0% found this document useful (0 votes)
206 views10 pagesManaging FNB Outlets
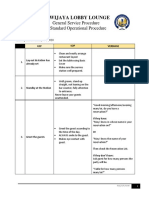
The document outlines the essential supervisory skills required for managing food and beverage outlets, including leadership, motivation, time management, technical skills, communication, problem-solving, and compassion. It details the duties of a supervisor, such as conducting briefings, managing tips, stock taking, staff training, sales and cost analysis, handling complaints, and maintaining discipline. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of standard operating procedures (SOPs) for consistency and quality in service delivery.
Uploaded by
Srijan SenCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
206 views10 pagesManaging FNB Outlets
The document outlines the essential supervisory skills required for managing food and beverage outlets, including leadership, motivation, time management, technical skills, communication, problem-solving, and compassion. It details the duties of a supervisor, such as conducting briefings, managing tips, stock taking, staff training, sales and cost analysis, handling complaints, and maintaining discipline. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of standard operating procedures (SOPs) for consistency and quality in service delivery.
Uploaded by
Srijan SenCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd