0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views2 pages8 Pracsheet Staticelect
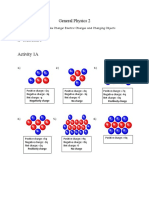
The worksheet for Std. VIII Physics focuses on electricity, specifically investigating static charges and their interactions. It includes questions about charge conclusions based on observations, true statements about static charges, and various scenarios involving Object A's charge. Additionally, it asks students to identify charges on metal pop cans and name a kitchen device that provides electric discharge.
Uploaded by
sparsh batraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views2 pages8 Pracsheet Staticelect
The worksheet for Std. VIII Physics focuses on electricity, specifically investigating static charges and their interactions. It includes questions about charge conclusions based on observations, true statements about static charges, and various scenarios involving Object A's charge. Additionally, it asks students to identify charges on metal pop cans and name a kitchen device that provides electric discharge.
Uploaded by
sparsh batraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd