Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MF - Basics
Uploaded by
siddulaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MF - Basics
Uploaded by
siddulaCopyright:
Available Formats
Mutual Fund Concept, Organizational Structure, Advantages and Types
CONCEPT ORGANISATION OF A MUTUAL FUND ADVANTAGES OF MUTUAL FUNDS TYPES OF MUTUAL FUND SCHEMES FREQUENTLY USED TERMS
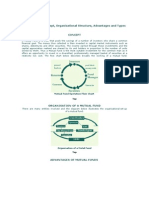
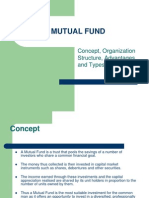
CONCEPT A Mutual Fund is a trust that pools the savings of a number of investors who share a common financial goal. The money thus collected is then invested in capital market instruments such as shares, debentures and other securities. The income earned through these investments and the capital appreciation realised are shared by its unit holders in proportion to the number of units owned by them. Thus a Mutual Fund is the most suitable investment for the common man as it offers an opportunity to invest in a diversified, professionally managed basket of securities at a relatively low cost. The flow chart below describes broadly the working of a mutual fund:
Mutual Fund Operation Flow Chart ORGANISATION OF A MUTUAL FUND There are many entities involved and the diagram below illustrates the organisational set up of a mutual fund:
Organization of a Mutual Fund ADVANTAGES OF MUTUAL FUNDS The advantages of investing in a Mutual Fund are: Professional Management Diversification Convenient Administration Return Potential
Low Costs Liquidity Transparency Flexibility Choice of schemes Tax benefits Well regulated TYPES OF MUTUAL FUND SCHEMES Wide variety of Mutual Fund Schemes exists to cater to the needs such as financial position, risk tolerance and return expectations etc. The table below gives an overview into the existing types of schemes in the Industry.
FREQUENTLY USED TERMS Net Asset Value (NAV) Net sset Value is the market value of the assets of the scheme minus its liabilities. The per unit NAV is the net asset value of the scheme divided by the number of units outstanding on the Valuation Date. Sale Price Is the price you pay when you invest in a scheme. Also called Offer Price. It may include a sales load. Repurchase Price Is the price at which units under open-ended schemes are repurchased by the Mutual Fund. Such prices are NAV related. Redemption Price Is the price at which close-ended schemes redeem their units on maturity. Such prices are NAV related. Sales Load Is a charge collected by a scheme when it sells the units. Also called, Front-end load. Schemes that do not charge a load are called No Load schemes. Repurchase or Back-endLoad Is a charge collected by a scheme when it buys back the units from the unitholders.
You might also like
- AMFI For PostalDocument3 pagesAMFI For PostalMurali KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Mutual Fund: Concept, Organisation Structure, Advantages and TypesDocument10 pagesMutual Fund: Concept, Organisation Structure, Advantages and TypesAnil SinghNo ratings yet
- ICICI Mutual Fund Project FinalDocument101 pagesICICI Mutual Fund Project FinalD PriyankaNo ratings yet
- Mutual Funds NotesDocument6 pagesMutual Funds Notes✬ SHANZA MALIK ✬100% (2)
- Mutual FundDocument13 pagesMutual Fundpuneetk20No ratings yet
- Mutual Funds FinalDocument17 pagesMutual Funds FinalswatitikkuNo ratings yet
- Mutual Fund - PPT TSMDocument30 pagesMutual Fund - PPT TSMGopi NathNo ratings yet
- Mutual Fund: Presented byDocument34 pagesMutual Fund: Presented byAshish SinghNo ratings yet
- Overview of Mutual Funds and InsuranceDocument17 pagesOverview of Mutual Funds and InsuranceKapil BajajNo ratings yet
- Mutual Fund: Concept, Organization Structure, Advantages and TypesDocument9 pagesMutual Fund: Concept, Organization Structure, Advantages and TypesCharu ModiNo ratings yet
- Customer Awareness on Mutual Funds at HSBC BankDocument82 pagesCustomer Awareness on Mutual Funds at HSBC BankbawamatharooNo ratings yet
- Camparative Study of Tata, Icici and HDFC Mutual FundsDocument86 pagesCamparative Study of Tata, Icici and HDFC Mutual FundsravikumarreddytNo ratings yet
- Mutual Funds SwethaDocument5 pagesMutual Funds SwethaSeetaramNo ratings yet
- An Overview On Mutual Fund InvestmentsDocument5 pagesAn Overview On Mutual Fund InvestmentsSeetaramNo ratings yet
- Mutual Fund: Concept, Organization Structure, Advantages and TypesDocument11 pagesMutual Fund: Concept, Organization Structure, Advantages and TypesvibhorjainNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mutual Fund and Its Various AspectsDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Mutual Fund and Its Various AspectsUzairKhanNo ratings yet
- .Mutual Funds Are Popular Among All Income Levels. With A Mutual Fund, We Get A Diversified Basket of Stocks Managed by A ProfessionalDocument17 pages.Mutual Funds Are Popular Among All Income Levels. With A Mutual Fund, We Get A Diversified Basket of Stocks Managed by A ProfessionalNaveenSemaltyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mutual FundsDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Mutual Fundsapi-3722617No ratings yet
- Mutual Funds: A Beginner'S ModuleDocument53 pagesMutual Funds: A Beginner'S ModuleNITIN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Mutual Fund: Concept, Organization Structure, Advantages and TypesDocument9 pagesMutual Fund: Concept, Organization Structure, Advantages and TypesMamatha PaiNo ratings yet
- Mutual Fund: Concept, Organisation Structure, Advantages and TypesDocument21 pagesMutual Fund: Concept, Organisation Structure, Advantages and Typesrprakash_33No ratings yet
- Mutual Fund Industry ProfileDocument37 pagesMutual Fund Industry ProfileGokul KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Pranav Kapse SIPDocument61 pagesPranav Kapse SIPAGRIFORCE SALESNo ratings yet
- FSM 1Document14 pagesFSM 1Sapna ShettyNo ratings yet
- MTFDocument2 pagesMTFchiragNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1: 1.1 Mutual Fund 1.1.1 DefinitionDocument64 pagesChapter - 1: 1.1 Mutual Fund 1.1.1 DefinitionSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Report of CPDocument15 pagesReport of CPVishal ShahNo ratings yet
- MF Module 1Document75 pagesMF Module 1Gouri K MakatiNo ratings yet
- Financial Services 3Document14 pagesFinancial Services 3Uma NNo ratings yet
- What Is A Mutual FundDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Mutual Fundlogu9225No ratings yet
- Executive SummaryDocument41 pagesExecutive SummaryArchana SinghNo ratings yet
- (Type The Document Title) : Mutual Fund - An IntroductionDocument31 pages(Type The Document Title) : Mutual Fund - An IntroductionAiti ShabongNo ratings yet
- Overview of Mutual Fund Performance MeasuresDocument12 pagesOverview of Mutual Fund Performance MeasuresLuthfunnahar SharminNo ratings yet
- Understanding Mutual FundsDocument29 pagesUnderstanding Mutual Fundsroshan_choudhury3269No ratings yet
- Mutual FundDocument51 pagesMutual Fundkuldeep_chand10No ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Introduction To Mutual FundsDocument122 pagesChapter - 1 Introduction To Mutual FundsJagjit KaurNo ratings yet
- Mutual Funds: Presented By: Saurabh Tamrakar Ravikant Tiwari Prateek DevraDocument25 pagesMutual Funds: Presented By: Saurabh Tamrakar Ravikant Tiwari Prateek DevraChanchal KansalNo ratings yet
- FM Mutual FundDocument9 pagesFM Mutual FundTanvi KansaraNo ratings yet
- Comparative Performance Evaluation of Selected Mutual Funds in IndiaDocument80 pagesComparative Performance Evaluation of Selected Mutual Funds in IndiaManish GargNo ratings yet
- Mutual FundsDocument36 pagesMutual FundsRavindra BabuNo ratings yet
- MUTUAL FUNDS: THEORITICAL BACKGROUND AND CONCEPTDocument25 pagesMUTUAL FUNDS: THEORITICAL BACKGROUND AND CONCEPTnagpalanishNo ratings yet
- Understanding Mutual FundsDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Mutual FundspareshhadkarNo ratings yet
- Comparative Performance Evaluation of Selected Mutual Funds in IndiaDocument87 pagesComparative Performance Evaluation of Selected Mutual Funds in IndiaKajal MahidaNo ratings yet
- Study of Mutual FundDocument8 pagesStudy of Mutual FundPRADIPNo ratings yet
- Mutual Funds ExplainedDocument3 pagesMutual Funds ExplainedafreenessaniNo ratings yet
- Project Mutual Fund in IndiaDocument16 pagesProject Mutual Fund in Indiasidhantha94% (31)
- Mutual Funds in IndiaDocument14 pagesMutual Funds in IndiaHarsh MittalNo ratings yet
- Mutual Funds: BY V.Sheeba JennipherDocument16 pagesMutual Funds: BY V.Sheeba Jennipherjenniphersheeba1520No ratings yet
- Lax MiDocument78 pagesLax MivsabhijitNo ratings yet
- Mutual Fund: Concept, Organisation Structure, Advantages and TypesDocument10 pagesMutual Fund: Concept, Organisation Structure, Advantages and TypesManjusha JoshiNo ratings yet
- d8c5cM&S IVDocument8 pagesd8c5cM&S IVashish_gupta_143No ratings yet
- Investors Capital Market Shares IncomeDocument15 pagesInvestors Capital Market Shares IncomeDevender PandeyNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1 Concept of Mutual FundDocument7 pages1.1.1 Concept of Mutual FundankitgrbsNo ratings yet
- Mutual Funds 1Document42 pagesMutual Funds 1Harsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Canadian Mutual Funds Investing for Beginners: A Basic Guide for BeginnersFrom EverandCanadian Mutual Funds Investing for Beginners: A Basic Guide for BeginnersNo ratings yet
- Ebook Exploring The Standardized Approach For Risk ManagementDocument14 pagesEbook Exploring The Standardized Approach For Risk ManagementsiddulaNo ratings yet
- Call For Papers For An Edited Volume BookDocument2 pagesCall For Papers For An Edited Volume BooksiddulaNo ratings yet
- Direct Taxes Circular - Sec. 10Document4 pagesDirect Taxes Circular - Sec. 10siddulaNo ratings yet
- Njogu Elizabeth Wanjira - Employee Perception of The Defined Contribution Pension Scheme in The Public SectorDocument66 pagesNjogu Elizabeth Wanjira - Employee Perception of The Defined Contribution Pension Scheme in The Public SectorsiddulaNo ratings yet
- Indian Stock Market and Great RecessionDocument18 pagesIndian Stock Market and Great RecessionsiddulaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Business Mathematics - CIMADocument23 pagesFundamentals of Business Mathematics - CIMAsiddulaNo ratings yet
- CAU Advertises Teaching PostsDocument8 pagesCAU Advertises Teaching PostssiddulaNo ratings yet
- Stock Return, Volatility and The Global Financial M PDFDocument13 pagesStock Return, Volatility and The Global Financial M PDFsiddulaNo ratings yet
- WWW Employmentnews Gov inDocument13 pagesWWW Employmentnews Gov insiddulaNo ratings yet
- Impact Analysis of Commodity Futures On Spot Prices PDFDocument14 pagesImpact Analysis of Commodity Futures On Spot Prices PDFsiddulaNo ratings yet
- HyderabadDocument5 pagesHyderabadsiddulaNo ratings yet
- UGC Major Project Guidelines 2012-17Document19 pagesUGC Major Project Guidelines 2012-17Manohargee ManoharNo ratings yet
- AP SET NotificationDocument1 pageAP SET NotificationsiddulaNo ratings yet
- Job Me La 2012Document2 pagesJob Me La 2012siddulaNo ratings yet
- January 2012 ETF ReportDocument3 pagesJanuary 2012 ETF ReportSandesh RaneNo ratings yet
- January 2012 ETF ReportDocument3 pagesJanuary 2012 ETF ReportSandesh RaneNo ratings yet