0% found this document useful (0 votes)
192 views12 pagesBasic Relationship Between Pixels
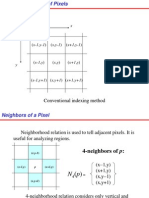
The document discusses pixel adjacency and connectivity in digital images, defining 4-neighbors and 8-neighbors of a pixel, as well as various types of adjacency (4-adjacency, 8-adjacency, and m-adjacency). It explains how paths between pixels are formed and the concept of connectivity within a subset of pixels, highlighting connected components. Examples illustrate the differences in connectivity based on the type of adjacency used.
Uploaded by
amitkrmandalcseCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
192 views12 pagesBasic Relationship Between Pixels
The document discusses pixel adjacency and connectivity in digital images, defining 4-neighbors and 8-neighbors of a pixel, as well as various types of adjacency (4-adjacency, 8-adjacency, and m-adjacency). It explains how paths between pixels are formed and the concept of connectivity within a subset of pixels, highlighting connected components. Examples illustrate the differences in connectivity based on the type of adjacency used.
Uploaded by
amitkrmandalcseCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd