0% found this document useful (0 votes)
241 views13 pagesNetworking Assignment
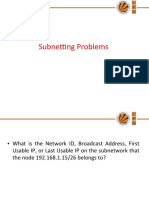
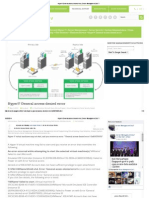
The document outlines various networking assignments involving subnetting, IP address configuration, and host calculations. It includes solutions for configuring servers, determining subnet masks, calculating the number of subnets and hosts, and converting binary to decimal. Additionally, it addresses issues related to network connectivity between devices.
Uploaded by
marcolifa167Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
241 views13 pagesNetworking Assignment
The document outlines various networking assignments involving subnetting, IP address configuration, and host calculations. It includes solutions for configuring servers, determining subnet masks, calculating the number of subnets and hosts, and converting binary to decimal. Additionally, it addresses issues related to network connectivity between devices.
Uploaded by
marcolifa167Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd