he Role of MHC Classes in Immune Function and Their Clinical Significance
T
The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) plays a central role in the immune system by
determining how antigens are processed and presented to T cells. Beyond their structural and
functional differences, MHC Class I and Class II molecules have critical roles in immunity,
transplantation, autoimmune diseases, and the development of immunotherapies.
HC Class I: Immune Surveillance and Viral Immunity
M
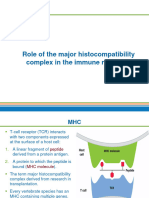
MHC Class I molecules are essential for immune surveillance, allowing cytotoxic CD8+ T cells
to detect and eliminate infected or abnormal cells. Viruses often replicate within host cells,
producing viral peptides that are processed in the proteasome and transported into the
endoplasmic reticulum by the transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP). Once bound
to MHC Class I molecules, these peptides are presented on the cell surface.
hen CD8+ T cells recognize non-self peptides in the context of MHC Class I, they release
W
cytotoxic granules containing perforin and granzymes, leading to the targeted cell's apoptosis.
This mechanism is crucial for controlling intracellular pathogens like viruses and detecting
transformed or cancerous cells. However, some viruses, such as cytomegalovirus and
Epstein-Barr virus, have evolved mechanisms to evade MHC Class I presentation, illustrating the
dynamic interplay between host immunity and pathogen survival strategies.
HC Class II: Coordinating the Immune Response
M
MHC Class II molecules play a pivotal role in activating CD4+ T helper cells, which are critical
for orchestrating the adaptive immune response. When an antigen-presenting cell (APC)
processes and presents an exogenous antigen, the CD4+ T cell recognizes the antigen-MHC
Class II complex through its T cell receptor (TCR). This interaction, along with co-stimulatory
signals, activates the CD4+ T cell, prompting it to differentiate into various subsets, such as Th1,
Th2, Th17, or T regulatory cells, depending on the cytokine environment.
h1 Cells promote cellular immunity by activating macrophages and supporting CD8+ T cell
T
responses against intracellular pathogens.
Th2 Cells stimulate humoral immunity by promoting B cell activation and antibody production,
which is particularly effective against extracellular pathogens like bacteria and parasites.
Th17 Cells play a role in combating fungal infections and contribute to inflammation.
T Regulatory Cells help maintain immune tolerance, preventing overactive responses that could
lead to autoimmunity.