y., (2014). Mobile Food Ordering Application using Android OS Platform. The European
Physical Journal Conferences 68.DOI:10.1051/epjconf/20146800041
4. Sharma, "Mission Swachhta : Mobile application based on Mobile Cloud Computing," 2020 10th
International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science & Engineering (Confluence), Noida, India,
2020, pp. 133-138.DOI: 10.1109/Confluence47617.2020.9057926
Volume 23, Issue 7, July - 2021 Page -769
Journal of University of Shanghai for Science and Technology ISSN: 1007-6735
5. Leong, W.H. (2016). Food Ordering System Using Mobile Phone. Available online at:
http://eprints.utar.edu.my/1943/1/IA-2016-1203135-1.pdf
6. Z. Cahyani, R. Nurcahyo and Farizal, "Popularity Analysis of Mobile Food Ordering Apps In
Indonesia," 2020 IEEE 7th International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Applications
(ICIEA), Bangkok, Thailand, 2020, pp. 1000-1004.DOI: 10.1109/ICIEA49774.2020.9102024
7. Alalwan A.A. (2020), Mobile food ordering apps: An empirical study of the factors affecting customer
e-satisfaction and continued intention to reuse, International Journal of Information Management, Vol
50, Pages 28-44, ISSN 0268-4012.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.04.008.
8. Raina A., Rana V., Thakur A. (2019), Popularity of Online Food Ordering and Delivery Services- A
Comparative study between Zomato, Swiggy and Uber Eats in Ludhiana. Available online at:
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/341109906_POPULARITY_OF_ONLINE_FOOD_ORDERIN
G_AND_DELIVERY_SERVICES-A_COMPARATIVE_STUDY_BETWEEN_ZOMATO_
SWIGGY_AND_UBER_EATS_IN_LUDHIANA
9. Tribhuvan A. (2020). A STUDY ON CONSUMERS PERCEPTION ON FOOD APPS. International
Journal Of Advance Research And Innovative Ideas In Education. 6. 36. Available online at:
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/342765294_A_STUDY_ON_CONSUMERS_PERCEPTION_
ON_FOOD_APPS
10. Gupta A., Gupta A., Singh S., Surana V. (2019). FACTORS AFFECTING ADOPTION OF FOOD
DELIVERY APPS. International Journal of Advanced Research. 7. 587-
599.DOI:10.21474/IJAR01/9871
11. Fan Y. (2014), MOBILE FOOD ORDERING APPLICATION, Vaasa University of Applied
Science.Available online at: http://urn.fi/URN:NBN:fi:amk-201405198481
12. Panigrahi A., Saha A., Shrinet A., Nauityal M., Gaur V. (2020). A case study on Zomato – The online
Foodking of India. Journal of Management Research and Analysis. 7. 25-33.
DOI:10.18231/j.jmra.2020.007
13. Anib A., Gayathri A., Shabu K. R., (2019). “Consumer Perception towards Swiggy Digital Food
Application Service: A Analytical Study with Special Reference to Ernakulam City.” International
Journal of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering (IJITEE) ISSN: 2278-3075, Volume-8
Issue-6S, 2019. Available online at: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Consumer-Perception-
towards-Swiggy-Digital-Food-A-Anib-Gayathri/e4f7fe78213a231cfa45c8a64f300621d486a16c
14. Leão A., Cabral L., Gomes R., Gonçalves B., Oliveira J., Alencar D. (2019). Shared Economy: A Uber-
Eats Case Study in Manaus City. International Journal for Innovation Education and Research. 7. 450-
466. 10.31686/ijier.Vol7.Iss11.1899. DOI:10.31686/ijier.Vol7.Iss11.1899
15. Ahmed J., Ahmed A. (2018). Foodpanda: Changing the Way Bangladeshi Eat Meals.
DOI: 10.4135/9781526444561
16. Prastiwi S., Iswari P. (2019). The Roles of Trust within Information Quality and Price to Engage
Impulsive Buying Behaviour to Generate Customer’s Repurchase Intention: A Case of M-Commerce in
Indonesia (GoFood). KnE Social Sciences. DOI: 10.18502/kss.v3i26.5391
17. Indraswari V. N., Suryono I. D., (2020) Comparative Analysis of Service Marketing Mix Variables
Considered in Food Delivery Services (Case Study on GoFood and GrabFood), Indonesian College of
Economics – 2020.
Available online at: http://repository.stei.ac.id/1865/2/87.%20jurnal%20skripsi.id.en.pdf
18. GrubHub: Grubhub Reports Fourth Quarter and Full Year 2020 Results. Available online
at: https://investors.grubhub.com/investors/press-releases/press-release-details/2021/Grubhub-Reports-
Fourth-Quarter-And-Full-Year-2020-Results/default.aspx
19. Ravishankar G.V., How Faasos disrupted its business model to create India’s largest cloud kitchen.
Available online at:https://www.sequoiacap.com/india/article/faasos-indias-largest-cloud-kitchen/
20. DoorDashThe Deep Dish: Food Trends in 2020. Available online at: https://blog.doordash.com/the-
deep-dish-food-trends-in-2020-74656ce7621f
21. Supermeal adds online food ordering platform to the UAE's home dining scene (2020). Available online
at: https://www.arabianbusiness.com/retail/451331-supermeal-adds-online-food-ordering-platform-to-
the-uaes-home-dining-scene
22. Gu X., Seamless ecoEATS Feature Integration Case Study (2018). Available online
at: https://medium.com/@xian.l.gu/seamless-ecoeats-feature-integration-case-study-11d54ad8184c
23. Iqbal M., Deliveroo Revenue and Usage Statistics (2020). Available online
at: https://www.businessofapps.com/data/deliveroo-statistics/
24. Mahesh V.J., Hari P., Customer’s perception towards DUNZO delivery service (2020), Journal of
Contemporary Issues in Business and Government Vol. 26, No. 2, 2020. Available online
at: https://cibg.org.au/article_7906_453328964553466b5a6adcb27e3da115.pdf
25. Potafo - A Food Delivery App From the Food Capital of God’s Own Country. Available online
at: https://www.bizencyclopedia.com/article/potafo-the-food-delivery-app-from-the-food-capital-of-
gods-own-country
26. Curry D., Postmates Revenue and Usage Statistics (2021).
Available online at: https://www.businessofapps.com/data/postmates-statistics/
Volume 23, Issue 7, July - 2021 Page -770
Journal of University of Shanghai for Science and Technology ISSN: 1007-6735
27. Curry D., Just Eat Revenue and Usage Statistics (2021).
Available online at:https://www.businessofapps.com/data/just-eat-statistics/
28. Writer S., Verbosec launches its Food-Delivery Service Square Eats in Botswana (2020). Available
online at:https://azhizhi.com/1664/verbosec-launches-its-food-delivery-service-square-eats-in-botswana/
29. Cissy, (2017) Ele.me, Digitizing the food delivery service in China.Available online
at:https://digital.hbs.edu/platform-rctom/submission/ele-me-digitizing-the-food-delivery-service-in-
china/
30. Fioravanti R., iFood delivers great results in Brazil going beyond connecting restaurants with customers.
Available online at:https://digital.hbs.edu/platform-digit/submission/ifood-delivers-great-results-in-
brazil-going-beyond-connecting-restaurants-with-customers/
31. Demae-can “出前館” The First Home Delivery Service in Japan.
Available online at:https://www.smileswallet.com/guide-of-demaecan-food-delivery/
32. Charlene L., Mirosa M., Bremer P. (2020), "Review of Online Food Delivery Platforms and their
Impacts on Sustainability" Sustainability 12, no. 14: 5528. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145528
33. Shina, Sharma S., Singla A. (2018), A Study of Tree Based Machine Learning Techniques for
Restaurant Reviews. 1-4. DOI:10.1109/CCAA.2018.8777649
34. Ahsan K., Nouman N., Kamran A., Hussain F., Ahmed S.N. “Cloud-Based Shared Food Ordering
System with Context Awareness: A Location Base Services Approach.” (2013). Available online
at:https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Cloud-Based-Shared-Food-Ordering-System-with-A-Base-
Ahsan-Nouman/416d5bd5170abb8a8881a7be859d5b62a04d5a33
35. Abid F. and Karim A. N., "Cross-platform development for an online food delivery application," 2017
International Conference on Computing Networking and Informatics (ICCNI), pp. 1-4.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCNI.2017.8123769
36. Ghosh R. and Saha T., “A STUDY OF E-PAYMENT SYSTEM ON FOOD DELIVERY INDUSTRY:
A CASE STUDY ON SWIGGY.” (2018). International Journal on Recent Trends in Business and
Tourism Vol. 2 NO. 3 (2018).Available online at:
http://ejournal.lucp.net/index.php/ijrtbt/article/download/187/152
37. Collison J. (2020), The Impact of Online Food Delivery Services on Restaurant Sales. Available online
at:https://web.stanford.edu/~leinav/teaching/Collison.pdf
38. Das S., Ghose D. (2019), Influence Of Online Food Delivery Apps On The Operations Of The
Restaurant Business, International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research ISSN 2277-8616, Vol 8,
Issue 12, Dec- 2019. Available online at:http://www.ijstr.org/final-print/dec2019/Influence-Of-Online-
Food-Delivery-Apps-On-The-Operations-Of-The-Restaurant-Business-.pdf
39. Bhat A. A. (2019). SATISFACTION OF CONSUMERS BY USING ONLINE FOOD SERVICES.
Social Science. 10 pages. Available online at:
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333642857_SATISFACTION_OF_CONSUMERS_BY_USIN
G_ONLINE_FOOD_SERVICES
40. Rathore S., Chaudhary M., Consumer's Perception on Online Food Ordering, International Journal of
Management & Business Studies (IJMBS) Vol. 8, Issue 4, Oct - Dec 2018. Available online
at:http://www.ijmbs.com/Vol8/issue4/2-suryadev-singh-rathore.pdf
Volume 23, Issue 7, July - 2021 Page -771
View publication stats
You might also like
- Programming Kotlin Enhance Your Skills For Android Development Using Kotlin by Alexander Aronowitz PDFDocument299 pagesProgramming Kotlin Enhance Your Skills For Android Development Using Kotlin by Alexander Aronowitz PDFPawan KumarNo ratings yet
- Writing Magazine April 2019Document131 pagesWriting Magazine April 2019Daniyal AbbasNo ratings yet
- Development of Abhidharma Theory of Citta and Caitasika - HuifengDocument75 pagesDevelopment of Abhidharma Theory of Citta and Caitasika - HuifengTenzin SopaNo ratings yet
- Ecommerce App ReportDocument39 pagesEcommerce App ReportHarsh JaniNo ratings yet
- IB MYP 1 3 p1 2 Spanish SAMPLECHAPTERDocument36 pagesIB MYP 1 3 p1 2 Spanish SAMPLECHAPTERBoss Mann Blues100% (2)
- College Management SystemDocument39 pagesCollege Management SystemdaffoNo ratings yet
- I Shall Paint My Nails Red Critical Appreciation: TitleDocument4 pagesI Shall Paint My Nails Red Critical Appreciation: TitleJoyce Diys & CraftsNo ratings yet
- Basics of English SpeakingDocument2 pagesBasics of English SpeakingHhimanshu UmraoNo ratings yet
- Celce Mucia Communicative Competence ModelDocument16 pagesCelce Mucia Communicative Competence Modelnjwoodward100% (2)
- Field Work Project (Raw) Swiggy/Zomato/Uber EatsDocument11 pagesField Work Project (Raw) Swiggy/Zomato/Uber EatsAmit ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Project Report Online Banking SystemDocument39 pagesProject Report Online Banking SystemAkash BansalNo ratings yet
- MB183210 Bharath M Gaddikeri - A Study On Opportunities and Challenges of Online Food Order Receiving and Delivery of Food With Special Reference To Zomato in BengaluruDocument39 pagesMB183210 Bharath M Gaddikeri - A Study On Opportunities and Challenges of Online Food Order Receiving and Delivery of Food With Special Reference To Zomato in BengaluruBharath GaddikeriNo ratings yet
- Mini ProjectDocument32 pagesMini ProjectDeepa ArunNo ratings yet
- ZomatoDocument7 pagesZomatoRenieNo ratings yet
- 19LCMD026 Dilip G - 220706 - 115618Document97 pages19LCMD026 Dilip G - 220706 - 115618Saif AdnanNo ratings yet
- Major Project Report FormatDocument6 pagesMajor Project Report Formatbiplabmandal50% (2)
- Report On School Management SystemDocument22 pagesReport On School Management SystemAKSHAT0% (1)
- Cheathen Cms FINAL-1Document91 pagesCheathen Cms FINAL-1Rishikeshav kumarNo ratings yet
- Gym Management System: G. S. College of Commerce & Economics, Nagpur (Autonomous) (Computer Application) Final YearDocument129 pagesGym Management System: G. S. College of Commerce & Economics, Nagpur (Autonomous) (Computer Application) Final YearS Mohamed AsifNo ratings yet
- Online Food Ordering Management System Project Report PDFDocument34 pagesOnline Food Ordering Management System Project Report PDFSwedha RNo ratings yet
- Project Report On CNDocument42 pagesProject Report On CNBittu kumar mandalNo ratings yet
- Web Traffic Time Series Forecasting Using ARIMA ModelDocument9 pagesWeb Traffic Time Series Forecasting Using ARIMA ModelIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Online Unused Medicine Donation PortalDocument3 pagesOnline Unused Medicine Donation PortalAsad Khan DadloNo ratings yet
- Food Ordering System Using QR CodeDocument19 pagesFood Ordering System Using QR Codejoker0% (1)
- Unit 1Document95 pagesUnit 1qra7yb1No ratings yet
- Edpp ProjectDocument40 pagesEdpp ProjectYash AnandNo ratings yet
- Crop Yeild SystemDocument71 pagesCrop Yeild Systemteja internet xeroxNo ratings yet
- DocumentsDocument46 pagesDocumentsAnkit GuravNo ratings yet
- Research Report B5Document88 pagesResearch Report B5Kuldeep GadhiaNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Website Using PythonDocument2 pagesE-Commerce Website Using PythonSaurabh ChopadeNo ratings yet
- Sectoral Analysis: Porter's 5 ForcesDocument1 pageSectoral Analysis: Porter's 5 ForcesIshan ShuklaNo ratings yet
- To Do App Using Flutter ReportDocument11 pagesTo Do App Using Flutter ReportSpoorthi KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 WT Dinesh DodejaDocument12 pagesAssignment 1 WT Dinesh DodejadineshNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On: Restaurant Management SystemDocument25 pagesA Project Report On: Restaurant Management SystemRijo vargheseNo ratings yet
- Mini Project Food AppDocument44 pagesMini Project Food AppAbilashi SinghNo ratings yet
- Secure Email Transaction SystemDocument32 pagesSecure Email Transaction SystemGautam Sharma100% (1)
- Android-Summer-Training-Report Imteyaj Part Part 1Document27 pagesAndroid-Summer-Training-Report Imteyaj Part Part 1Utkarsh MauryaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Covid-19 On Digital Payment Services at Towns and VillagesDocument11 pagesImpact of Covid-19 On Digital Payment Services at Towns and VillagesShameerNo ratings yet
- Pune Institute of Computer Technology, DHANKWADI, PUNE - 411043Document7 pagesPune Institute of Computer Technology, DHANKWADI, PUNE - 411043Yash Doke100% (1)
- E-Commerce Website Publication PaperDocument9 pagesE-Commerce Website Publication PaperSoham Shrikant manjrekarNo ratings yet
- A Report On Analysis of Medical Equipment's PresentablyDocument45 pagesA Report On Analysis of Medical Equipment's PresentablySubrat PatnaikNo ratings yet
- Smart CrawlerDocument92 pagesSmart CrawlerAmmuNo ratings yet
- Project Report ON Online Food Oerdering SystemDocument101 pagesProject Report ON Online Food Oerdering SystemHIMANSHU MISHRA 1847227No ratings yet
- Medical Shop MGT - Black BookDocument61 pagesMedical Shop MGT - Black Bookmas libraryNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Consumer Purchase IntensionDocument4 pagesPrediction of Consumer Purchase IntensionIJARSCT Journal100% (1)
- IMIS Full Paper A Conceptual Study of Q Commerce Sustainability in IndiaDocument11 pagesIMIS Full Paper A Conceptual Study of Q Commerce Sustainability in IndiaHARSH KUMAR SINGHNo ratings yet
- A Report On Social NetworkingDocument38 pagesA Report On Social Networkingqazplm2007No ratings yet
- Project ON E-Commerce in Global Scenario: Submitted To: Submitted byDocument36 pagesProject ON E-Commerce in Global Scenario: Submitted To: Submitted byraghav bansalNo ratings yet
- Order Processing SystemDocument70 pagesOrder Processing SystemAmruth ThangamNo ratings yet
- Major Project ReportDocument82 pagesMajor Project ReportNaveen RajputNo ratings yet
- Food Donation and Waste ManagementApplicationDocument3 pagesFood Donation and Waste ManagementApplicationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Ignou Mca Mini Project Report 83734067Document123 pagesIgnou Mca Mini Project Report 83734067sohailNo ratings yet
- Library Management System: A Minor Project Report OnDocument5 pagesLibrary Management System: A Minor Project Report OnAbhay JainNo ratings yet
- Study On Consumer Perception and Attitude TowardsDocument48 pagesStudy On Consumer Perception and Attitude Towardsgaurav gargNo ratings yet
- Minor Project Report Piku CompressDocument47 pagesMinor Project Report Piku CompressRAHUL MAURYANo ratings yet
- Hensole Client Management SystemDocument89 pagesHensole Client Management SystemMako KazamaNo ratings yet
- Share and Care: A Food Donation Web ApplicationDocument9 pagesShare and Care: A Food Donation Web ApplicationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Automobile Inventory VB - Net ProjectDocument21 pagesAutomobile Inventory VB - Net ProjectAsim MahatoNo ratings yet
- Python ProgrammingDocument17 pagesPython ProgrammingBad Man100% (1)
- Developing A Service Delivery Model To Bridge The Gap Between Services Expected and Provided by ICICI Home Loans.Document43 pagesDeveloping A Service Delivery Model To Bridge The Gap Between Services Expected and Provided by ICICI Home Loans.johnashmitNo ratings yet
- Dbms Course ReportDocument35 pagesDbms Course ReportJames williamNo ratings yet
- Finally ReportDocument56 pagesFinally ReportAnishSahniNo ratings yet
- Student Examination Data Card: Micro Project Report OnDocument17 pagesStudent Examination Data Card: Micro Project Report OnRohan KambleNo ratings yet
- Iftm University, Moradabad: A Research Project Report ONDocument4 pagesIftm University, Moradabad: A Research Project Report ONMadhur GuptaNo ratings yet
- Home Service ProviderDocument75 pagesHome Service ProviderVansh RanaNo ratings yet
- A Study On Customers' Perception and Satisfaction Towards Online Food Delivery System in Coimbatore CityDocument5 pagesA Study On Customers' Perception and Satisfaction Towards Online Food Delivery System in Coimbatore CityBrindhaNo ratings yet
- IRJMETS137399 ZomatocasestudyDocument9 pagesIRJMETS137399 ZomatocasestudyAMBIKA BANERJEENo ratings yet
- IOT Proj - Report 1Document31 pagesIOT Proj - Report 1Diksha NasaNo ratings yet
- IOT Proj - ReportDocument17 pagesIOT Proj - ReportDiksha NasaNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusDiksha NasaNo ratings yet
- ASTW RA03 PracticalManualDocument18 pagesASTW RA03 PracticalManualDiksha NasaNo ratings yet
- Final Record Analog Consists of All The Materials That U Can Get Full MarksDocument171 pagesFinal Record Analog Consists of All The Materials That U Can Get Full MarksDiksha NasaNo ratings yet
- IJSRP Paper Submission Format Single ColumnDocument3 pagesIJSRP Paper Submission Format Single ColumnDiksha NasaNo ratings yet
- MC250 International Preselection Kit 2023 (Updated Oct 22)Document31 pagesMC250 International Preselection Kit 2023 (Updated Oct 22)Diksha NasaNo ratings yet
- Material Point MethodDocument37 pagesMaterial Point MethodJoe SatchNo ratings yet
- BIDNEY 1950 American AnthropologistDocument11 pagesBIDNEY 1950 American AnthropologistasturgeaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Selection Screen Generation For SAP SolutionsDocument13 pagesDynamic Selection Screen Generation For SAP SolutionsAbhijeet GuptaNo ratings yet
- Present Continous TenseDocument13 pagesPresent Continous TenseaaulNo ratings yet
- BlueZone Display & Printer HelpDocument688 pagesBlueZone Display & Printer HelpLalo EscuderoNo ratings yet
- Notre Dame of Salaman College Inc.: Children and Adolescent Literature ELT 111-BSED 3 English Week 9-12Document13 pagesNotre Dame of Salaman College Inc.: Children and Adolescent Literature ELT 111-BSED 3 English Week 9-12Rosalie Mallorca BlancaNo ratings yet
- Compare Contrast ParagraphDocument3 pagesCompare Contrast ParagraphmoonNo ratings yet
- Sample Test BlueprintDocument9 pagesSample Test BlueprintLOUIE ALVAREZNo ratings yet
- Imagined Conditions: Conditionals: IfDocument2 pagesImagined Conditions: Conditionals: IfDerya ışılNo ratings yet
- 4 G - CENG03cd. Ev.Document105 pages4 G - CENG03cd. Ev.Even mathiasNo ratings yet
- Msp430 ManualDocument582 pagesMsp430 ManualSilambarasan MadhaiyanNo ratings yet
- CP2K: Introduction and Orientation: 4 CECAM CP2K Tutorial, 31 Aug - 4 Sep 2015 Iain Bethune Ibethune@epcc - Ed.ac - UkDocument48 pagesCP2K: Introduction and Orientation: 4 CECAM CP2K Tutorial, 31 Aug - 4 Sep 2015 Iain Bethune Ibethune@epcc - Ed.ac - UkDr. Dinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Century Literature in The PhilDocument7 pagesCentury Literature in The PhilAnonymous awqKHCnNo ratings yet
- SnmpHttpAssignment Fall2023Document3 pagesSnmpHttpAssignment Fall2023hamza.nayefNo ratings yet
- CPM System Guide ScreenDocument232 pagesCPM System Guide ScreenJose Luis ColladoNo ratings yet
- XCP Pro User ManualDocument64 pagesXCP Pro User ManualdataromaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 SemanticsDocument18 pagesChapter 9 SemanticsSadafz channelNo ratings yet
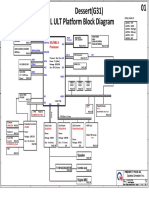
- Quanta G31a Dag31amb6d0 Y61x-6l Rev 1aDocument49 pagesQuanta G31a Dag31amb6d0 Y61x-6l Rev 1aKrystian PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Style of TranslationDocument325 pagesStyle of Translationmerve sultan vuralNo ratings yet
- Oracle Financial FaqDocument259 pagesOracle Financial FaqAndrea NguyenNo ratings yet
- SPCC AssignmentDocument6 pagesSPCC AssignmentKennethNo ratings yet
- Protobuf TutorialDocument112 pagesProtobuf Tutorialvaram10No ratings yet
- Ambuhay Ambuhay Ambuhay Ambuhay: A More Profound PresenceDocument4 pagesAmbuhay Ambuhay Ambuhay Ambuhay: A More Profound PresenceJoviner Yabres LactamNo ratings yet