Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Present Simple VB Present Continuous
Uploaded by
razvandkOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Present Simple VB Present Continuous
Uploaded by
razvandkCopyright:
Available Formats
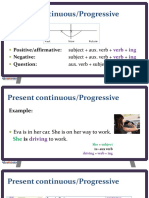
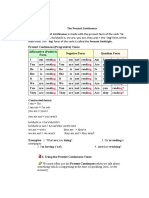
PRESENT TENSE SIMPLE
PRESENT TENSE CONTINUOUS
Forma Forma Forma verbului la prezent simplu se schimb doar y forma de baz + -ing: to draw-> drawing; dup he, she ori it. Astfel,adaug m: y forma de baz terminat n e + -ing: to y -s la forma de baz : I read-> he reads; take->taking; to receive->receiving; to create-> creating; y -es dup o, s, sh, ch, x: I go-> he goes; I miss-> she misses; I wash-> he washes; I y forma de baz terminat n consoan + watch-> she watches; I fix-> she fixes. ing: to swim->swimming; to run-> running. y -ies dup y: I cry-> she cries. to read I read a book. You read a book. He She reads a book. It We read a book. You read a book. They read a book. Negative form I don t read a book. You don t read a book. He She doesn t read a book. It We don t read a book. You don t read a book. They don t read a book. Interrogative form Do you read a book? he Does she read a book? it Do we read a book? Do you read a book? Do they read a book? to write I am writing a poem. You are writing a poem. He She is writing a poem. It We are writing a poem. You are writing a poem. They are writing a poem. Negative form I am not writing a poem. You are not (=aren t) writing a poem. He She is not (=isn t) writing a poem. It We are not (=aren t) writing a poem. You are not (=aren t) writing a poem. They are not (=aren t) writing a poem. Interrogative form Am I writing a poem? Are you writing a poem? he Is she writing a poem? It Are we writing a poem? Are you writing a poem? Are they writing a poem? Use y We often use the present simple to state truths and to describe things which we feel are facts or permanent situations. y The present continuous describes action in progress at the moment speaking or around the moment speaking. The action is possible an of of to
Use
Things that are generally true: British people drink a lot of tea. Facts: Broken bones in adults don t heal as fast as they do in children. Permanent situations: A colony of Antarctic penguins lives in Marwell Zoo. y
continue after the time of speaking, but it is temporary. I ll be with you in a minute. I m just finishing something in the kitchen. We are studying the writings of Gunter Grass on the German now.
We use the present simple to describe y We also use present continuous to repeated events/actions. describe things which are changing. With the approach of winter, the temperatures all British summers are getting hotter and winters are getting wetter. and the soil freezes. y It is possible to use the present continuous We use the present simple to describe a to talk about repeated actions or events, series of events or actions (for example, to usually if they happen within a temporary give directions). period. Cross the road, go through an iron gate and follow I m feeding the neighbour s cat this week while the path. shes s in the hospital. y We use the present continuous to describe complaints about annoying habits. You are always making rude remarks about my cooking. We often use the present continuous with adverbs as: now, just, still, at the moment. y VERY IMPORTANT!!! An exception to the use of the present continuous to describe action in progress is HERE COMES and THERE GOES, which are always in the present simple. Here comes the postman. There goes the last bus.
We often use the present simple with adverbs of frequency: always, usually, often, sometimes, never. We also use the present simple with expressions of frequency: every day, every week,etc.
There are some verbs which we rarely use in a continuous tense: be, exist, adore, dislike, hate, like, love, need, prefer, want, wish, believe, forget, imagine, know, remember, think, understand, depend, hear, see, smell, taste, etc.
You might also like
- The Present Continuous Is A Verb Tense Used To Show Actions (Autoguardado)Document41 pagesThe Present Continuous Is A Verb Tense Used To Show Actions (Autoguardado)diana31mayoNo ratings yet
- English Tenses: Simple Past TenseDocument5 pagesEnglish Tenses: Simple Past TenseHasnaoui DiaNo ratings yet
- Simple TensesDocument12 pagesSimple TensesHienNo ratings yet
- Essential Grammar Is USE UNITS 5, 6, 7: Instructor: Sarah TorabianDocument21 pagesEssential Grammar Is USE UNITS 5, 6, 7: Instructor: Sarah TorabiansaratorabianNo ratings yet
- Tenses PresentDocument6 pagesTenses Presentleyla azhdarovaNo ratings yet
- Present TenseDocument8 pagesPresent TensepxtndknypnNo ratings yet
- Definition of The Present Perfect TenseDocument20 pagesDefinition of The Present Perfect TenseSelebriti Rafiq ChikidotNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Students NotesDocument63 pagesGrade 7 Students NotesloislauNo ratings yet
- نص 2Document5 pagesنص 2kassabelbialy99No ratings yet
- Unit:2 Group One: The TittlesDocument25 pagesUnit:2 Group One: The TittlesKh fcNo ratings yet
