0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views37 pagesJEE Triangle Geometry Concepts Explained
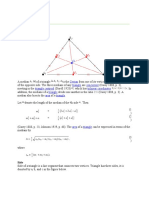
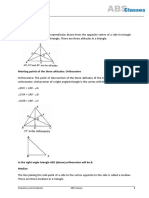
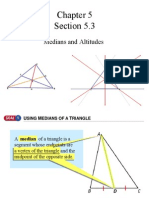
The document provides an overview of geometric concepts related to triangles, including definitions and properties of median, centroid, incentre, excentre, orthocentre, and circumcentre. It includes various problems and questions related to these concepts, aimed at students preparing for the JEE exam. Additionally, it features live polls and feedback links for interactive learning.
Uploaded by
krt.137936689377Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views37 pagesJEE Triangle Geometry Concepts Explained
The document provides an overview of geometric concepts related to triangles, including definitions and properties of median, centroid, incentre, excentre, orthocentre, and circumcentre. It includes various problems and questions related to these concepts, aimed at students preparing for the JEE exam. Additionally, it features live polls and feedback links for interactive learning.
Uploaded by
krt.137936689377Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd