0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views1 pageGlycolysis
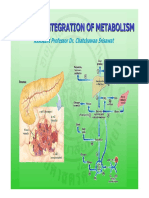
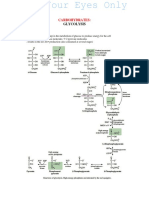
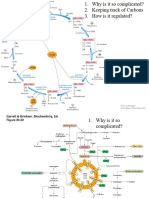
The document outlines various metabolic pathways including glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, glycogenesis, glycogenolysis, HMP, citric acid cycle, fatty acid synthesis, and beta-oxidation, detailing their locations, rate-determining steps, stimulation, inhibition, and occurrence. Each pathway is characterized by specific regulatory factors such as hormones and metabolites that influence their activity. The information is organized in a comparative format, highlighting the differences and similarities among these metabolic processes.
Uploaded by
Marione Thea RodriguezCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views1 pageGlycolysis
The document outlines various metabolic pathways including glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, glycogenesis, glycogenolysis, HMP, citric acid cycle, fatty acid synthesis, and beta-oxidation, detailing their locations, rate-determining steps, stimulation, inhibition, and occurrence. Each pathway is characterized by specific regulatory factors such as hormones and metabolites that influence their activity. The information is organized in a comparative format, highlighting the differences and similarities among these metabolic processes.
Uploaded by
Marione Thea RodriguezCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd