0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views2 pagesDeriving Student's t-Distribution Basics
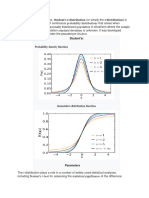
The document explains the derivation of the Student's t-distribution, which is used for estimating the mean of a normally distributed population with unknown standard deviation, particularly for small sample sizes. It outlines the process of standardization, estimating the population standard deviation, and incorporating the chi-square distribution to derive the probability density function (PDF) of the t-distribution. Key points include the t-distribution's similarity to the normal distribution, its heavier tails, and its application in hypothesis testing and confidence interval estimation.
Uploaded by
ggggggkul143Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views2 pagesDeriving Student's t-Distribution Basics
The document explains the derivation of the Student's t-distribution, which is used for estimating the mean of a normally distributed population with unknown standard deviation, particularly for small sample sizes. It outlines the process of standardization, estimating the population standard deviation, and incorporating the chi-square distribution to derive the probability density function (PDF) of the t-distribution. Key points include the t-distribution's similarity to the normal distribution, its heavier tails, and its application in hypothesis testing and confidence interval estimation.
Uploaded by
ggggggkul143Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd