0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views6 pagesQualitative Characteristics in Accounting
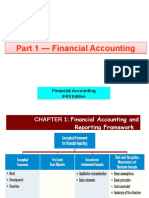
The document discusses the qualitative characteristics of accounting information that make it useful for decision making. It identifies relevance and faithful representation as the two fundamental qualities, and also discusses enhancing qualities like comparability, verifiability, timeliness, and understandability. An exercise is included that tests understanding of applying the different characteristics.
Uploaded by
camlansuc09993Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views6 pagesQualitative Characteristics in Accounting
The document discusses the qualitative characteristics of accounting information that make it useful for decision making. It identifies relevance and faithful representation as the two fundamental qualities, and also discusses enhancing qualities like comparability, verifiability, timeliness, and understandability. An exercise is included that tests understanding of applying the different characteristics.
Uploaded by
camlansuc09993Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd