Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acute Choleylithiasis
Uploaded by
Angela LuceOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acute Choleylithiasis
Uploaded by
Angela LuceCopyright:
Available Formats
Acute Choleylithiasis
The main symptom is abdominal pain that is located on the upper right side or upper middle of the abdomen. The pain may:
y y y y
Be sharp, cramping, or dull Come and go Spread to the back or below the right shoulder blade Occur within minutes of a meal
Other symptoms that may occur include:
y y y y y
Abdominal fullness Clay-colored stools Fever Nausea and vomiting Yellowing of skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice)
Bile duct obstruction
URL of this page: http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000263.htm
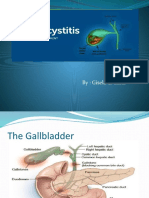
Bile duct obstruction is a blockage in the tubes that carry bile from the liver to the gallbladder and small intestine. See also:
y y y
Acute cholecystitis Choledocholithiasis Gallstones
Causes
Bile is a liquid released by the liver. It contains cholesterol, bile salts, and waste products such as bilirubin. Bile salts help your body break down (digest) fats. Bile passes out of the liver through the bile ducts and is stored in the gallbladder. After a meal, it is released into the small intestine. When the bile ducts become blocked, bile builds up in the liver, and jaundice (yellow color of the skin) develops due to the increasing levels of bilirubin in the blood.
The possible causes of a blocked bile duct include:
y y y y y y y
Cysts of the common bile duct Enlarged lymp nodes in the porta hepatis Gallstones Inflammation of the bile ducts Trauma including injury from gallbladder surgery Tumors of the bile ducts or pancreas Other tumors that have spread to the biliary system
The risk factors include:
y y y y
History of gallstones, chronic pancreatitis, or pancreatic cancer Injury to the abdominal area Recent biliary surgery Recent biliary cancer (such as bile duct cancer)
The blockage can also be caused by infections. This is more common in persons with weakened immune systems.
Symptoms
y y y y y y y
Abdominal pain in the upper right side Dark urine Fever Itching Jaundice (yellow skin color) Nausea and vomiting Pale-colored stools
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will examine your abdomen and may be able to feel the gallbladder. The following blood test results could be a sign of a possible blockage:
y y y
Increased bilirubin level Increased alkaline phosphatase level Increased liver enzymes
The following tests may be used to investigate a possible blocked bile duct:
y y y
Abdominal ultrasound Abdominal CT scan ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography)
y y
Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiogram (PTCA) Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
A blocked bile duct may also alter the results of the following tests:
y y y
Amylase blood test Gallbladder radionuclide scan Urine bilirubin
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to relieve the blockage. Stones may be removed using an endoscope during an ERCP. In some cases, surgery is required to bypass the blockage. The gallbladder will usually be surgically removed if the blockage is caused by gallstones. Your health care provider may prescribe antibiotics if an infection is suspected. If the blockage is caused by cancer, the duct may need to be widened. This procedure is called endoscope or percutaneous (through the skin next to the liver) dilation. A tube may need to be placed to allow drainage.
Outlook (Prognosis)
If the blockage is not corrected, it can lead to life-threatening infection and a dangerous buildup of bilirubin. If the blockage lasts a long time, chronic liver disease can result. Most obstructions can be treated with endoscopy or surgery. Obstructions caused by cancer often have a worse outcome.
Possible Complications
Left untreated, the possible complications include infections, sepsis, and liver disease, such as biliary cirrhosis.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if you notice a change in the color of your urine and stools or you develop jaundice.
You might also like
- The Diseases of GallbladderDocument27 pagesThe Diseases of GallbladderAroosha IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Chole Cyst IsDocument8 pagesChole Cyst IsJose Adrian Mendoza OrejuelaNo ratings yet
- Biliary DisordersDocument2 pagesBiliary DisordersNoemi GarciaNo ratings yet
- Introduction and EpidemiologyDocument3 pagesIntroduction and EpidemiologyZhy CaluzaNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Emergencies: OutlinesDocument19 pagesGastrointestinal Emergencies: OutlinesMohamed HassanNo ratings yet
- Gallbladder DiseaseDocument67 pagesGallbladder DiseaseKhadira MohammedNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis - Gallstones: Overview, Causes, & Risk FactorsDocument3 pagesCholelithiasis - Gallstones: Overview, Causes, & Risk FactorsPipih Pertiwi Days'No ratings yet
- 1 GallbladderDocument36 pages1 Gallbladdercephas chinkoliNo ratings yet
- CholelithiasisDocument5 pagesCholelithiasisrgflores1979100% (2)
- PH Le BotomyDocument15 pagesPH Le BotomyPatty MenéndezNo ratings yet
- What Is Obstructive JaundiceDocument1 pageWhat Is Obstructive JaundiceNicole PramonoNo ratings yet
- Stomach CancerDocument6 pagesStomach CancerhelloaNo ratings yet
- CholecystitisDocument10 pagesCholecystitisCris Pin BumatangNo ratings yet
- YunisDocument5 pagesYunisEunice BautistaNo ratings yet
- BlehDocument59 pagesBlehLord Allen B. GomezNo ratings yet
- "Gallstone": Article About Digestive SystemDocument6 pages"Gallstone": Article About Digestive SystemMaharani IndriNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis in ChildrenDocument4 pagesCirrhosis in ChildrenFakhri DesktopNo ratings yet
- Pancreatitis: What Is The Pancreas and What Does It Do?Document5 pagesPancreatitis: What Is The Pancreas and What Does It Do?NonameNo ratings yet
- GallstonesDocument2 pagesGallstoneskingNo ratings yet
- What Are GallstonesDocument7 pagesWhat Are GallstonesImtiazAhmedNo ratings yet
- Calculous CholecystitisDocument20 pagesCalculous CholecystitisҮйжин ӨлзийхутагNo ratings yet
- Jaundice: (Yellowing of Skin)Document4 pagesJaundice: (Yellowing of Skin)mrmr92No ratings yet
- Arythmia and GI BleedingDocument8 pagesArythmia and GI BleedingMary Jane TiangsonNo ratings yet
- Disease of The Biliary TreeDocument7 pagesDisease of The Biliary TreeAbedinego MalukaNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis TreatmentDocument5 pagesLiver Cirrhosis TreatmentPrajith NairNo ratings yet
- Primary Billiary CirrhosisDocument6 pagesPrimary Billiary CirrhosisElvantia MarilynNo ratings yet
- Acute Cholecystitis: BSN208 - Group29Document13 pagesAcute Cholecystitis: BSN208 - Group29Sophia Dayao LopezNo ratings yet
- Exocrine Pancreatic and Biliary Disorders and ManagementDocument77 pagesExocrine Pancreatic and Biliary Disorders and ManagementAnthon Kyle TropezadoNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Cholelithiasis 2018ADocument14 pagesGroup 1 Cholelithiasis 2018Amaya dwiNo ratings yet
- English ThemeDocument4 pagesEnglish ThemeJu BuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 34 Lower GIDocument8 pagesChapter 34 Lower GIRebeccaNo ratings yet
- CholelithiasisDocument69 pagesCholelithiasisRashmita DahalNo ratings yet
- STOMACCANCEREDITEDDocument12 pagesSTOMACCANCEREDITEDhelloaNo ratings yet
- 8 Causes of Periumbilical Pain and When To Seek Emergency HelpDocument8 pages8 Causes of Periumbilical Pain and When To Seek Emergency HelpJohn Rodney PicaNo ratings yet
- Progesterone Has Been Shown To Decrease Gall-Bladder Motility, WhichDocument9 pagesProgesterone Has Been Shown To Decrease Gall-Bladder Motility, WhichFerreze AnnNo ratings yet
- Progesterone Has Been Shown To Decrease Gall-Bladder Motility, WhichDocument9 pagesProgesterone Has Been Shown To Decrease Gall-Bladder Motility, WhichFerreze AnnNo ratings yet
- JundiceDocument2 pagesJundiceJanineLingayoCasilenNo ratings yet
- Gastrectomy Post OpDocument5 pagesGastrectomy Post Opfeirri100% (4)
- Cholecystectomy and Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesCholecystectomy and Nursing Care PlanLara GatbontonNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis FinalDocument16 pagesLiver Cirrhosis FinalAmanda ScarletNo ratings yet
- Sharmistha DasDocument5 pagesSharmistha DasSharmistha DasNo ratings yet
- Mid Semester SupplementaryDocument9 pagesMid Semester SupplementaryKing EbenGhNo ratings yet
- Liver CirrhosisDocument7 pagesLiver CirrhosisJohn Yves B. SantosNo ratings yet
- Chole CystitisDocument20 pagesChole CystitisAnjene BurgosNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis - OverviewDocument2 pagesCholecystitis - OverviewValerie DelmundoNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis With CholecystolithiasisDocument33 pagesCholecystitis With CholecystolithiasisDino V EscalonaNo ratings yet
- Title Biliary Obstructive Disease: BY:-Degu TegegneDocument42 pagesTitle Biliary Obstructive Disease: BY:-Degu TegegneBeyene FelekeNo ratings yet
- Nikhilesh Choudhury 2023Document18 pagesNikhilesh Choudhury 2023palashshome091No ratings yet
- Activity 8-Liver Cirrhosis-DonghitDocument8 pagesActivity 8-Liver Cirrhosis-DonghitAllona Jane Beatrice DonghitNo ratings yet
- Acute EnteritisDocument12 pagesAcute Enteritishend_aserNo ratings yet
- Disease of The Biliary TractDocument7 pagesDisease of The Biliary TractMae DoctoleroNo ratings yet
- Abscess CausesDocument2 pagesAbscess CausesMudatsir N. MileNo ratings yet
- Dengue FeverDocument6 pagesDengue FeverRiza RacionNo ratings yet
- Ntroduction: (1) (2) (3) Go ToDocument6 pagesNtroduction: (1) (2) (3) Go ToretnaNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis: What Is It?Document6 pagesCholecystitis: What Is It?Aziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Surgery Lect 5 LiverDocument39 pagesSurgery Lect 5 Liveraparna shamaNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis ShirleyDocument6 pagesAcute and Chronic Pancreatitis ShirleyVictor AladejanaNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Root WordsDocument4 pagesGastrointestinal Root WordsPaula McAuliffeNo ratings yet
- Diverticulitis Cure: The Ultimate Diverticulitis Diet: Diverticulitis Recipes: Your Ultimate Diverticulitis CookbookFrom EverandDiverticulitis Cure: The Ultimate Diverticulitis Diet: Diverticulitis Recipes: Your Ultimate Diverticulitis CookbookNo ratings yet