Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Shoe Maker Buys Materials and Makes Them Into Lace
Uploaded by
deepakdec0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views4 pagesCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views4 pagesA Shoe Maker Buys Materials and Makes Them Into Lace
Uploaded by
deepakdecCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Management Science
Assignment On Simplex Method Using Artificial Variables
Prof. Veerachamy.R
Submitted by
Group 4
M.B.A 1uly`2011
By,
Mr. DEEPAK.R
Mr. PRANAV AGARWAL
Mr. SUMIT GHIDIA
Mr. PRITAM 1INDAL
Mr. SHARAD ANAND
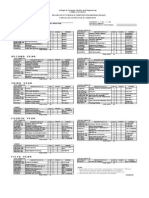
Simplex Method using ArtiIicial Variables
O A shoe maker buys materials and makes them into lace, tongue, and sole. In a month he can make 500 units oI one type
or all the items together. Lace and tongue combined order per month is at least 150 units. Sole order per month exceeds
lace and tongue by 100 units. The revenue Irom lace, tongue and sole are Rs.75, Rs.125 and Rs.150 per unit
respectively. Formulate this statement into a linear programming problem and obtain its solution. (Using artiIicial
variables).
Solution:
Let X
1
, X
2
, X
3
be the number oI units oI lace, tongue, and sole.
For simplex Iormat, introduce one slack to the Iirst constraint. Subtract one surplus to constraint 2. To have the initial
basis we add two artiIicial variables to second and third constraints respectively. But now note that in the objective Iunction
minus unit coeIIicients are being introduced Ior artiIicial variables because oI maximization problem.
To have the initial basis we add two artiIicial variables to second and third constraints respectively.
Max C = 0X
1
+ 0X
2
+ 0X
3
+ 0E
1'
+ 0E
2'
- 1A
1
- 1A
2
S.to X
1
+ X
2
+ X
3
+ S
1
= 500
X
1 + X
2 - E
2 + A
1 = 150
X
1 - X
2 - X
3 + A
2 = 100
X
1
; X
2
; X
3
; S
1
; E
2
; A
1
; A
2
0 K
Phase 1
Ci Basis X
1
X
2
X
3
S
1
E
2
A
1
A
2
X
b Ratio
0 S
1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 500 500
-1 A
1 1 1 0 0 -1 1 0 150 150
-1 A
2
1 -1 -1 0 0 0 1 100 100
C
j
0 0 0 0 0 -1 -1
Z
j -2 0 1 0 1 -1 -1 -250
C
j
-Z
j 2 0 -1 0 -1 0 0
Tablau 1
Maximize 75X
1
+ 125X
2
+ 150X
3
S.to X
1
+ X
2
+ X
3
500
X
1
+ X
2
150
X
1
- X
2
- X
3
= 100
X
1
; X
2
; X
3
0 K
A
K
Ci Basis X
1
X
2
X
3
S
1
E
2
A
1
X
b Ratio
0 S
1 0 2 2 1 0 0 400 200
-1 A
1 0 2 1 0 -1 1 50 25
0 X
1
1 -1 -1 0 0 0 100 -100
C
j
0 0 0 0 0 -1
Z
j 0 -2 -1 0 1 -1 -50
C
j
-Z
j 0 2 1 0 -1 0
Tableau 2
Ci Basis X
1
X
2
X
3
S
1
E
2
X
b Ratio
0 S
1 0 0 1 1 1 350 200
0 X
2 0 1 0.5 0 -0.5 25 25
0 X
1
1 0 -0.5 0 -0.5 125 -100
C
j
0 0 0 0 0
Z
j 0 0 0 0 0 0
C
j
-Z
j 0 0 0 0 0
Tableau 3
Phase II
Ci Basis X
1
X
2
X
3
S
1
E
2
X
b Ratio
0 S
1 0 0 1 1 1 350 350
125 X
2 0 1 0.5 0 -0.5 25 50
75 X
1
1 0 -0.5 0 -0.5 125 -250
C
j
75 125 150 0 0
Z
j 75 125 25 0 -100 12500
C
j
-Z
j 0 0 125 0 100
Tableau 4
Ci Basis X
1
X
2
X
3
S
1
E
2
X
b Ratio
0 S
1 0 -2 0 1 2 300 150
150 X
3 0 2 1 0 -1 50 -50
75 X
1
1 1 0 0 -1 150 -150
C
j
75 125 150 0 0
Z
j 75 375 150 0 -225 18750
C
j
-Z
j 0 -250 0 0 225
Tableau 5
Ci Basis X
1
X
2
X
3
S
1
E
2
X
b Ratio
0 E
2 0 -1 0 0.5 1 150 150
150 X
3 0 1 1 0.5 0 200 -50
75 X
1
1 0 0 0.5 0 300 -150
C
j
75 125 150 0 0
Z
j 75 150 150 112.5 0 52500
C
j
-Z
j 0 -25 0 -112.5 0
Tableau 6
FinalResult:
So the optimum values are: X
1
300, X
3
200, Z 52500.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Camera Parts and FunctionsDocument29 pagesCamera Parts and FunctionslizaNo ratings yet
- 24 Trig Identity ProblemsDocument4 pages24 Trig Identity ProblemsAldrean TinayaNo ratings yet
- Service Manual Cat G3416eDocument753 pagesService Manual Cat G3416eUsaha MandiriNo ratings yet
- Moody's Report 2005Document52 pagesMoody's Report 2005as111320034667No ratings yet
- Business Research Methods: Session 6 To 7Document109 pagesBusiness Research Methods: Session 6 To 7Contact InfoNo ratings yet
- SPC1 Single Phase Power Controller PDFDocument6 pagesSPC1 Single Phase Power Controller PDFMin ZayarNo ratings yet
- BDSP Lecture 3Document79 pagesBDSP Lecture 3Mohammed FarisNo ratings yet
- Lcs Lab 9 M.ZahadatDocument17 pagesLcs Lab 9 M.ZahadatAhmed Hassan RajpootNo ratings yet
- BS Computer Engineering 2009 CurriculumDocument1 pageBS Computer Engineering 2009 CurriculumChristopher KusumiNo ratings yet
- Datalogic P51 Operator's ManualDocument2 pagesDatalogic P51 Operator's ManualGodzilNo ratings yet
- AMOS Business Suite Vrs. 10.1.00 Getting Started User GuideDocument35 pagesAMOS Business Suite Vrs. 10.1.00 Getting Started User GuideAttrapezioNo ratings yet
- 2018 Math QuizDocument15 pages2018 Math Quizmaria arliza torioNo ratings yet
- CEC2017 After Revision Final VersionDocument9 pagesCEC2017 After Revision Final VersionAli GhavamiNo ratings yet
- S N Ne C Las Es L: Quantitative AptitudeDocument33 pagesS N Ne C Las Es L: Quantitative AptitudeanuragNo ratings yet
- Burnishing Is A Process by Which A Smooth Hard Tool (UsingDocument9 pagesBurnishing Is A Process by Which A Smooth Hard Tool (UsingΒασίλης ΜπουντιούκοςNo ratings yet
- Interrupts and Traps in Oberon-ARMDocument3 pagesInterrupts and Traps in Oberon-ARMmqt99311zwoho.comNo ratings yet
- TLM Ports in UVMDocument8 pagesTLM Ports in UVMtejaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test ResultsDocument1 pageDiagnostic Test ResultsGUILMOR PADILLANo ratings yet
- Priorclave Autoclave Benchtop 40 60 Smart Data SheetDocument2 pagesPriorclave Autoclave Benchtop 40 60 Smart Data Sheetbrayo4No ratings yet
- Chapters 29 and 35 Thermochemistry and Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument54 pagesChapters 29 and 35 Thermochemistry and Chemical ThermodynamicsDanice Amie ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- KR C1 A: Technical DataDocument11 pagesKR C1 A: Technical Dataayxworks eurobotsNo ratings yet
- MM 1Document6 pagesMM 1Rana Naveed0% (1)
- Sinumerik 802dDocument212 pagesSinumerik 802dThanh BuiNo ratings yet
- Graphing Absolute Value WorksheetDocument20 pagesGraphing Absolute Value WorksheetRudyr BacolodNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE Unit 2E Homeostasis and Excretion - Self-Assessment SheetDocument6 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Unit 2E Homeostasis and Excretion - Self-Assessment SheetAli ALEBRAHIMNo ratings yet
- Ee701-N Interconnected Power SystemDocument4 pagesEe701-N Interconnected Power Systemayan PatelNo ratings yet
- Physical: MetallurgyDocument4 pagesPhysical: MetallurgySanjanaNo ratings yet
- HMT SKDocument60 pagesHMT SKsunilkewat11390No ratings yet
- Components of A CAD/CAM System: 2.1 General PointsDocument2 pagesComponents of A CAD/CAM System: 2.1 General PointsaffanNo ratings yet
- The OscilloscopeDocument6 pagesThe OscilloscoperiverajluizNo ratings yet