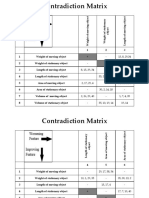
Weight of moving object
Weight of stationary
object
Length of moving object
Length of stationary
object
Area of moving object
Area of stationary object
Volume of moving
object
Volume of stationary
object
Speed
Force (Intensity)
Contradiction Matrix
10
29, 17,
38, 34
29, 2,
40, 28
Weight of moving object
Weight of stationary
object
15, 8,
29,34
Length of moving object
Area of moving object
14, 15,
18, 4
17, 7,
10, 40
2, 17,
29, 4
35, 28,
40, 29
15, 17,
4
Length of stationary
object
8, 15,
29, 34
10, 1,
29, 35
Area of stationary object
Volume of moving
object
Volume of stationary
object
2, 26,
29, 40
26, 7,
9, 39
7, 14,
17, 4
1, 7, 4,
17
7
8
9
Speed
30, 2,
14, 18
-
1, 7, 4,
35
35, 10,
35, 8,
19, 14
19, 14
2, 14
2, 28,
13, 14,
29, 30,
13, 38
8
34
35, 30,
13, 2
-
7, 17,
4, 35
-
7, 29,
34
2, 8, 8, 10,
15, 38 18, 37
5, 35,
8, 10,
14, 2
19, 35
17, 10,
13, 4, 8
4
35, 8,
28, 10
2,14
29, 30, 19, 30,
4, 34 35, 2
1, 18,
35, 36
29, 4, 15, 35,
38, 34 36, 37
2, 18,
+
37
13, 28,
+
15, 19
-
�6
7
8
9
Illumination intensity
Use of energy by
moving object
Use of energy by
stationary object
Temperature
Duration of action of
stationary object
Duration of action of
moving object
Weight of stationary
object
Strength
Stability of the object's
composition
Weight of moving object
Shape
Stress or pressure
Contradiction Matrix
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
10, 36,
37, 40
13, 29,
10, 18
10, 14,
35, 40
13, 10,
29, 14
1, 8,
10, 29
13, 14,
15, 7
5, 34,
29, 4
1, 35,
19, 39
26, 39,
1, 40
1, 8,
15, 34
39, 37,
35
11, 2,
13, 39
Length of moving object 1, 8, 35
1, 14,
35
10, 15,
Area of moving object
36, 28
10, 15,
Area of stationary object
36, 37
6, 35, 1, 15,
Volume of moving
object
36, 37 29, 4
Volume of stationary
24, 35 7, 2, 35
object
6, 18, 35, 15,
Speed
38, 40 18, 34
Length of stationary
object
2, 38
28, 10,
1, 39
34, 28,
35, 40
28, 33,
1, 18
28, 27, 5, 34,
18, 40 31, 35
28, 2,
10, 27
8, 35,
19
29, 34
15, 14,
28, 26
3, 15,
6, 3
40, 14
40
2, 27,
19, 6
1, 10,
35
2, 10,
19, 30
6, 29,
4, 38
28, 19,
32, 22
10, 15,
19
3, 35,
38, 18
2, 15,
16
35, 39,
38
34, 39,
10, 18
19, 1, 35, 12,
32
34, 31
19, 32,
18, 19,
35
28, 1
8, 35,
32
24
3, 25
15, 32,
19, 32
19, 13
9, 14,
2, 13,
6, 35, 4
35
15, 7
10
9, 14,
35, 34,
35, 6, 4
17, 15
38
8, 3, 3, 19,
28, 30, 10, 13, 8, 15,
26, 14 35, 5
36, 2
19
35, 38
�1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Power
Loss of Energy
Loss of Substance
Loss of Information
Loss of Time
Quantity of substance
Reliability
Measurement accuracy
Manufacturing
precision
Object-affected harmful
factors
Contradiction Matrix
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
12, 36, 6, 2, 5, 35,
18, 31 34, 19 3, 31
15, 19, 18, 19, 5, 8,
Weight of stationary
object
18, 22 28, 15 13, 30
7, 2, 4, 29,
Length of moving object 1, 35
35, 39 23, 10
10, 28,
Length of stationary
12, 8 6, 28
object
24, 35
19, 10, 15, 17, 10, 35,
Area of moving object
32, 18 30, 26 2, 39
17, 7, 10, 14,
Area of stationary object 17, 32
30
18, 39
35, 6, 7, 15, 36, 39,
Volume of moving
object
13, 18 13, 16 34, 10
10, 39,
Volume of stationary
30, 6
object
35, 34
19, 35, 14, 20, 10, 13,
Speed
38, 2 19, 35 28, 38
Weight of moving object
10, 24,
35
10, 15,
35
10, 35,
20, 28
10, 20,
35, 26
15, 2,
1, 24
29
30, 29,
24, 26,
14
30, 26
30, 16
2, 22
13, 26
26, 4
10, 35,
4, 18
2, 6,
34, 10
35, 16,
32 18
3, 26, 1, 3,
18, 31 11, 27
19, 6, 10, 28,
18, 26 8, 3
10, 14,
29, 35
29, 40
15, 29,
28
29, 30,
29, 9
6, 13
2, 18, 32, 35,
40, 4 40, 4
29, 30, 14, 1,
7
40, 11
2, 35,
35, 3
16
10, 19, 11, 35,
29, 38 27, 28
28, 27,
35, 26
18, 26,
28
28, 32,
4
32, 28,
3
26, 28,
32, 3
26, 28,
32, 3
25, 26,
28
28, 35,
26, 18
10, 1,
35, 17
10, 28,
29, 37
2, 32,
10
22, 21,
18, 27
2, 19,
22, 37
1, 15,
17, 24
2, 32
2, 29,
18, 36
25, 28,
2, 16
35, 10,
25
28, 32, 10, 28,
1, 24 32, 25
1, 18
22, 33,
28, 1
27, 2,
39, 35
22, 21,
27, 35
34, 39,
19, 27
1, 28,
35, 23
�1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Object-generated
harmful factors
Ease of manufacture
Ease of operation
Ease of repair
Adaptability or
versatility
Device complexity
Difficulty of detecting
and measuring
Extent of automation
Productivity
Contradiction Matrix
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
22, 35, 27, 28,
31, 39 1, 36
35, 22,
Weight of stationary
28, 1, 9
object
1, 39
1, 29,
Length of moving object 17, 15
17
15, 17,
Length of stationary
object
27
17, 2, 13, 1,
Area of moving object
18, 39 26, 24
22, 1,
Area of stationary object
40, 16
40
17, 2, 29, 1,
Volume of moving
object
40, 1
40
Volume of stationary 30, 18,
35
object
35, 4
2, 24, 35, 13,
Speed
35, 21 8, 1
Weight of moving object
35, 3,
2, 24
6, 13,
1, 32
15, 29,
35, 4
2, 25
2, 27, 29, 5, 26, 30,
28, 11 15, 8 36, 34
2, 27, 19, 15, 1, 10,
28, 11
29
26, 39
1, 28, 14, 15, 1, 19,
10
1, 16 26, 24
1, 35
1, 26
15, 17, 15, 13,
15, 30
13, 16 10, 1
14, 1,
13
1, 18,
36
16, 4
15, 13,
30, 12
32, 28,
13, 12
28, 29,
26, 32
25, 28,
17, 15
35, 1,
26, 24
26, 35
18, 19
2, 26,
35
17, 24,
26, 16
35, 3,
24, 37
1, 28,
15, 35
14, 4,
28, 29
30, 14,
7, 26
10, 26,
34, 2
10, 15,
17, 7
10, 6,
2, 34
35, 37,
10, 2
26
2, 36,
26, 18
2, 35,
16
15, 16
30, 18
29, 26,
10
15, 29 26, 1
4
2, 17,
1
1, 31
26
34, 2, 15, 10, 10, 28, 3, 34,
28, 27
26
4, 34 27, 16
14, 30,
28, 23
23
35, 34,
16, 24
10, 18
�16
17
18
Volume of moving
object
Volume of stationary
object
Speed
Force (Intensity)
15
Area of stationary object
14
Area of moving object
13
Length of stationary
object
12
Length of moving object
11
Weight of stationary
object
10
Weight of moving object
Contradiction Matrix
10
18, 13,
1, 28
13, 29,
10, 18
15, 10,
26, 3
26, 39,
1, 40
40, 26,
27, 1
17, 19,
9, 36
35, 10,
36
29, 34,
5, 4
13, 15,
1, 28
1, 15,
8, 35
2, 19, 9
8, 1,
37, 18
10, 36,
Stress or pressure
37, 40
8, 10,
Shape
29, 40
Stability of the object's 21, 35,
composition
2, 39
1, 8,
Strength
40, 15
19, 5,
Duration of action of
moving object
34, 31
Duration of action by
stationary object
36,22,
Temperature
6, 38
19, 1,
Illumination intensity
32
Force (Intensity)
28, 10
35, 1,
14, 16
13, 14,
10, 7
37
15, 14,
28, 26
-
6, 27,
1, 40,
19, 16
35
22, 35, 15, 19, 15, 19,
32
9
9
2, 35, 19, 32,
32
16
19, 10,
15
10, 15,
36, 28
5, 34,
4, 10
2, 11,
13
3, 34,
40, 29
3, 17,
19
1, 18, 15, 9, 2, 36,
36, 37 12, 37 18, 37
10, 15, 6, 35,
35, 24
36, 37
10
14, 4,
7, 2, 35
15, 22
28, 10, 34, 28,
39
19, 39 35, 40
9, 40, 10, 15, 9, 14,
28
14, 7 17, 15
10, 2,
19, 30
35, 34,
38
3, 35,
34, 39,
35, 38
35, 6, 4
39, 18
40, 18
19, 32,
2, 13,
26
10
13, 28,
15, 12
6, 35,
36
35, 15,
34, 18
33, 15,
28, 18
8, 13,
26, 14
36, 35,
21
35, 10,
37, 40
10, 35,
21, 16
10, 18,
3, 14
19, 2,
3, 35, 5
16
2, 28, 35, 10,
36, 30 3, 21
10, 13, 26, 19,
19
6
�10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
Stress or pressure
Shape
Stability of the object's
composition
Strength
Duration of action of
moving object
Duration of action of
stationary object
Temperature
Illumination intensity
Use of energy by
moving object
Use of energy by
stationary object
Contradiction Matrix
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
18, 21, 10, 35,
11
40, 34
35, 4,
Stress or pressure
+
15, 10
34, 15,
Shape
+
10, 14
Stability of the object's 2, 35, 22, 1,
composition
40
18, 4
10, 3, 10, 30,
Strength
18, 40 35, 40
19, 3, 14, 26,
Duration of action of
moving object
27
28, 25
Duration of action by
stationary object
35, 39, 14, 22,
Temperature
19, 2 19, 32
Force (Intensity)
Illumination intensity
35, 10,
21
35, 33,
2, 40
33, 1,
18, 4
35, 10,
14, 27
9, 18,
3, 40
30, 14,
10, 40
17, 9,
15
13, 17,
35
13, 3,
35
39, 3,
35, 23
1, 35,
32
32, 3,
32, 30
27
+
27, 3,
10
19, 2
19, 3,
27
14, 26,
9, 25
13, 27,
10, 35
27, 3,
26
+
-
10, 30, 19, 13,
22, 40
39
35, 19 2, 19, 6
35, 10,
21
35, 39,
19, 2
22, 14,
19, 32
39, 3, 35, 1,
35, 23
32
30, 10,
40
19, 35,
39
19, 18,
+
36, 40
19, 18,
+
36, 40
32, 35,
19
19, 17, 1, 16,
10
36, 37
14, 24,
10, 37
13, 15, 2, 6,
32
34, 14
32, 3,
27, 4,
13, 19
27, 16
29, 18
19, 35,
35, 19
35
10
2, 19, 28, 6,
4, 35 35, 18
-
32, 30, 19, 15,
21, 16 3, 17
32, 1, 32, 35,
+
19
1, 15
�10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
Power
Loss of Energy
Loss of Substance
Loss of Information
Loss of Time
Quantity of substance
Reliability
Measurement accuracy
Manufacturing
precision
Object-affected harmful
factors
Contradiction Matrix
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
19, 35,
8, 35,
14, 15
18, 37
40, 5
10, 35, 2, 36, 10, 36,
Stress or pressure
14
25
3, 37
35, 29,
Shape
4, 6, 2
14
3, 5
Stability of the object's 32, 35, 14, 2, 2, 14,
composition
27, 31 39, 6 30, 40
10, 26,
35, 28,
Strength
35
35, 28
31, 40
28, 27,
Duration of action of 19, 10,
moving object
35, 38
3, 18
27, 16,
Duration of action by
16
stationary object
18, 38
2, 14, 21, 17, 21, 36,
Temperature
17, 25 35, 38 29, 31
13, 16,
Illumination intensity
32
13, 1
1, 6
Force (Intensity)
10, 37,
36
37, 36,
4
14, 10,
34, 17
14, 29,
18, 36
10, 14,
36
35, 27
10
10
1, 6
29, 3,
28, 10
20, 10,
28, 18
28, 20,
10, 16
35, 28,
21, 18
19, 1,
26, 17
3, 35,
13, 21
10, 13,
19, 35
10, 40,
36, 22
16
15, 32,
35
29, 10,
11, 3
27
3, 35, 11, 2,
10, 40
13
3, 35, 34, 27,
31
6, 40
3, 17, 19, 35,
30, 39 3, 10
1, 19
35, 10, 28, 29,
23, 24 37, 36
6, 28,
3, 35
25
28, 32, 32, 30,
1
40
1, 35,
40, 18
22, 2,
37
22, 1,
2, 35
35, 24,
13
18
30, 18
3, 27,
18, 35,
3, 27
16
37, 1
3, 27, 22, 15,
3
16, 40 33, 28
10, 26,
17, 1,
24
40, 33
32, 19,
22, 33,
24
24
35, 2
11, 15,
3, 32 15, 19
32
�10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
Object-generated
harmful factors
Ease of manufacture
Ease of operation
Ease of repair
Adaptability or
versatility
Device complexity
Difficulty of detecting
and measuring
Extent of automation
Productivity
Contradiction Matrix
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
13, 3, 15, 37,
36, 24 18, 1
2, 33, 1, 35,
Stress or pressure
27, 18
16
1, 32,
Shape
35, 1
17, 28
Stability of the object's 35, 40,
35, 19
composition
27, 39
15, 35, 11, 3,
Strength
22, 2 10, 32
Duration of action of 21, 39,
27, 1, 4
moving object
16, 22
Duration of action by
22
35, 10
stationary object
22, 35,
Temperature
26, 27
2, 24
35, 19, 19, 35,
Illumination intensity
32, 39 28, 26
Force (Intensity)
1, 28,
3, 25
11
32, 15,
26
32, 35,
30
32, 40,
25, 2
12, 27
1
15, 1, 15, 17, 26, 35,
11
18, 20 10, 18
19, 1,
2
35
35
1, 15, 16, 29,
2, 13, 1
29
1, 28
2, 35, 35, 30, 2, 35,
10, 16 34, 2 22, 26
27, 11, 15, 3, 2, 13,
3
32
25, 28
29, 10, 1, 35, 10, 4,
27
13
29, 15
1
4, 10, 2, 18,
16
27
28, 26, 15, 17, 15, 1,
19
13, 16
19
26, 27
36, 37,
10, 19
2, 36,
37
15, 13,
39
35, 22,
39, 23
27, 3,
15, 40
19, 29,
39, 35
25, 34,
6, 35
2, 17, 3, 27,
16
35, 31
6, 32,
32, 15
13
2, 35
35, 24
15, 1,
32
1, 8, 35
15
6, 10
1
26, 2,
19, 16
2, 26,
10
3, 28,
35, 37
10, 14,
35, 37
17, 26,
34, 10
23, 35,
40, 3
29, 35,
10, 14
35, 17,
14, 19
20, 10,
16, 38
15, 28,
35
2, 25,
16
�20
21
Power
22
Loss of Energy
23
Loss of substance
24
Loss of Information
25
Loss of Time
26
Quantity of
substance/the matter
27
Reliability
Length of moving object
Length of stationary
object
Area of moving object
Area of stationary object
Volume of moving
object
Volume of stationary
object
Speed
Force (Intensity)
Use of energy by
moving object
Use of energy by
stationary object
Weight of stationary
object
19
Weight of moving object
Contradiction Matrix
10
12,18,2
8,31
12, 28
15, 19,
25
35, 13,
18
8, 36,
38, 31
15, 6,
19, 28
35, 6,
23, 40
10, 24,
35
10, 20,
37, 35
35, 6,
18, 31
3, 8,
10, 40
19, 9,
6, 27
19, 26,
17, 27
19, 6,
18, 9
35, 6,
22, 32
10, 35,
5
10, 20,
26, 5
27, 26,
18, 35
3, 10,
8, 28
1, 10,
35, 37
7, 2, 6,
6, 38, 7
13
14, 29, 10,
10, 39 28,24
1, 26
26
15, 2, 30, 24,
29
14, 5
29, 14,
35, 18
15, 9, 15, 29,
14, 4 28, 11
8, 35, 16, 26,
35
21, 2
-
36, 37
26, 2,
36, 35
17, 32,
13, 38
17, 7,
30, 18
10, 18,
39, 31
35, 6, 30, 6,
38
25
7, 18,
7
23
1, 29, 3, 39,
30, 36 18, 31
15, 35,
2
16, 35,
38
10, 13,
28, 38
30, 26 30, 16
2, 22
26, 32
19, 38
15, 26,
17, 30
35, 2,
10, 31
26, 4, 10, 35,
5, 16 17, 4
15, 14, 2, 18,
29
40, 4
17, 10, 32, 35,
14, 16 40, 4
36, 38
14, 15,
18, 40
2, 5, 35, 16,
10, 37,
34, 10 32, 18
36,5
15, 20,
35, 29, 35, 14,
29
34, 28
3
3, 10, 2, 35, 21, 35, 8, 28,
14, 24
24
11, 28 10, 3
�19
20
Use of energy by
moving object
Use of energy by
stationary object
21
Power
22
Loss of Energy
23
Loss of substance
24
Loss of Information
25
Loss of Time
26
Quantity of
substance/the matter
27
Reliability
Stress or pressure
Shape
Stability of the object's
composition
Strength
Duration of action of
moving object
Duration of action of
stationary object
Temperature
Illumination intensity
Use of energy by
moving object
Use of energy by
stationary object
Contradiction Matrix
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
23, 14, 12, 2, 19, 13,
25
29
17, 24
27, 4,
29, 18
22, 10, 29, 14, 35, 32,
35
2, 40 15, 31
14, 2,
39, 6
3, 36, 29, 35, 2, 14,
37, 10 3, 5 30, 40
5, 19, 28, 35,
9, 35 6, 18
19, 24, 2, 15,
3, 14
19
19, 2,
35
35, 32
26, 10, 19, 35,
2, 14, 16, 6,
16
28
10, 38
17, 25
19
19, 38, 1, 13,
26
7
32, 15
35, 28, 28, 27, 27, 16, 21, 36,
1, 6, 13
31, 40 3, 18 18, 38 39, 31
10
37,
36,4
10, 36,
14, 3
10, 24,
35, 19
4, 10,
34, 17
35, 3, 29, 3, 20, 10,
22, 5 28, 18 28, 18
15, 2, 14, 35, 3, 35,
35, 14
17, 40 34, 10 10, 40
35, 1,
2, 35,
11, 28
16, 11
3, 25
10
28, 20,
10, 16
3, 35,
31
34, 27,
6, 40
16, 6,
19, 37
35, 18, 28, 27,
24, 5 12, 31
19
35, 29, 1, 19, 35, 38,
1
21, 18 26, 17 19, 18
3, 17,
34, 29, 3, 35,
39
16, 18
31
3, 35, 11, 32, 21, 11,
36, 23
10
13
27, 19
�19
20
Use of energy by
moving object
Use of energy by
stationary object
21
Power
22
Loss of Energy
23
Loss of substance
24
Loss of Information
25
Loss of Time
26
Quantity of
substance/the matter
27
Reliability
Power
Loss of Energy
Loss of Substance
Loss of Information
Loss of Time
Quantity of substance
Reliability
Measurement accuracy
Manufacturing
precision
Object-affected harmful
factors
Contradiction Matrix
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
6, 19, 12, 22, 35, 24,
35, 38,
37, 18 15, 24 18, 5
19, 18
28, 27,
18, 31
10, 35, 28, 27,
35, 20,
+
10, 19
38
18, 38
10, 6
35, 27,
10, 18,
3, 38
+
19, 10
2, 37
32, 7
28, 27, 35, 27,
15, 18,
+
18, 38 2, 31
35, 10
24, 26,
10, 19 19, 10
+
28, 32
35, 20, 10, 5, 35, 18, 24, 26,
+
10, 6 18, 32 10, 39 28, 32
7, 18, 6, 3, 24, 28, 35, 38,
35
25
10, 24
35
18, 16
21, 11, 10, 11, 10, 35,
10, 30,
10, 28
26, 31
35
29, 39
4
34, 23,
16, 18
3, 35,
31
4, 34,
19
7, 18,
25
6, 3,
10, 24
24, 28,
35
35, 38,
18, 16
19, 21,
11, 27
10, 36,
23
19, 24,
26, 31
11, 10,
35
10, 29,
39, 35
10, 28,
23
10, 30,
4
18, 3,
28, 40
+
21, 28,
40, 3
3, 1, 32
32, 15,
2
32, 2
32
16, 34, 35, 10,
31, 28 24, 31
24, 34,
28, 32
13, 2,
28
32, 3,
11, 23
24, 26,
28, 18
33, 30
11, 32,
1
1, 35,
6, 27
10, 2,
22, 37
19, 22,
31, 2
21, 22,
35, 2
33, 22,
30, 40
22, 10,
1
35, 18,
34
35, 33,
29, 31
27, 35,
2, 40
�19
20
Use of energy by
moving object
Use of energy by
stationary object
21
Power
22
Loss of Energy
23
Loss of substance
24
Loss of Information
25
Loss of Time
26
Quantity of
substance/the matter
27
Reliability
Object-generated
harmful factors
Ease of manufacture
Ease of operation
Ease of repair
Adaptability or
versatility
Device complexity
Difficulty of detecting
and measuring
Extent of automation
Productivity
Contradiction Matrix
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
2, 35, 6
28, 26,
1, 15, 15, 17, 2, 29,
19, 35
35, 38 32, 2
30
17, 28 13, 16 27, 28
19, 35,
1, 4
16, 25
26, 10, 26, 35, 35, 2, 19, 17, 20, 19, 19, 35, 28, 2,
34
10
10, 34
34
30, 34
16
17
35, 32,
35, 3,
2, 19
7, 23
2
1
15, 23
15, 34, 32, 28, 2, 35, 15, 10, 35, 10, 35, 18, 35, 10,
33
2, 24 34, 27
2
28, 24 10, 13
18
19, 22,
18
2, 35,
18
21, 35,
2, 22
10, 1,
34, 29
10, 21,
32
22
35, 22, 35, 28,
18, 39 34, 4
3, 35, 29, 1,
40, 39 35, 27
35, 2,
40, 26
27, 22
35, 33
35
12, 28,
35
1, 6
28, 35,
34
28, 10,
29, 35
28, 35,
10, 23
13, 23,
15
4, 28, 32, 1,
18, 28, 24, 28,
35, 28 6, 29
10, 34
10
32, 10 35, 30
35, 29, 2, 32, 15, 3, 3, 13, 3, 27,
13, 29,
8, 35
25, 10 10, 25
29
27, 10 29, 18
3, 27
27, 17,
13, 35, 13, 35, 27, 40, 11, 13, 1, 35,
1, 11
40
8, 24
1
28
27
29, 38
�28, 26,
5, 16
10, 28,
29, 37
17, 1,
39, 4
17, 15,
16, 22
1, 29,
13, 17
1, 17,
13, 12
1, 28,
10, 25
35, 1,
29, 2
1, 19,
26, 24
Force (Intensity)
36
28, 35,
25, 26
28, 35,
27, 9
2, 22,
13, 24
35, 22,
1, 39
1, 27,
36, 13
6, 13,
1, 25
2, 27,
35, 11
19, 15,
29, 16
2, 26,
35, 39
32, 35,
26, 28
28, 32,
Manufacturing precision
13, 18
Object-affected harmful 22, 21,
factors
27, 39
19, 22,
Object-generated
harmful factors
15, 39
28, 29,
Ease of manufacture
15, 16
25, 2,
Ease of operation
13, 15
2, 27
Ease of repair
35, 11
1, 6,
Adaptability or
versatility
15, 8
26, 30,
Device complexity
34, 36
Measurement accuracy
Speed
35
Volume of stationary
object
34
Volume of moving
object
33
Area of stationary object
32
Area of moving object
31
Length of stationary
object
30
Length of moving object
29
Weight of stationary
object
28
Weight of moving object
Contradiction Matrix
10
26, 28,
32, 3
2, 29,
18, 36
27, 2,
39, 35
22, 1,
40
32, 13,
6
32, 23,
2
22, 23,
37, 35
17, 2,
40
13, 29,
1, 40
1, 16,
35, 15
25, 2,
35, 11
15, 35,
29
34, 26,
6
32, 28, 26, 28,
3, 16 32, 3
2, 32, 28, 33,
10
29, 32
22, 1,
1, 18
33, 28
17, 2,
18, 39
15, 17, 13, 1,
27
26, 12
1, 17,
13, 16
3, 18, 15, 13,
31
32
1, 35, 35, 30,
16
29, 7
14, 1,
26
13, 16
16, 40
18, 16,
15, 39
16, 25
15, 16
6, 36
25, 10,
35
34, 39,
19, 27
30, 18,
35, 4
35
4, 18,
39, 31
1
1, 16
28, 13,
32, 24
10, 28,
32
21, 22,
35, 28
35, 28,
3, 23
35, 13,
8, 1
18, 13,
34
32, 2
28, 19,
34, 36
13, 35,
39, 18
35, 28,
1, 40
35, 12
28, 13
35
1, 11,
34, 9
10
35, 10, 15, 17,
14
20
34, 10,
26, 16
28
�28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
Stress or pressure
Shape
Stability of the object's
composition
Strength
Duration of action of
moving object
Duration of action of
stationary object
Temperature
Illumination intensity
Use of energy by
moving object
Use of energy by
stationary object
Contradiction Matrix
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
6, 28,
32
32, 30,
Manufacturing precision 3, 35
40
Object-affected harmful 22, 2, 22, 1,
factors
37
3, 35
2, 33,
Object-generated
35, 1
harmful factors
27, 18
35, 19, 1, 28,
Ease of manufacture
1, 37 13, 27
2, 32, 15, 34,
Ease of operation
12
29, 28
1, 13,
Ease of repair
13
2, 4
15, 37,
Adaptability or
35, 16
versatility
1, 8
19, 1, 29, 13,
Device complexity
35
28, 15
Measurement accuracy
6, 28,
32
32, 35, 28, 6,
13
32
28, 6,
32
3, 27,
30, 18 3, 27
40
35, 24, 18, 35, 22, 15,
30, 18 37, 1 33, 28
35, 40, 15, 35, 15, 22,
27, 39 22, 2 33, 31
11, 13, 1, 3,
27, 1, 4
1
10, 32
32, 35, 32, 40, 29, 3,
30
3, 28 8, 25
11, 1, 11, 29,
2, 35
2, 9 28, 27
35, 30, 35, 3, 13, 1,
14
32, 6
35
2, 22, 2, 13, 10, 4,
17, 19
28
28, 15
10, 26, 6, 19,
24
28, 24
6, 1,
32
3, 6, 32
19, 26
3, 32
32, 2
17, 1, 22, 33,
40, 33 35, 2
21, 39, 22, 35,
16, 22 2, 24
27, 26,
35, 16
18
1, 16, 26, 27,
25
13
1
2, 16
1, 19,
32, 13
19, 24,
39, 32
28, 24,
27, 1
13, 17,
1, 24
15, 1,
4, 10
13
27, 2, 6, 22,
3, 35 26, 1
2, 17, 24, 17,
13
13
1, 24,
6, 27
10, 2,
22, 37
19, 22,
2, 35, 6
18
28, 26,
1, 4
27, 1
1, 13,
24
15, 1,
28, 16
19, 35,
29, 13
27, 2,
29, 28
�28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
Power
Loss of Energy
Loss of Substance
Loss of Information
Loss of Time
Quantity of substance
Reliability
Measurement accuracy
Manufacturing
precision
Object-affected harmful
factors
Contradiction Matrix
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
26, 32,
27
13, 32,
Manufacturing precision 32, 2
2
Object-affected harmful 19, 22, 21, 22,
factors
31, 2 35, 2
2, 35, 21, 35,
Object-generated
harmful factors
18
2, 22
27, 1,
Ease of manufacture
19, 35
12, 24
35, 34, 2, 19,
Ease of operation
2, 10
13
15, 10, 15, 1,
Ease of repair
32, 2 32, 19
19, 1, 18, 15,
Adaptability or
versatility
29
1
20, 19, 10, 35,
Device complexity
30, 34 13, 2
Measurement accuracy 3, 6, 32
10, 16,
31, 28
35, 31,
10, 24
33, 22,
19, 40
10, 1,
34
15, 34,
33
28, 32,
2, 24
2, 35,
34, 27
15, 10,
2, 13
35, 10,
28, 29
24, 34,
28, 32
32, 26,
28, 18
22, 10, 35, 18,
2
34
10, 21,
1, 22
29
32, 24, 35, 28,
18, 16 34, 4
4, 10, 4, 28,
27, 22 10, 34
32, 1,
10, 25
2, 6, 32
32, 30
35, 33,
29, 31
3, 24,
39, 1
35, 23,
1, 24
12, 35
2, 28,
10, 25
3, 35,
35, 28
15
13, 3,
6, 29
27, 10
5, 11,
+
1, 23
11, 32,
+
1
27, 24, 28, 33, 26, 28,
2, 40 23, 26 10, 18
24, 2, 3, 33, 4, 17,
40, 39
26
34, 26
1, 35,
12, 18
17, 27, 25, 13, 1, 32,
8, 40 2, 34 35, 23
11, 10, 10, 2,
25, 10
1, 16
13
35, 13, 35, 5,
8, 24 1, 10
13, 35, 2, 26, 26, 24,
1
10, 34
32
28, 24,
22, 26
26, 28,
10, 36
+
24, 2
2, 25,
28, 39
35, 10,
2, 16
35, 11,
32, 31
22, 19,
29, 40
�Object-generated
harmful factors
Ease of manufacture
Ease of operation
Ease of repair
Adaptability or
versatility
Device complexity
Difficulty of detecting
and measuring
Extent of automation
Productivity
Contradiction Matrix
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
3, 33, 6, 35,
39, 10 25, 18
4, 17,
29 Manufacturing precision
34, 26
24, 35,
Object-affected harmful
30
factors
2
Object-generated
31
+
harmful factors
1, 13, 1, 32, 13, 35,
17, 34 13, 11
2
1, 32,
25, 10
35, 23
2, 25, 35, 10, 35, 11,
28, 39
2
22, 31
28
Measurement accuracy
32
Ease of manufacture
2, 5,
13, 16
33
Ease of operation
2, 5, 12
34
Ease of repair
35
Adaptability or
versatility
36
Device complexity
1, 35,
11, 10
1, 13,
31
27, 26,
1, 13
1, 12,
26, 15
15, 34,
1, 16
27, 9,
26, 24
19, 1
27, 35,
10, 34
26, 2,
18
22, 19,
29, 40
19, 1,
31
35, 1, 2, 13, 27, 26,
11, 9
15
1
12, 26, 15, 34, 32, 26,
1, 32 1, 16 12, 17
7, 1, 4, 35, 1,
+
16
13, 11
1, 16,
15, 29,
+
7, 4
37, 28
29, 15,
1, 13
+
28, 37
26, 24, 28, 2,
32, 28 10, 34
26, 28,
18, 23
22, 19, 33, 3,
29, 40
34
2, 21,
2
27, 1
6, 28,
8, 28, 1
11, 1
1, 34,
12, 3
34, 35,
7, 13
27, 34,
1
35
15, 10, 15, 1,
37, 28
24
10, 34,
28, 32
10, 18,
32, 39
22, 35,
13, 24
22, 35,
18, 39
35, 1,
10, 28
15, 1,
28
1, 32,
10
35, 28,
6, 37
12, 17,
28
�Volume of moving
object
Volume of stationary
object
Speed
Force (Intensity)
Productivity
Area of stationary object
39
Area of moving object
Extent of automation
Length of stationary
object
38
Length of moving object
Difficulty of detecting
and measuring
Weight of stationary
object
37
Weight of moving object
Contradiction Matrix
10
27, 26,
28, 13
28, 26,
18, 35
35, 26,
24, 37
6, 13,
28, 1
28, 26,
35, 10
28, 27,
15, 3
16, 17,
26
26, 24
14, 13,
23
17, 28
18, 4, 30, 7,
28, 38 14, 26
2, 13, 2, 39, 29, 1, 2, 18, 3, 4,
18, 17 30, 16 4, 16 26, 31 16, 35
17, 14,
35, 13,
28, 10
13
16
10, 26, 10, 35, 2, 6, 35, 37,
34, 31 17, 7 34, 10 10, 2
30, 28,
40, 19
2, 35
28, 15,
10, 36
�37
Difficulty of detecting
and measuring
38
Extent of automation
39
Productivity
Stress or pressure
Shape
Stability of the object's
composition
Strength
Duration of action of
moving object
Duration of action of
stationary object
Temperature
Illumination intensity
Use of energy by
moving object
Use of energy by
stationary object
Contradiction Matrix
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
35, 36, 27, 13,
37, 32 1, 39
15, 32,
13, 35
1, 13
10, 37, 14, 10,
14
34, 40
11, 22, 27, 3, 19, 29, 25, 34, 3, 27, 2, 24,
19, 35,
35, 38
39, 30 15, 28 39, 25 6, 35 35, 16
26
16
26, 2, 8, 32, 2, 32,
18, 1 25, 13 6, 9
19
19
13
35, 3, 29, 28, 35, 10, 20, 10, 35, 21, 26, 17, 35, 10,
1
22, 39 10, 18 2, 18 16, 38 28, 10 19, 1 38, 19
�37
Difficulty of detecting
and measuring
38
Extent of automation
39
Productivity
Power
Loss of Energy
Loss of Substance
Loss of Information
Loss of Time
Quantity of substance
Reliability
Measurement accuracy
Manufacturing
precision
Object-affected harmful
factors
Contradiction Matrix
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
18, 1,
16, 10
28, 2,
27
35, 20,
10
35, 3, 1, 18,
15, 19 10, 24
35, 10,
23, 28
18, 5
28, 10, 28, 10,
29, 35 35, 23
35, 33, 18, 28,
27, 22 32, 9
24, 28,
35, 33
35, 30
13, 15,
23
3, 27, 27, 40,
29, 18 28, 8
11, 27,
35, 13
32
1, 35,
35, 38
10, 38
26, 24,
22, 19,
32, 28
29, 28
28, 26, 28, 26,
2, 33
10, 34 18, 23
1, 10, 18, 10, 22, 35,
34, 28 32, 1 13, 24
�37
Difficulty of detecting
and measuring
38
Extent of automation
39
Productivity
Object-generated
harmful factors
Ease of manufacture
Ease of operation
Ease of repair
Adaptability or
versatility
Device complexity
Difficulty of detecting
and measuring
Extent of automation
Productivity
Contradiction Matrix
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
5, 28,
2, 5
11, 29
1, 26, 1, 12,
2
13
34, 3
35, 22, 35, 28, 1, 28,
18, 39 2, 24 7, 10
2, 21
12, 26
1, 15
1, 35, 27, 4,
13
1, 35
1, 32, 1, 35,
10, 25 28, 37
15, 10,
+
34, 21 35, 18
37, 28
15, 24, 34, 27,
5, 12,
+
10
25
35, 26
12, 17, 35, 18, 5, 12,
+
28, 24 27, 2 35, 26
�The 40 Inventive Principles
ID
TRIZ Principle
Explanation
Segmentation
Divide an object into independent parts.
Take out
Separate the interfering part or property from an object, or single
out the only necessary part or property.
Local Quality
Change an object's structure from uniform to non-uniform or
change an external environment (or external influence) from
uniform to non-uniform.
Asymmetry
Merging
Bring closer together (or merge) identical or similar objects,
assemble identical or similar parts to perform parallel operations.
Universality
Make a part or object perform multiple functions; eliminate the
need for other parts.
Nested Doll
Place one object inside another; place each object, in turn, inside
the other.
Anti-weight
To compensate for the weight of an object, merge it with other
objects that provide lift.
Preliminary anti-action
If it will be necessary to do an action with both harmful and useful
effects, this action should be replaced with anti-actions to control
harmful effects.
Change the shape of an object from symmetrical to asymmetrical.
10 Preliminary action
Perform, before it is needed, the required change of an object
(either fully or partially).
11 Cushion in advance
Prepare emergency means beforehand to compensate for the
relatively low reliability of an object.
12 Equipotentiality
In a potential field, limit position changes (e.g. change operating
conditions to eliminate the need to raise or lower objects in a
gravity field).
13 Other way around
Invert the action(s) used to solve the problem (e.g. instead of
cooling an object, heat it).
Spheroidality or use of
14
curves
Instead of using rectilinear parts, surfaces, or forms, use
curvilinear ones; move from flat surfaces to spherical ones; from
parts shaped as a cube (parallelepiped) to ball-shaped structures.
Page 21
�The 40 Inventive Principles
ID
TRIZ Principle
Explanation
15 Dynamism
Allow (or design) the characteristics of an object, external
environment, or process to change to be optimal or to find an
optimal operating condition.
16 Partial / excessive action
If 100% of an object is hard to achieve using a given solution
method then by using 'slightly less' or 'slightly more' of the same
method the problem may be considerably easier to solve.
17 Another dimension
To move an object in two- or three-dimensional space.
18 Mechanical Vibration
Cause an object to oscillate or vibrate.
19 Periodic action
Instead of continuous action, use periodic or pulsating actions.
20 Continuity of action
Carry on work continuously; make all parts of an object work at full
load, all the time.
21 Skipping (do fast)
Conduct a process, or certain stages (e.g. destructible, harmful or
hazardous operations) at high speed.
22 Blessing in disguise
Use harmful factors (particularly, harmful effects of the
environment or surroundings) to achieve a positive effect.
23 Feedback
Introduce feedback (referring back, cross-checking) to improve a
process or action.
24 Intermediary
25 Self-service
Use an intermediary carrier article or intermediary process.
Make an object serve itself by performing auxiliary helpful
functions.
26 Copying
Instead of an unavailable, expensive, fragile object, use simpler
and inexpensive copies.
27 Cheap short life
Replace an inexpensive object with a multiple of inexpensive
objects, comprising certain qualities (such as service life, for
instance).
28
Replace mechanical system Replace a mechanical means with a sensory (optical, acoustic,
taste or smell) means.
with fields
Page 22
�The 40 Inventive Principles
ID
TRIZ Principle
Explanation
29 Pneumatic / hydraulic
Use gas and liquid parts of an object instead of solid parts (e.g.
inflatable, filled with liquids, air cushion, hydrostatic, hydroreactive).
30 Flexible shell, films
Use flexible shells and thin films instead of three dimensional
structures.
31 Porous materials
Make an object porous or add porous elements (inserts, coatings,
etc.).
32 Change color
Change the color of an object or its external environment.
33 Homogeneity
Make objects interacting with a given object of the same material
(or material with identical properties).
34 Discard / recover
Make portions of an object that have fulfilled their functions go
away (discard by dissolving, evaporating, etc.) or modify these
directly during operation.
Change an object's physical state (e.g. to a gas, liquid, or solid).
35 Change parameters
Use phenomena occurring during phase transitions (e.g. volume
changes, loss or absorption of heat, etc.).
36 Use phase transition
Use thermal expansion (or contraction) of materials.
37 Use thermal expansion
Replace common air with oxygen-enriched air.
38 Stong Oxidants
Replace a normal environment with an inert one.
39 Inert Atmosphere
Change from uniform to composite (multiple) materials.
40 Composite materials
Page 23
�Example
Replace mainframe computer by personal computers.
Locate a noisy compressor outside the building where
compressed air is used.
Use a temperature, density, or pressure gradient instead of
constant temperature, density or pressure.
Asymmetrical mixing vessels or asymmetrical vanes in
symmetrical vessels improve mixing (cement trucks, cake
mixers, blenders).
Personal computers in a network.
Handle of a toothbrush contains toothpaste.
Measuring cups or spoons.
Inject foaming agent into a bundle of logs, to make it float
better.
Buffer a solution to prevent harm from extremes of pH.
Pre-pasted wall paper.
Magnetic strip on photographic film that directs the
developer to compensate for poor exposure.
Spring loaded parts delivery system in a factory.
To loosen stuck parts, cool the inner part instead of heating
the outer part.
Use arches and domes for strength in architecture.
Page 24
�Example
Adjustable steering wheel (or seat, or back support, or
mirror position).
Over spray when painting, then remove excess (or use a
stencil).
Infrared computer mouse moves in space, instead of on a
surface, for presentations.
Electric carving knife with vibrating blades.
Hitting something repeatedly with a hammer.
Flywheel (or hydraulic system) stores energy when a
vehicle stops, so the motor can keep running at optimum
power.
Use a high speed dentist's drill to avoid heating tissue.
Use waste heat to generate electric power.
Automatic volume control in audio circuits.
Carpenter's nailset used between the hammer and the nail.
A soda fountain pump that runs on the pressure of the
carbon dioxide that is used to "fizz" the drinks. This assures
that drinks will not be flat, and eliminates the need for
sensors.
Virtual reality via computer instead of an expensive
vacation.
Use disposable paper objects to avoid the cost of cleaning
and storing durable objects. Plastic cups in motels,
disposable diapers, many kinds of medical supplies.
Replace a physical fence to confine a dog or cat with an
acoustic "fence" (signal audible to the animal).
Page 25
�Example
Comfortable shoe sole inserts filled with gel.
Use inflatable (thin film) structures as winter covers on
tennis courts.
Drill holes in a structure to reduce the weight.
Use safe lights in a photographic darkroom.
Make the container out of the same material as the
contents, to reduce chemical reactions.
Use a dissolving capsule for medicine.
Freeze the liquid centers of filled candies, then dip in melted
chocolate, instead of handling the messy, gooey, hot liquid.
Water expands when frozen, unlike most other liquids.
Hannibal is reputed to have used this when marching on
Rome a few thousand years ago. Large rocks blocked
passages in the Alps. He poured water on them at night.
The overnight cold froze the water, and the expansion split
the rocks into small pieces which could be pushed aside.
Fit a tight joint together by cooling the inner part to contract,
heating the outer part to expand, putting the joint together,
and returning to equilibrium.)
Scuba diving with Nitrox or other non-air mixtures for
extended endurance.
Prevent degradation of a hot metal filament by using an
argon atmosphere.
Composite epoxy resin/carbon fiber golf club shafts are
lighter, stronger, and more flexible than metal. Same for
airplane parts.
Page 26
�The 39 Design Features
ID
1
TRIZ Feature
Weight of moving object
Explanation
The measurable force, resulting from gravity, that a moving object exerts on the
surface which prevents it from falling. A moving object is one which changes
position on its own as a result of some external force.
The measurable force, resulting from gravity, that a stationary object exerts on the
surface which it rests. A stationary object is one which cannot change position on its
own or as the result of some external force.
Weight of stationary object
Length of moving object
Length of stationary object
The linear measurement of an object's length, height, or width in the direction of the
observed movement of that object. Movement may be caused by internal or
external forces.
The linear measurement of an object's length, height or width in the direction for
which no observed movement occurs.
Area of moving object
The square measurement of any plane or portion of a plane of an object which,
when acted on by internal or external forces, can change position in space.
Area of stationary object
The square measurement of any plane or portion of a plane of an object which,
when acted on by internal or external forces, cannot change position in space.
Volume of moving object
The cubic measurement of an object which can change its position in space when
acted by internal or external forces.
Volume of stationary object
The cubic measurement of an object which cannot change its position in space
when acted by internal or external forces.
Speed
The rate at which an action or process is completed over time.
10
Force (Intensity)
11
Stress or pressure
12
Shape
The capacity to cause physical change in an object or system. The change may be
full or partial, and permanent or temporary.
The intensity of forces acting on an object or system, measured as a force of
compression or tension of a unit area.
The outward appearance or contour of an object or a system. Shape may be full or
partial and permanent or temporary changes due to forces acting on the object or
system.
13
Stability of the object's
composition
The resistance of a whole object or system to change caused by the interactions of
its associated objects or systems.
14
Strength
Under definable conditions and limits, the ability of an object or system to absorb
the effects of force, speed, stress, etc. without breaking.
Duration of action of moving
object
Duration of action by stationary
object
The length of time over which an object that changes position in space is able to
fulfill its function.
The length of time over which an object that does not change position in space is
able to fulfill its function.
17
Temperature
The loss or addition of heat to an object or system during required functions, which
may cause potentially undesirable changes to the object, system or product.
18
Illumination intensity
The ratio of light energy to the area which is being lit by or in a system. Brightness
includes the quality of light, degree of illumination and other characteristics of light.
19
The energy requirements of an object which changes position in space by its own
Use of energy by moving object means or by external forces.
20
Use of energy by stationary
object
The energy requirements of an object which does not change position in space by
its own means or by external forces.
Power
The ratio of the work to the time required to perform that work. Usede to measuree
the required but potentially undesireable changes in power evident in an object or
system under given conditions.
15
16
21
Page 27
�The 39 Design Features
ID
TRIZ Feature
Explanation
Increased inability of an object or system to exert force, especially when no work or
product is produced.
22
Loss of Energy
23
Loss of substance
24
Loss of Information
Decrease or elimination of material from an object or system, especially when no
work or product is produced.
Decrease or elimination of data or input from a system.
25
Loss of Time
Increase in the amount of time needed to complete a given action.
26
Quantity of substance/the
matter
The number of elements or the quality of an element used to create an object or
system.
27
Reliability
The ability of an object or system to adequately perform its required function during
some period of time or cycles.
28
Measurement accuracy
The degree to which measurement close to the actual value or the quantity being
measured.
29
Manufacturing precision
The degree of correspondence between elements of an object or system to its
design specification.
30
Externally produced influences acting on an object or system which reduce
Object-affected harmful factors efficiency or quality.
31
Object-generated harmful
factors
Internally produced influences acting on an object or system which reduce
efficiency or quality.
32
Ease of manufacture
Convenience and facility with which an object or system is produced.
33
Ease of operation
Convenience and facility with which an object or system is operated.
34
Ease of repair
Convenience and facility with which an object or system is restored to operating
condition after damage or extensive use.
35
Adaptability or versatility
The ability of an object or system to reshape itself or reorder itself as external
conditions (environment, function, etc.) change.
36
Device complexity
The quantity or diversity of elements forming an object or system, including the
relationships between elements. Complexity may also descibe the difficulty in
mastering the use of an object or system.
37
Difficulty of detecting and
measuring
The quantity and diversity of elements used in measuring and monitoring an object
or system, as well as the cost of measuring acceptable error.
38
Extent of automation
39
Productivity
The ability of an object or system to perform operations without human interaction.
The relationship between the number of times an operation is completed and the
amount of time it takes to do it.
Page 28