0% found this document useful (0 votes)
438 views13 pagesCausal Research Design Classification
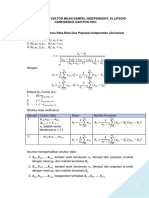
Causal research uses experimental design to determine "if-then" relationships and make claims about causality, unlike other non-experimental designs that can only find associations. There are three key conditions for determining causality: covariation between variables, proper time ordering, and ruling out other possible causes. Experimental designs involve manipulating an independent variable and measuring its effect on a dependent variable, while controlling for extraneous variables. Common experimental designs include pre-experimental, true experimental, quasi-experimental, and statistical designs that allow for statistical analysis and control of external factors. Limitations of experiments include time/cost requirements and difficulty administering experiments without interference.
Uploaded by
rahulmittaCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
438 views13 pagesCausal Research Design Classification
Causal research uses experimental design to determine "if-then" relationships and make claims about causality, unlike other non-experimental designs that can only find associations. There are three key conditions for determining causality: covariation between variables, proper time ordering, and ruling out other possible causes. Experimental designs involve manipulating an independent variable and measuring its effect on a dependent variable, while controlling for extraneous variables. Common experimental designs include pre-experimental, true experimental, quasi-experimental, and statistical designs that allow for statistical analysis and control of external factors. Limitations of experiments include time/cost requirements and difficulty administering experiments without interference.
Uploaded by
rahulmittaCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd