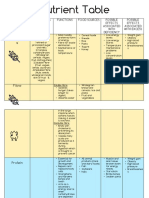
Food Exercise related function Source
group
Carbohydrat -Primary source of energy Simple – fruits, sweets
es -Main fuel for anaerobic / high intensity work Complex – bread, pasta, rice, vegetables
Fats -Source of energy for low intensity aerobic exercise as Saturated – butter, red meat
fats require o2 to be broken down so can’t be used for Unsaturated – olive oil, salmon
anaerobic work Trans fats – processed foods
-Can cause excessive weight gain if too much LDL–
affects stamina and flexibility
Protein -For muscle growth and repair Meat, fish, eggs
-Make enzymes, hormones, and haemoglobin
-Minor source of energy and mainly used by power
athletes who need to develop muscle tissue
Vitamins -C – protects cells and keeps them healthy, helps with -C – Green veg and fruit
maintenance of bones and ligaments -D – Made by body when exposed to
-D – role in absorption of magnesium sunlight
-B 1&2 – Help break down and release energy -B1- Eggs, liver, wholegrain bread, nuts,
-B1 – keeps nervous system healthy, read meat
-B2- keeps skin, eyes, and nervous system healthy, -B2 – Dairy, liver, veg, eggs, cereals
-B6 – Helps form haemoglobin, helps body use and store -B6 – Meat, fish, eggs, bread, veg, cereals
energy for protein and carbohydrates, -B12 – Red meat, dairy products, and fish
-B12- Makes RBC, and keeps nervous system healthy,
releases energy from food
Minerals -Assist in bodily functions Meat, fish, eggs, dairy products, cereals,
-Dissolved into the body as ions and are called vegetables, fruits and nuts
electrolytes
-Facilitate the transmission of nerve impulses
-Enable effective muscle contraction
Fibre -Can slow down the time it takes to break down food – Wholemeal bread, pasta, potatoes, nuts,
means slower more sustained release of energy seeds, fruit, vegetables and pulses
-Dietary fibre causes bulk in the small intestine helping
to prevent constipation and aiding digestion
�Water -Transports nutrients, hormones, and waste products Water regularly
around the body