0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views15 pagesUnderstanding Central Tendency and Variability
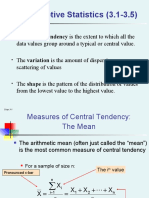
The document provides an overview of statistical concepts, including descriptive measurements, measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode), and measures of variability (range, variance, standard deviation). It distinguishes between parameters calculated from populations and statistics calculated from samples. Examples are given to illustrate how to calculate these measures using ungrouped data.
Uploaded by
akicat520Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views15 pagesUnderstanding Central Tendency and Variability
The document provides an overview of statistical concepts, including descriptive measurements, measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode), and measures of variability (range, variance, standard deviation). It distinguishes between parameters calculated from populations and statistics calculated from samples. Examples are given to illustrate how to calculate these measures using ungrouped data.
Uploaded by
akicat520Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd