0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views2 pagesPlasmid Mapping Activity Answers
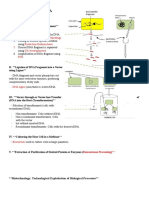
The document outlines the steps for transferring a useful gene from bacteria to a plant, including isolation, fragmentation, and amplification of the DNA. It details the use of restriction enzymes, gel electrophoresis, and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) to prepare the gene for insertion. Finally, it describes the transformation of Agrobacterium to facilitate the incorporation of the gene into the plant genome.
Uploaded by
Mark Angelo AustriaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views2 pagesPlasmid Mapping Activity Answers
The document outlines the steps for transferring a useful gene from bacteria to a plant, including isolation, fragmentation, and amplification of the DNA. It details the use of restriction enzymes, gel electrophoresis, and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) to prepare the gene for insertion. Finally, it describes the transformation of Agrobacterium to facilitate the incorporation of the gene into the plant genome.
Uploaded by
Mark Angelo AustriaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd