0% found this document useful (0 votes)
61 views19 pagesVertex Cover & Bin Packing Guide
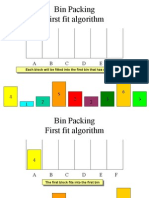
The document discusses the vertex cover problem, set cover problem, and bin packing problem. It provides examples and describes greedy algorithms that can be used to find approximate solutions for set covering and bin packing.
Uploaded by
abcxyz19691969Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
61 views19 pagesVertex Cover & Bin Packing Guide
The document discusses the vertex cover problem, set cover problem, and bin packing problem. It provides examples and describes greedy algorithms that can be used to find approximate solutions for set covering and bin packing.
Uploaded by
abcxyz19691969Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd