0% found this document useful (0 votes)
60 views24 pagesPlate Tectonic Boundaries Notes
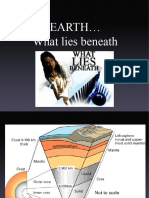
The document discusses plate boundaries, which are locations where tectonic plates meet, and categorizes them into three types: convergent, divergent, and transform. It also explains the two types of crust (continental and oceanic), the features formed at each boundary type, and introduces the concept of seafloor spreading and continental drift theory. Additionally, it highlights the historical supercontinent Pangea and the role of convection currents in plate movement.
Uploaded by
augusann000Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
60 views24 pagesPlate Tectonic Boundaries Notes
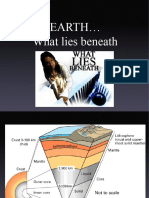
The document discusses plate boundaries, which are locations where tectonic plates meet, and categorizes them into three types: convergent, divergent, and transform. It also explains the two types of crust (continental and oceanic), the features formed at each boundary type, and introduces the concept of seafloor spreading and continental drift theory. Additionally, it highlights the historical supercontinent Pangea and the role of convection currents in plate movement.
Uploaded by
augusann000Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd