THE HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM VOCABULARY
Word Meaning
To take something in, as in absorbing something through the skin or the
Absorption intestine. The large and small intestines use this method to receive
important nutrients from the foods and beverages we consume.
the opening at the end of the large intestine
anus
the process by which soluble food molecules carried by the blood are
Assimilation
absorbed by our body cells
green liquid used in digestion (emulsification) of fat
bile
teeth for shredding food
canines
cecum connected to the appendix, this pouch marks the beginning of the large
intestine.
process by which large molecules are broken down into smaller molecules
chemical digestion
This is a term for food that is partially digested. It passes from your
chyme
stomach into the upper part of your small intestine.
This is a part of the large intestine that runs from the cecum to the rectum.
It is an extensive hollow tube that removes water from digested food so it
colon
can be reused by the body. The remaining solid waste or stool moves
through the colon to the rectum, leaving the body through the anus.
a condition in which the contents of the large intestine are dry causing
constipation
bowel movements to be difficult and less frequent
diarrhea a condition in which bowel movements are frequent and watery
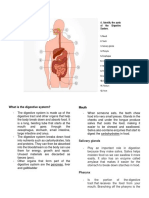
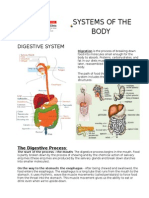
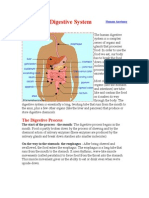
The digestive system consists of organs that get food in and out of the
body and use what is available from it. These organs include the mouth,
digestive system
salivary glands, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, liver, gallbladder,
pancreas, large intestine, rectum, and anus.
a series of tube-like organs that are joined end to end
digestive tract
the first portion of the small intestine; connects the stomach and the small
duodenum intestine
Egestion The process through which undigested food is removed from the body
enamel the outermost layer of a tooth; the hardest material in the body.
special substances that break down some nutrients into smaller particles
enzymes
that the body can use.
epiglottis small flap of tissue that covers the windpipe (trachea) when you swallow
a long, straight tube that connects the mouth and throat to the stomach.
oesophagus There are also glands that line the oesophagus and produce mucus,
which also aids in swallowing.
waste product that has been formed into a soft, solid mass
faeces
This is a pear-shaped organ found below the liver. It stores an important
digestive enzyme, bile, which is secreted by the liver. After consuming a
meal with fats in it, the gallbladder will deliver bile through bile ducts into
gall bladder the intestines to help with digestion.
Ileum The ileum is the lowest part of the small intestine. It can be found after the
duodenum and jejunum, just before the colon.
� teeth for cutting food
incisors
Part of the small intestine. It is half-way down the small intestine between
Jejunum
its duodenum and ileum sections.
Found after the small intestine. It is termed the large intestine because it is
large intestine wider than the small intestine. It absorbs extra water from undigested
materials
a large, reddish organ that produces bile and stores nutrients. It helps
liver with digestion and removes waste products and worn-out cells from the
blood
mechanical physical breaking down of large pieces of food into smaller pieces
digestion
teeth for grinding food
molars
an organ between the stomach and small intestine that produces enzymes
pancreas for chemical digestion.
rhythmic muscle contractions that forces food into the stomach.
peristalsis
a series of muscular contractions that pushes material through the
peristalsis digestive system
teeth for mashing food
premolars
rectum the last section of the large intestine
liquid from the salivary glands; begins chemical digestion of carbohydrates
saliva
– liquid from the salivary glands; begins chemical digestion of
saliva carbohydrates
a muscular tube about 6 m long; the site of most chemical digestion. The
part of the digestive tract found after the stomach and before the large
small intestine intestine. This is where most nutrients are absorbed from food.
sphincters bands of muscles at either end of the stomach
a muscular, J-shaped organ of the digestive tract; attached to the lower
stomach end of the oesophagus.
finger like projections sticking out of the walls of the intestines increasing
villi the surface area improving the body's ability to absorb nutrients