0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views1 pageUniversal Pulseless Arrest Algorithm
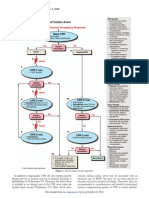
The Universal Pulseless Arrest Algorithm outlines the steps to manage a patient in pulseless arrest, emphasizing the importance of initiating chest compressions and using an AED within 60 seconds. It includes performing rhythm checks every two minutes and considering reversible causes of arrest. If return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) occurs, post-cardiac arrest care and advanced life support (ALS) assessment should follow.
Uploaded by
EnesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views1 pageUniversal Pulseless Arrest Algorithm
The Universal Pulseless Arrest Algorithm outlines the steps to manage a patient in pulseless arrest, emphasizing the importance of initiating chest compressions and using an AED within 60 seconds. It includes performing rhythm checks every two minutes and considering reversible causes of arrest. If return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) occurs, post-cardiac arrest care and advanced life support (ALS) assessment should follow.
Uploaded by
EnesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd