0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views17 pagesFuture Simple Tense
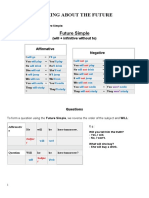
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the simple future tense in English, detailing its formation and usage with 'will' and 'going to'. It explains when to use each form, including spontaneous decisions, promises, planned actions, and predictions. Additionally, it includes examples and practice activities to reinforce understanding of the tense.
Uploaded by
Camila LopezCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views17 pagesFuture Simple Tense
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the simple future tense in English, detailing its formation and usage with 'will' and 'going to'. It explains when to use each form, including spontaneous decisions, promises, planned actions, and predictions. Additionally, it includes examples and practice activities to reinforce understanding of the tense.
Uploaded by
Camila LopezCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd