SCIENCE Q3 SCIENCE Q3
Activity 1 Activity 1
Write TRUE if the statement is correct and FALSE if it is Write TRUE if the statement is correct and FALSE if it is
not. not.
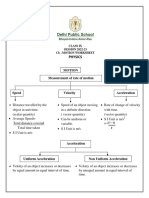
__________1. The x-axis on a distance-time graph represents distance. __________1. The x-axis on a distance-time graph represents distance.
__________2. The y-axis on a distance -time graph represents time. __________2. The y-axis on a distance -time graph represents time.
__________3. Understanding the orientation and labeling of axes is unnecessary __________3. Understanding the orientation and labeling of axes is unnecessary
for for
interpreting a distance-time graph. interpreting a distance-time graph.
__________4. Both axes on a distance-time graph must have clearly labeled units. __________4. Both axes on a distance-time graph must have clearly labeled units.
__________5. Data points on a distance-time graph represent specific __________5. Data points on a distance-time graph represent specific
measurements measurements
of distance only. of distance only.
__________6. The steepness of the line in a distance-time graph provides __________6. The steepness of the line in a distance-time graph provides
information about the objects speed. information about the objects speed.
__________7. A steeper angle of incline on a distance-time graph indicates a __________7. A steeper angle of incline on a distance-time graph indicates a
slower slower
speed. speed.
__________8. Lines or curves on a distance-time graph connect data __________8. Lines or curves on a distance-time graph connect data
points, illustrating the relationship between time and distance. points, illustrating the relationship between time and distance.
SCIENCE Q3 SCIENCE Q3
Activity 1 Activity 1
Write TRUE if the statement is correct and FALSE if it is Write TRUE if the statement is correct and FALSE if it is
not. not.
__________1. The x-axis on a distance-time graph represents distance.
__________1. The x-axis on a distance-time graph represents distance.
__________2. The y-axis on a distance -time graph represents time.
__________2. The y-axis on a distance -time graph represents time.
__________3. Understanding the orientation and labeling of axes is unnecessary
__________3. Understanding the orientation and labeling of axes is unnecessary
for
for
interpreting a distance-time graph.
interpreting a distance-time graph.
__________4. Both axes on a distance-time graph must have clearly labeled units.
__________4. Both axes on a distance-time graph must have clearly labeled units.
__________5. Data points on a distance-time graph represent specific
__________5. Data points on a distance-time graph represent specific
measurements
measurements
of distance only.
of distance only.
__________6. The steepness of the line in a distance-time graph provides
__________6. The steepness of the line in a distance-time graph provides
information about the objects speed.
information about the objects speed.
__________7. A steeper angle of incline on a distance-time graph indicates a
__________7. A steeper angle of incline on a distance-time graph indicates a
slower
slower
speed.
speed.
__________8. Lines or curves on a distance-time graph connect data
__________8. Lines or curves on a distance-time graph connect data
points, illustrating the relationship between time and distance.
points, illustrating the relationship between time and distance.
+
� Choose the letter of the correct answer and write them on the
blank before each number.
_____1. What is the result of force applied against an objects motion?
A. stability B. slowing down C. stationary D.
invisibility
_____2. In the example of a car speeding up on highway , what force propels the
car
forward?
A. Air resistance C. Friction
B. Gravity D. force generated by the accelerator
_____3. How does the direction of an applied force affect the motion of an object?
A. It determines the objects mass C. It changes the objects volume.
B. It affects the object’s speed D. It increases the objects density.
_____4. What does a horizontal line on distance-time graph represent for a
stationary object?
A. Increasing speed C. constant position
B. Decreasing speed D. rapid change in direction
_____5. How is a slow, uniform speed represented on a distance-time graph?
A. With a steep diagonal line C. with a horizontal line
B. With a shallow diagonal line D. with a vertical line
_____6. How is a fast uniform speed represented on a distance-time graph?
A. With a shallow diagonal line C. with a horizontal line
B. With a steep diagonal line D. with a vertical line
_____7. What is the effect of applying force by squeezing a sponge?
A. It starts to move forward.
B. It starts to increase the speed
C. It compresses and reduces in size.
D. It expands and becomes larger in size.
_____8. Which of the following is an example of how force changes an object’s
direction?
A. An apple falling to the ground
B. A cart moving downward a straight hill
C. A heavy truck speeding up in a highway.
D. A ball hitting a wall then bouncing back.
____9. A rock is balanced on the side of a long, sloping hill. Although the rock is
very heavy , a gentle push causes it to start moving down the slope.
How can a small force cause a large mass to move?
A. To make an object move, the direction of the force is important , but
not the amount of force.
B. The push on the rock increased the amount of friction , so the rock
started to move.
C. The small push balanced the forces that were keeping the rock in
place and caused it to moved.
D. The forces on the rock were balanced , and a small additional force
caused them to be unbalanced.
____10. Which graphs shows the one of the runners started 10 meters farther
ahead of another runner?
A. B. C. D.