- Slides Uni I (MS) (RF)Document64 pagesSlides Uni I (MS) (RF)Marilia PucciNo ratings yet
- Unit 4-7 of Oxford Practice GrammarDocument23 pagesUnit 4-7 of Oxford Practice GrammarHarjinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Tense AbdoDocument7 pagesSimple Present Tense AbdoAbdelhadi Ait AllalNo ratings yet
- Present SimpleDocument4 pagesPresent SimpleDuru Emek KaraNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple and ContinuousDocument4 pagesPresent Perfect Simple and ContinuousCindyNo ratings yet
- 4º "C" Jhon Pulache AlburquequeDocument14 pages4º "C" Jhon Pulache AlburquequeMónica VillegasNo ratings yet
- Affirmative Negative Interrogative Short Answers: Unit 1-Day In, Day OutDocument11 pagesAffirmative Negative Interrogative Short Answers: Unit 1-Day In, Day OutTuana YanarNo ratings yet
- Verbs TypesDocument24 pagesVerbs TypesSairamTirumalaiGovindarajuNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses TESTDocument13 pagesVerb Tenses TESTEniahl Nuñez PescanteNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 CuadernilloDocument22 pagesMODULE 1 CuadernilloLuciNo ratings yet
- English - Verbs TensesDocument10 pagesEnglish - Verbs TensesjenelynNo ratings yet
- English Intermediate 1Document276 pagesEnglish Intermediate 1Alejandro ANo ratings yet
- Present TenseDocument11 pagesPresent TenseMeli PasikNo ratings yet
- 1 Present TensesDocument14 pages1 Present TensesdorksideNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document15 pagesUnit 2Fernando AbdalaNo ratings yet
- InglesDocument19 pagesInglesBrian ShawNo ratings yet
- Present ContinuousDocument3 pagesPresent ContinuousAndreea BalabanNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect VS Present Perfect ContinuousDocument3 pagesPresent Perfect VS Present Perfect ContinuousBtari BungaNo ratings yet
- Using The Present ContiDocument10 pagesUsing The Present ContiLi CastilloNo ratings yet
- InversionsDocument4 pagesInversionsSunny De Los Santos0% (1)
- The Present Continuous TenseDocument21 pagesThe Present Continuous TenseGuerrero AgeNo ratings yet
- The Present Continuous TenseDocument21 pagesThe Present Continuous TensedebbyNo ratings yet
- Present ContinuousDocument6 pagesPresent ContinuousAyy SykesNo ratings yet
- Active VoiceDocument125 pagesActive VoiceAyesha AfzalNo ratings yet
- Advanced Learners 1Document5 pagesAdvanced Learners 1oldhastonianNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument39 pagesEnglish TensesDavid ArévalosNo ratings yet
- Simple Present TenseDocument7 pagesSimple Present Tensehepy dianaNo ratings yet
- Inbound 676430358566289743Document8 pagesInbound 676430358566289743LamijaNo ratings yet
- Delgado Rivera Susana Portfolio 5to ADocument22 pagesDelgado Rivera Susana Portfolio 5to ASILVIA EDITH ESTRADA CAÑIZARESNo ratings yet
- Present Simple TenseDocument9 pagesPresent Simple Tensemind vomitNo ratings yet
- Universidad Tecnologica Del Suroeste de Guanajuato: Obed Armando Cabrera YbarraDocument17 pagesUniversidad Tecnologica Del Suroeste de Guanajuato: Obed Armando Cabrera YbarraObed Armando Cabrera YbarraNo ratings yet
- The Present Perfect Simple TenseDocument6 pagesThe Present Perfect Simple Tensealucario92No ratings yet
- Adverbs - Teorie I (Compendiu)Document5 pagesAdverbs - Teorie I (Compendiu)IulianaLacramioaraNo ratings yet
- 16 TensesDocument18 pages16 TensesAnonymous eCws3ENo ratings yet
- Verb Tense Review: The Importance of TimeDocument32 pagesVerb Tense Review: The Importance of Timebaba ioana100% (1)
- Gramática Del InglésDocument12 pagesGramática Del InglésLuis Enrique Ramirez PadillaNo ratings yet
- The Present ContinuousDocument4 pagesThe Present ContinuousIlma AuliaNo ratings yet
- Word Order in English: Subject Verbs Indirect Object Direct Object Manner (How?) Place (Where?) Time (When?how Often?)Document12 pagesWord Order in English: Subject Verbs Indirect Object Direct Object Manner (How?) Place (Where?) Time (When?how Often?)Radu NicoletaNo ratings yet
- Simple Past, Past Perfect, Past ContinuousDocument23 pagesSimple Past, Past Perfect, Past ContinuousAli Mohamad RezzaNo ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument9 pagesPresent Perfectsherry0% (1)
- The English Tenses: Theory, Practice and KEY: Stefana BalanDocument22 pagesThe English Tenses: Theory, Practice and KEY: Stefana BalanStefana BalanNo ratings yet
- Present Simple ContinuousDocument8 pagesPresent Simple ContinuousJosmaツNo ratings yet
- English Module-Kurikulum Lama-GASAL 2018-2019 PDFDocument50 pagesEnglish Module-Kurikulum Lama-GASAL 2018-2019 PDFdesdesNo ratings yet
- 3 Present Continuous, Singular and PluralDocument47 pages3 Present Continuous, Singular and PluralHaydarbek YuldoshevNo ratings yet
- English Grammar ExplanationsDocument13 pagesEnglish Grammar ExplanationsНикола Каранфиловски100% (3)
- Pet Grammar PointsDocument69 pagesPet Grammar PointsTatiana ZaraNo ratings yet
- Let's Learn English Together!Document27 pagesLet's Learn English Together!Vir PesceNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument67 pagesEnglish Tensesdonisparta5No ratings yet