Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trex 00032
Uploaded by
OSDocs2012Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Trex 00032
Uploaded by
OSDocs2012Copyright:
Available Formats
Report Outline
. 1. Background
Deepwater Horizon- 5th generation
Used for drilling exploration wells
Crew was recognized for high performance in personal safety
Macondo was an Infrastructure Led well (ILX) .
Had a fair idea there were cOmmercial quantities available
Plan to temporarily suspend well, later tie-in to Pompano
Spudded with Marianas, which was damaged in Hurricane Ida
2. Decisions
2. A. Soft Formation (Choice of Bore Size, Drilling Fluid, Casing, Centralizers, )
Issues encountered in well bore
Weaker well than anticipated
Had to commit two more casing strings
2. B. Bore Size Options
TD: 18,360'
8-1/2" bit; used a 9-7/8" side arm reamer (created elliptical bore to reduce Equivalent
Circulation Density (ECD))
Soft formation, narrow margins; better for reducing ECD if bore is wider
Miocene, friable; easy to drill, formation not as hard as in the Rockies
2. C. Dtilling Fluid Options
Drilling fluid was chemically inert
Tools were used to evaluate well : resistivity, gamma ray, ...
Determined hydrocarbons available
Pressure:
13.1 12.6
14.1 formation; 14.2 mud weight
If used less weight, would flow
If used more weight, cause losses
2. D. Casing Options
Had to make a decision regarding: Long String vs. Liner options
Risk Assessment:
Liner with cement had lower ECD than Long String
WIT: _____ _
BP-HZN-BLY0008783E
EXHIBIT TREX-00032
Long String: Could have cemented
Liner risk:
Long String risk:
Risk of trapped annulus, but less ECD required
Less risk of trappihg annulus, but higher ECD reqd.
2. E. Centralizer Options
Centralizers: intended to 1) reduce channelization, and 2) mitigate effects of the cement
losinghydrostatics when phase shifts from liquid to solid
Casing bought from:
9-5/8" from BP
7" from Nexus, who provided only 6 centralizers
Halliburton specified 21 centralizers; BP ordered 15 more
Atlantis centralizers failed- integrity concerns
Thunderhorse centralizers sent- were available
Wells Team Ldr didn't know, so decided to go with 6
Risk consideration: Centralizers can get stuck in BOP or acute angle below
2. F. Cement Options
Subsequent report from geologists - HC zone above cement
Sophisticated cement slurry, three volumes- cap, nitrified, tail
Used base oil 10.6, to displace 14.6 mud (transition will not be smooth)
Defoamer blended
More difficult
More surfactant needed
Riskier design
Tried to inject at high end ofN2 capacity (extreme end)
Question regarding slurry stability
3. Chronology of Events
3. A. Float Collar
Set float collar at bottom of casing; run in slowly to minimize surge
First anomaly - 9 attempts to convert; (blockage may have been at float collar or shoe?)
Checked with Weatherford for guidance to continue, said acceptable to increase pressure
May not have set sleeves
3. B. Cement Job
Cement job went as expected
BP-HZN-BLY00087837
No significant losses (some, 6- 9 bbls.)
Returns suggest no kick
Displaced cement with rubber plug
3. C. Positive Pressure Test {to test casing and plug integrity)
Set seal assembly, pressurized from above -
Positive test (tests rubber plug, not cement)- successful
3. D. Negative Test (to test integrity ofweli under sea waterhydrostatic pressure)
.Performed Negative test (had not set locking device yet)
Negative test simulates sea water hydrostatic on well in preparation for suspending
DP stinger down to 83 67'
Spacer to displace synthetic oil based mud 14.1
Spacer is viscous
. Empty pits to recover and transfer to boat
Guidance to pump X strokes of pill, Y strokes of sea water to result in pill 1000' above
stack
May have misinterpreted; they pumped X total strokes; resulted in pill across BOP stack
Shut in Annular
Displace Choke, Kill to seawater
Shift handover was occurring (Bob going off for short change, Don coming on for short-
change)
Started to monitor DP press
Don said must accomplish on Kill line per :Ml\1S
May have bled viscous into Kill line
Press on DP was 1400 psi, Kill line was 0 psi (though there was aU-tube connection)
Bled off larger amount than should have expected (15 to 23 bbls, vice- 2 bbls.).
Question whether they were monitoring
Test took 3 hrs, vice 45 min.
Kill line: 0 psi - may have been blocked
DP: 1400 psi.:.. explained away with "bladder effect" (Don had reservations about this
explanation; was on his 4th trip, heard crew was good; eventually went along with the
groupexplanation; Bob was a replacement for Ronnie)
3. E. Begilming of Influx
Well started to kick
3. F. Sheen Test (to determine if returns were oil-free, to allow dumping overboard)
Sheen test - good results
Began to dump overboard; flow sensors downstream, therefore can' t read flow from well
3. G. Crew Response (after Abnormal Indications first recognized)
2131 - abnormal pressure begins to build
Crew tried to shut in well
Mud through rig floor
BP-HZN-BLY00087838
Diverter lines (may have failed)
Gas heard escaping
Small explosion (possible over speed of motor heard)
Catastrophic explosion
One light on bridge panel : "Lower Annular,.,
Attempt to EDS- didn't get desired result
Shut diverter, lined up to Mud Gas Sep ( 100 psi constrained system)
May have been a conservative approach to avoid dumping to sea, or following
procedures
Deadman- No evidence that activated
Autoshear- Not conclusive if motion occurred
4. Critical Factor 1 -Cement Barriers, Casing Mechanical
Cement failed to isolate
Hydrocarbons into casing (strong possibility through the bottom)
Though can't determine, there were factors that introduce weakness and potential risk
Quality of reviews, engineering checks, to see if could have been captured
Unforgiving well
Bought expensive cement
Remember, "Cement failure does not equal blowout"
Possible recommendation -More rigorous reviews
5. Critical Factor 2 - Integrity Test
Narrow pore press I fracture gradient
Integrity test is the last chance to determine if we got it right
Rig crew didn't come to correct conclusion; looked at information, drew wrong
conclusion
Test not specifically req'd by l\1M:S; but once we specify in our plan, becomes mandatory
Still had control of well; had chance to remediate
1. If detailed procedure, -with pass/fail criteria
2. lf different instincts, . . .
6. Critical Factor 2 - Well bore monitoring
As you circulate sea water, less pressure, encourage more flow
BP-HZN-BLY00087839
Normally.monitored by Driller and support staff
Well flowing for one hour, not identified
Critical, fundamental drilling process
Because they concluded they had integrity, because they had other things going on,
because they formed an incorrect mental modeL .. '
It appears they didn't identify flow; not in realm of possibility .
Trarisferi-ing 10 active pits out of pits (not transferring directly to boat)
7. Critical Factor 3- Shut in Response
2131- Crew realized something not right
[Before these last 18 minutes, crew was running out of margin; from this time forward,
they had to respond flawlessly, and everi then they still would have had gas release]
Next 18 minutes - initial response fr01ri a Driller that appeared to have not known was in
a serious well control incident
1. Response was slow [trying to get approval?]
2. Equipment selected indicated minor response actions (Mud Gas Separator, which
directed gas to the rig
3. Equipment took a long time to conduct operation [still analyzing?]
If overboard, might have delayed rig explosion
If concerned with dumping overboard, may indicate had minor concern
Also, could be following prescriptive training (procedure step says use Mud Gas
Separator, then Diverter)
8. Critical Factor 4- Ignition Source
9. Critical Factor 3- Shut in Response
Difficult to determine
Plausible the equipment was damaged post-explosion, so EDS couldn't work
Deadman, Autoshear- By this time, a lot has gone wrong
10. Conclusions
Cost cutting? Inappropriate to say cost is not a consideration
Number of choices made- none were cost-cutting choices
As we went through decisions, was the quality of risk decision on the side of
conservatism?
BP-HZN-BLY00087840
Believed we could do it safely, but lost track of aggregate risk
All the following are expensive options:
Casing
Connections
Mud
Cement
Three company Men (vice one)
Boats on the side
11. Recommendations
There were opportunities that could have reduced the likelihood
Ensure we don't miss the those opportunities in the future
1. Design of equipment
2. Checks and balances in place
3. Always monitor
4. Shut in response commensurate with magnitude
5. Emergency System function under duress
BP-HZN-BLY00087841
You might also like
- BP's Proposed Findings - Combined FileDocument1,303 pagesBP's Proposed Findings - Combined FileOSDocs2012No ratings yet
- 2013-9-18 Aligned Parties Pre-Trial Statement Doc 11411Document41 pages2013-9-18 Aligned Parties Pre-Trial Statement Doc 11411OSDocs2012No ratings yet
- 2013-9-11 BPs Phase II PreTrial Reply Memo For Source Control Doc 11349Document13 pages2013-9-11 BPs Phase II PreTrial Reply Memo For Source Control Doc 11349OSDocs2012No ratings yet
- DOJ Pre-Trial Statement On QuantificationDocument14 pagesDOJ Pre-Trial Statement On QuantificationwhitremerNo ratings yet
- BP Pre-Trial Statement On QuantificationDocument13 pagesBP Pre-Trial Statement On Quantificationwhitremer100% (1)
- BP's Post-Trial BriefDocument72 pagesBP's Post-Trial BriefOSDocs2012No ratings yet
- To's Proposed FOF and COLDocument326 pagesTo's Proposed FOF and COLOSDocs2012No ratings yet
- 2013-09-05 BP Phase 2 Pre-Trial Memo - Source ControlDocument13 pages2013-09-05 BP Phase 2 Pre-Trial Memo - Source ControlOSDocs2012No ratings yet
- To's Post-Trial BriefDocument57 pagesTo's Post-Trial BriefOSDocs2012No ratings yet
- Plaintiffs Proposed Findings and Conclusions (Phase One) (Doc 10459) 6-21-2013Document199 pagesPlaintiffs Proposed Findings and Conclusions (Phase One) (Doc 10459) 6-21-2013OSDocs2012No ratings yet
- HESI's Post-Trial BriefDocument52 pagesHESI's Post-Trial BriefOSDocs2012No ratings yet
- HESI's Proposed FOF and COLDocument335 pagesHESI's Proposed FOF and COLOSDocs2012No ratings yet
- USAs Proposed Findings Phase I (Doc. 10460 - 6.21.2013)Document121 pagesUSAs Proposed Findings Phase I (Doc. 10460 - 6.21.2013)OSDocs2012No ratings yet
- State of LAs Post Trial Brief Phase I (Doc. 10462 - 6.21.2013)Document23 pagesState of LAs Post Trial Brief Phase I (Doc. 10462 - 6.21.2013)OSDocs2012No ratings yet
- State of ALs Post Trial Brief Phase I (Doc. 10451 - 6.21.2013)Document22 pagesState of ALs Post Trial Brief Phase I (Doc. 10451 - 6.21.2013)OSDocs2012No ratings yet
- USAs Post Trial Brief Phase I (Doc. 10461 - 6.21.2013)Document49 pagesUSAs Post Trial Brief Phase I (Doc. 10461 - 6.21.2013)OSDocs2012No ratings yet
- PSC Post-Trial Brief (Phase One) (Doc 10458) 6-21-2013Document72 pagesPSC Post-Trial Brief (Phase One) (Doc 10458) 6-21-2013OSDocs2012100% (1)
- April 20, BLOWOUT: BP Misreads Logs Does Not IdentifyDocument22 pagesApril 20, BLOWOUT: BP Misreads Logs Does Not IdentifyOSDocs2012No ratings yet
- Macondo Bod (Basis of Design)Document23 pagesMacondo Bod (Basis of Design)OSDocs2012No ratings yet
- Driller HITEC Display CCTV Camera System: Source: TREX 4248 8153Document1 pageDriller HITEC Display CCTV Camera System: Source: TREX 4248 8153OSDocs2012No ratings yet
- Exterior: Circa 2003Document1 pageExterior: Circa 2003OSDocs2012No ratings yet
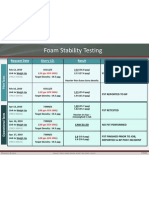
- Foam Stability Testing: Request Date Slurry I.D. Result CommentsDocument1 pageFoam Stability Testing: Request Date Slurry I.D. Result CommentsOSDocs2012No ratings yet
- Arnaud Bobillier Email: June 17, 2010: "I See Some Similarities With What Happened On The Horizon"Document5 pagesArnaud Bobillier Email: June 17, 2010: "I See Some Similarities With What Happened On The Horizon"OSDocs2012No ratings yet
- Circa 2003Document1 pageCirca 2003OSDocs2012No ratings yet
- DR Gene: CloggedDocument1 pageDR Gene: CloggedOSDocs2012No ratings yet
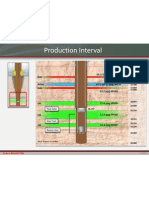
- Production Interval: 14.1-14.2 PPG M57B Gas Brine GasDocument1 pageProduction Interval: 14.1-14.2 PPG M57B Gas Brine GasOSDocs2012No ratings yet
- Circa 2003Document1 pageCirca 2003OSDocs2012No ratings yet
- Laboratory Results Cement Program Material Transfer TicketDocument13 pagesLaboratory Results Cement Program Material Transfer TicketOSDocs2012No ratings yet
- Webster:: Trial Transcript at 3975:2-4Document1 pageWebster:: Trial Transcript at 3975:2-4OSDocs2012No ratings yet
- End of Transmission: Transocean Drill Crew Turned The Pumps Off To InvestigateDocument1 pageEnd of Transmission: Transocean Drill Crew Turned The Pumps Off To InvestigateOSDocs2012No ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Fiery Training 1Document346 pagesFiery Training 1shamilbasayevNo ratings yet
- Wsi PSDDocument18 pagesWsi PSDДрагиша Небитни ТрифуновићNo ratings yet
- Zhihua Yao - Dignaga and The 4 Types of Perception (JIP 04)Document24 pagesZhihua Yao - Dignaga and The 4 Types of Perception (JIP 04)Carlos Caicedo-Russi100% (1)
- Eudragit ReviewDocument16 pagesEudragit ReviewlichenresearchNo ratings yet
- Crash Cart - General Checklist For Medical Supplies On Crash CartsDocument3 pagesCrash Cart - General Checklist For Medical Supplies On Crash CartsYassen ManiriNo ratings yet
- Believer - Imagine Dragons - CIFRA CLUBDocument9 pagesBeliever - Imagine Dragons - CIFRA CLUBSilvio Augusto Comercial 01No ratings yet
- All MeterialsDocument236 pagesAll MeterialsTamzid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Marksmanship: Subject: III. Definition of TermsDocument16 pagesMarksmanship: Subject: III. Definition of TermsAmber EbayaNo ratings yet
- Shimano Brakes ManualDocument36 pagesShimano Brakes ManualKon Arva100% (1)
- Riedijk - Architecture As A CraftDocument223 pagesRiedijk - Architecture As A CraftHannah WesselsNo ratings yet
- Flexible AC Transmission SystemsDocument51 pagesFlexible AC Transmission SystemsPriyanka VedulaNo ratings yet
- RestrukturisasiDocument17 pagesRestrukturisasimuhammad hayel wallaNo ratings yet
- Long Run Average Cost (LRAC) : Economies of ScaleDocument3 pagesLong Run Average Cost (LRAC) : Economies of ScaleA PNo ratings yet
- Where On Earth Can Go Next?: AppleDocument100 pagesWhere On Earth Can Go Next?: Applepetrushevski_designeNo ratings yet
- LGFL Service GuideDocument24 pagesLGFL Service GuideThe Return of the NoiristaNo ratings yet
- Medical filter performance specificationsDocument1 pageMedical filter performance specificationsPT.Intidaya Dinamika SejatiNo ratings yet
- Overview for Report Designers in 40 CharactersDocument21 pagesOverview for Report Designers in 40 CharacterskashishNo ratings yet
- Ogl422 Milestone Three Team 11 Intro Training Session For Evergreen MGT Audion Recording Due 2022apr18 8 30 PM PST 11 30pm EstDocument14 pagesOgl422 Milestone Three Team 11 Intro Training Session For Evergreen MGT Audion Recording Due 2022apr18 8 30 PM PST 11 30pm Estapi-624721629No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocument42 pagesChapter 1 - IntroductionShola ayipNo ratings yet
- Principles of Cost Accounting 1Document6 pagesPrinciples of Cost Accounting 1Alimamy KamaraNo ratings yet
- April 3rd - Asynchronous Class - Questions-4Document3 pagesApril 3rd - Asynchronous Class - Questions-4alidrissiNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute OF Management, BangaloreDocument20 pagesIndian Institute OF Management, BangaloreGagandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Strain Gauge Sensor PDFDocument12 pagesStrain Gauge Sensor PDFMario Eduardo Santos MartinsNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 - Mock Test - English - Feb - 2023Document12 pagesGrade 10 - Mock Test - English - Feb - 2023rohanNo ratings yet
- The Graduation Commencement Speech You Will Never HearDocument4 pagesThe Graduation Commencement Speech You Will Never HearBernie Lutchman Jr.No ratings yet
- Donaldson 004117 PDFDocument6 pagesDonaldson 004117 PDFNSNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast High School and College EssayDocument6 pagesCompare and Contrast High School and College Essayafibkyielxfbab100% (1)
- Motivations for Leaving Public Accounting FirmsDocument33 pagesMotivations for Leaving Public Accounting Firmsran0786No ratings yet
- Av1 OnDocument7 pagesAv1 OnLê Hà Thanh TrúcNo ratings yet