0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views10 pagesQuick Guide To QRI
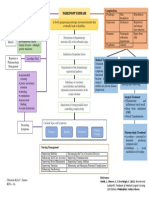
This document provides guidance on administering and interpreting the QRI-5 reading assessment. It outlines procedures for administering word lists, concept questions, reading passages, and comprehension questions. It also provides guidance on interpreting student performance in areas like word recognition, automaticity, oral vs silent reading, familiar vs unfamiliar texts, and identifying potential reading disabilities.
Uploaded by
Rashida MaynardCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views10 pagesQuick Guide To QRI
This document provides guidance on administering and interpreting the QRI-5 reading assessment. It outlines procedures for administering word lists, concept questions, reading passages, and comprehension questions. It also provides guidance on interpreting student performance in areas like word recognition, automaticity, oral vs silent reading, familiar vs unfamiliar texts, and identifying potential reading disabilities.
Uploaded by
Rashida MaynardCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd